
Rice Science ›› 2015, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (3): 123-131.DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60294-8
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chang Shu1, Jing-hao Wu1, Gao-ling Shi1, Lai-qing Lou1, Jun-xia Deng1, Jian-lin Wan2, Qing-sheng Cai1
Received:2014-04-15
Accepted:2015-02-11
Online:2015-05-28
Published:2015-03-27
Chang Shu, Jing-hao Wu, Gao-ling Shi, Lai-qing Lou, Jun-xia Deng, Jian-lin Wan, Qing-sheng Cai. Different Aluminum Tolerance among Indica, Japonica and Hybrid Rice Varieties[J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(3): 123-131.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.org/EN/10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60294-8
| Label | Designation | Generation | Subspecies | Label | Designation | Generation | Subspecies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9001 | Dakanala | Parent | japonica | 9030 | IR70369B | Parent | indica |
| 9003 | Dharial | Parent | japonica | 9031 | IR73013-95-1-3-2R | Parent | indica |
| 9004 | LGC1 | Parent | japonica | 9032 | IR73885-1-4-3-2-1-10R | Parent | indica |
| 9006 | Longjing 9 | Parent | japonica | 9033 | IR78371B | Parent | indica |
| 9009 | Ribenyou | Parent | japonica | 9034 | IR79156B | Parent | indica |
| 9010 | Koshihikari | Parent | japonica | 9035 | IR29723-143-3-2-1R | Parent | indica |
| 9012 | Srt 1 | Parent | japonica | 9136 | LGC1/Dali | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9014 | Dali | Parent | japonica | 9146 | LGC1/Dali | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9016 | Aus 373 | Parent | indica | 9158 | Koshihikari/LGC1 | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9017 | Aus 373 | Parent | indica | 9166 | Srt 1/Koshihikari | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9018 | 9194 | Parent | indica | 9177 | Srt 1/Ribenyou | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9019 | Ganwanxian 32 | Parent | indica | 9194 | 9194/LGC1 | Advanced generation | indica × japonica |
| 9020 | Ganwanxian 9 | Parent | indica | 9204 | Srt 1/9194 | Advanced generation | japonica × indica |
| 9021 | Ganwanxian 30 | Parent | indica | 9233 | Srt 1/9194 | Advanced generation | japonica × indica |
| 9022 | 9311 (awned) | Parent | indica | 9280 | Koshihikari/9194 | Advanced generation | japonica × indica |
| 9023 | 9311 (smooth) | Parent | indica | 9297 | Ganwanxian 32/Ribenyou | Advanced generation | indica × japonica |
| 9024 | Ganzaoxian 58 | Parent | indica | 9317 | Srt 1/Dali | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9025 | Ganzaoxian 59 | Parent | indica | 9364 | 9194/Ribenyou | Advanced generation | indica × japonica |
| 9026 | Lijiangheigu | Parent | indica | 9365 | Dongye/Koshihikari | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9027 | Doongara | Parent | indica | Fan 12 | Koshihikari/9194 | Strain | japonica × indica |
| 9028 | IR58025B | Parent | indica | Fan 13 | Koshihikari/9194 | Strain | japonica × indica |
| 9029 | IR60819-34-2R | Parent | indica |
Table 1 Genetic background of different rice germplasms.
| Label | Designation | Generation | Subspecies | Label | Designation | Generation | Subspecies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9001 | Dakanala | Parent | japonica | 9030 | IR70369B | Parent | indica |
| 9003 | Dharial | Parent | japonica | 9031 | IR73013-95-1-3-2R | Parent | indica |
| 9004 | LGC1 | Parent | japonica | 9032 | IR73885-1-4-3-2-1-10R | Parent | indica |
| 9006 | Longjing 9 | Parent | japonica | 9033 | IR78371B | Parent | indica |
| 9009 | Ribenyou | Parent | japonica | 9034 | IR79156B | Parent | indica |
| 9010 | Koshihikari | Parent | japonica | 9035 | IR29723-143-3-2-1R | Parent | indica |
| 9012 | Srt 1 | Parent | japonica | 9136 | LGC1/Dali | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9014 | Dali | Parent | japonica | 9146 | LGC1/Dali | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9016 | Aus 373 | Parent | indica | 9158 | Koshihikari/LGC1 | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9017 | Aus 373 | Parent | indica | 9166 | Srt 1/Koshihikari | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9018 | 9194 | Parent | indica | 9177 | Srt 1/Ribenyou | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9019 | Ganwanxian 32 | Parent | indica | 9194 | 9194/LGC1 | Advanced generation | indica × japonica |
| 9020 | Ganwanxian 9 | Parent | indica | 9204 | Srt 1/9194 | Advanced generation | japonica × indica |
| 9021 | Ganwanxian 30 | Parent | indica | 9233 | Srt 1/9194 | Advanced generation | japonica × indica |
| 9022 | 9311 (awned) | Parent | indica | 9280 | Koshihikari/9194 | Advanced generation | japonica × indica |
| 9023 | 9311 (smooth) | Parent | indica | 9297 | Ganwanxian 32/Ribenyou | Advanced generation | indica × japonica |
| 9024 | Ganzaoxian 58 | Parent | indica | 9317 | Srt 1/Dali | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9025 | Ganzaoxian 59 | Parent | indica | 9364 | 9194/Ribenyou | Advanced generation | indica × japonica |
| 9026 | Lijiangheigu | Parent | indica | 9365 | Dongye/Koshihikari | Advanced generation | japonica × japonica |
| 9027 | Doongara | Parent | indica | Fan 12 | Koshihikari/9194 | Strain | japonica × indica |
| 9028 | IR58025B | Parent | indica | Fan 13 | Koshihikari/9194 | Strain | japonica × indica |
| 9029 | IR60819-34-2R | Parent | indica |
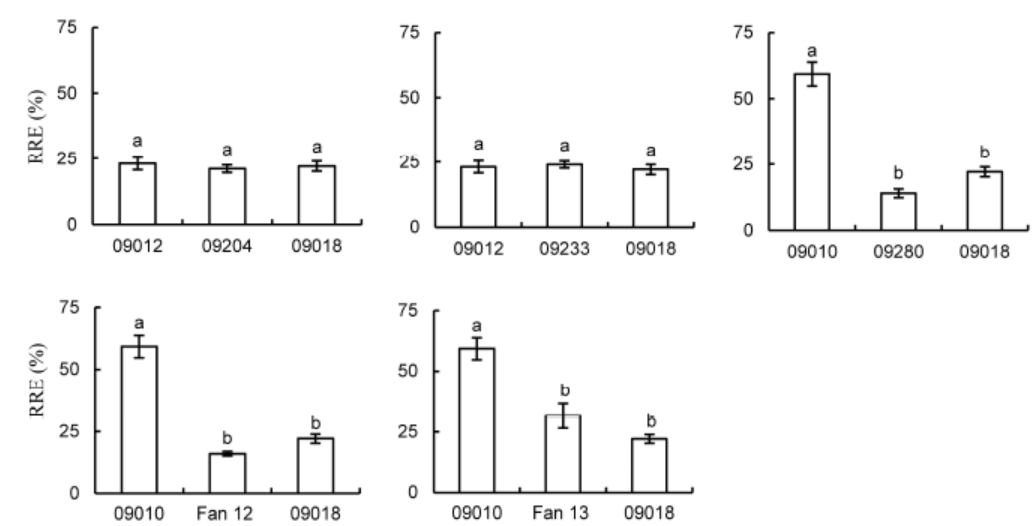
Fig. 3. RRE (relative root elongation) of japonica × indica hybrids and their parents under aluminum (50 μmol/L) stress for 24 h (means ± SE, n = 10). Different letters mean significant difference at P ˂ 0.05, according to the Duncan’s test.
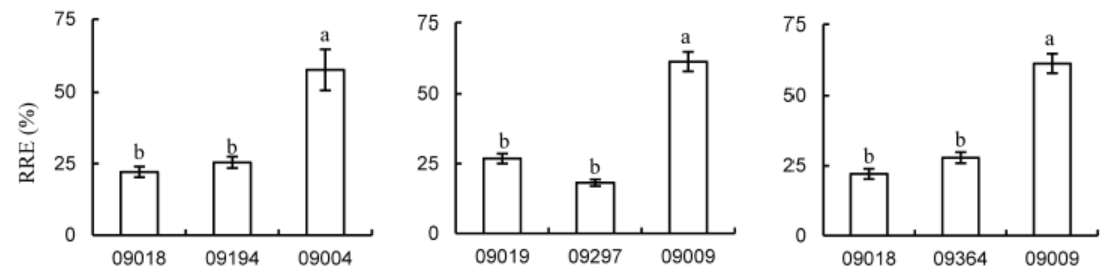
Fig. 4. RRE (relative root elongation) of indica × japonica hybrids and their parents under aluminum (50 μmol/L) stress for 24 h (means ± SE, n = 10). Different letters mean significant difference at P ˂ 0.05, according to the Duncan’s test.
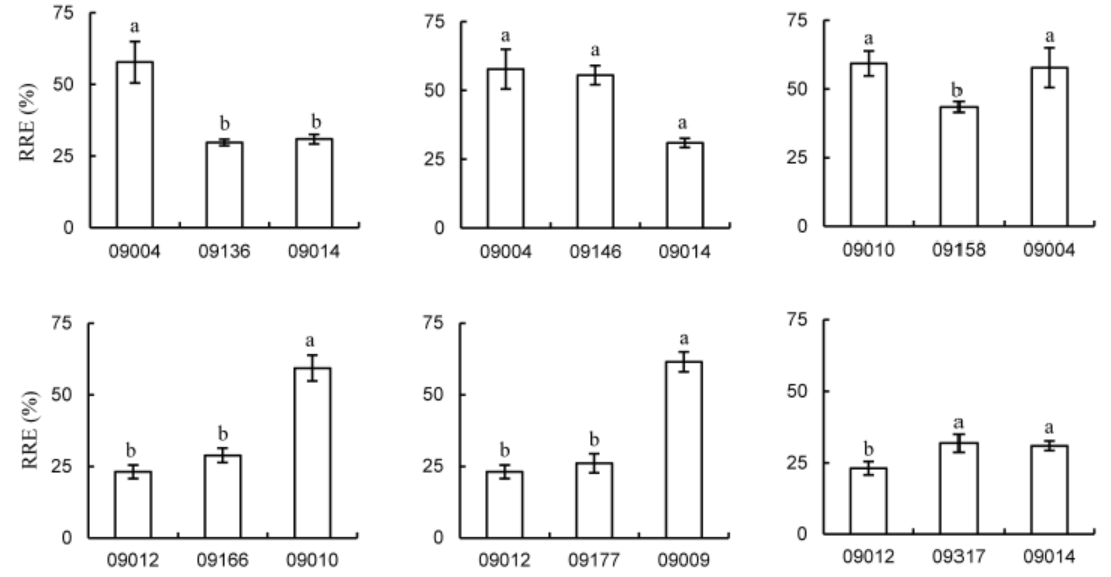
Fig. 5. RRE (relative root elongation) of japonica × japonica hybrids and their parents under aluminum (50 μmol/L) stress for 24 h (means ± SE, n = 10). Different letters mean significant difference at P ˂ 0.05, according to the Duncan’s test.
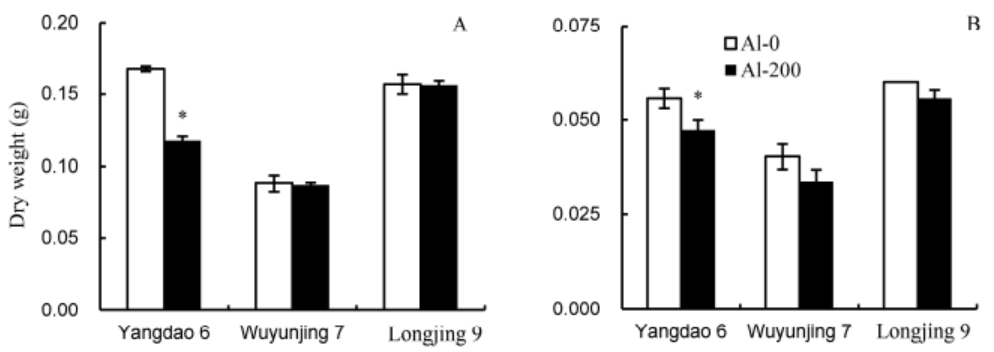
Fig. 6. Biomass of shoots (A) and roots (B) for three rice varieties after exposure to 200 μmol/L aluminum (Al) for 12 d (means ± SE, n = 3). * means significant difference at P ˂ 0.05, according to the Duncan’s test.
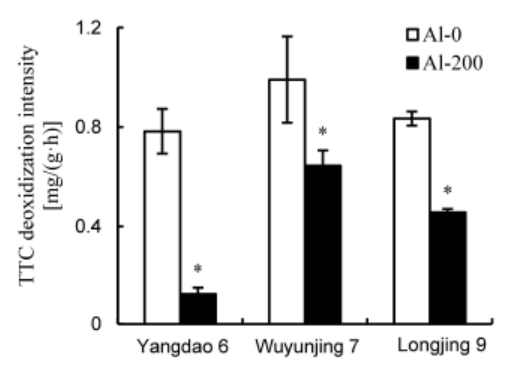
Fig. 7. Triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) deoxidization intensity of three rice varieties after exposure to 200 μmol/L aluminum (Al) for 12 d (means ± SE, n = 3). * means significant difference at P ˂ 0.05, according to the Duncan’s test.
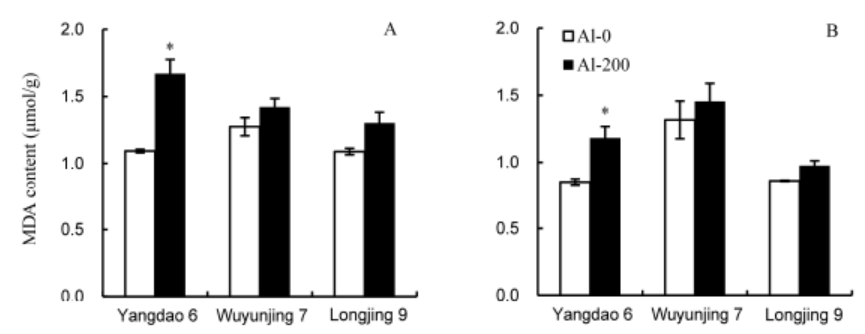
Fig. 8. Malondialdehyde (MDA) content in shoots (A) and roots (B) of three rice varieties after exposure to 200 μmol/L aluminum (Al) for 12 d (means ± SE, n = 3). * means significant difference at P ˂ 0.05, according to the Duncan’s test.
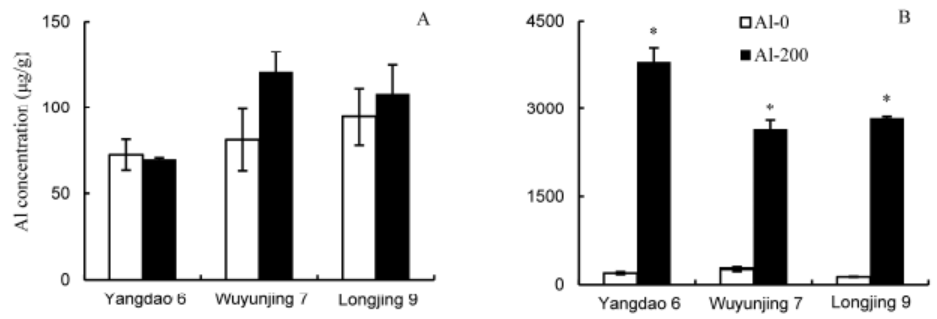
Fig. 9. Aluminum (Al) concentration in shoots (A) and roots (B) of three rice varieties after exposure to 200 μmol/L Al for 12 d (mean ± SE, n = 3). * means significant difference at P ˂ 0.05, according to the Duncan’s test.
| Element | Yangdao 6 | Wuyunjing 7 | Longjing 9 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-0 | Al+ | Al-0 | Al+ | Al-0 | Al+ | |||||
| P | 5.83 ± 0.17 | 5.10 ± 0.24 | 6.17 ± 0.05 | 7.08 ± 0.50 * | 4.75 ± 0.11 | 6.46 ± 0.21 * | ||||
| K | 11.39 ± 0.18 | 7.55 ± 0.65 * | 9.40 ± 0.20 | 6.36 ± 0.35 * | 12.93 ± 0.32 | 10.59 ± 0.02 * | ||||
| Ca | 1.90 ± 0.12 | 1.16 ± 0.08 * | 1.95 ± 0.09 | 1.47 ± 0.16 * | 2.39 ± 0.03 | 1.19 ± 0.05 * | ||||
| Mg | 2.98 ± 0.27 | 1.39 ± 0.19 * | 1.82 ± 0.07 | 0.97 ± 0.07 * | 1.32 ± 0.01 | 0.88 ± 0.04 | ||||
| Mn | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.00 * | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | ||||
Table 2 Effects of aluminum (Al) (200 μmol/L) stress on phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg) and manganese (Mn) contents in roots of three rice varieties. (mg/g)
| Element | Yangdao 6 | Wuyunjing 7 | Longjing 9 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-0 | Al+ | Al-0 | Al+ | Al-0 | Al+ | |||||
| P | 5.83 ± 0.17 | 5.10 ± 0.24 | 6.17 ± 0.05 | 7.08 ± 0.50 * | 4.75 ± 0.11 | 6.46 ± 0.21 * | ||||
| K | 11.39 ± 0.18 | 7.55 ± 0.65 * | 9.40 ± 0.20 | 6.36 ± 0.35 * | 12.93 ± 0.32 | 10.59 ± 0.02 * | ||||
| Ca | 1.90 ± 0.12 | 1.16 ± 0.08 * | 1.95 ± 0.09 | 1.47 ± 0.16 * | 2.39 ± 0.03 | 1.19 ± 0.05 * | ||||
| Mg | 2.98 ± 0.27 | 1.39 ± 0.19 * | 1.82 ± 0.07 | 0.97 ± 0.07 * | 1.32 ± 0.01 | 0.88 ± 0.04 | ||||
| Mn | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.00 * | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | ||||
| Element | Yangdao 6 | Wuyunjing 7 | Longjing 9 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-0 | Al+ | Al-0 | Al+ | Al-0 | Al+ | |||
| P | 8.42 ± 0.52 | 7.54 ± 0.28 | 11.11 ± 0.35 | 11.07 ± 0.82 | 8.50 ± 0.23 | 7.30 ± 0.14 | ||
| K | 20.03 ± 1.09 | 19.83 ± 0.62 | 20.41 ± 0.40 | 19. 56 ± 1.20 | 18.75 ± 0.07 | 15.36 ± 0.22 * | ||
| Ca | 5.31 ± 0.60 | 3.28 ± 0.10 * | 4.60 ± 0.23 | 3.77 ± 0.13 | 3.39 ± 0.05 | 2.85 ± 0.02 | ||
| Mg | 6.77 ± 0.41 | 4.20 ± 0.14 * | 5.08 ± 0.19 | 4.19 ± 0.13 * | 3.19 ± 0.03 | 3.31 ± 0.08 | ||
| Mn | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.02 * | 0.67 ± 0.02 | 0.53 ± 0.02 * | 0.31 ± 0.00 | 0.24 ± 0.00 * | ||
Table 3 Effects of aluminum (Al) (200 μmol/L) stress on phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg) and manganese (Mn) contents in shoots of three rice varieties. (mg/g)
| Element | Yangdao 6 | Wuyunjing 7 | Longjing 9 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-0 | Al+ | Al-0 | Al+ | Al-0 | Al+ | |||
| P | 8.42 ± 0.52 | 7.54 ± 0.28 | 11.11 ± 0.35 | 11.07 ± 0.82 | 8.50 ± 0.23 | 7.30 ± 0.14 | ||
| K | 20.03 ± 1.09 | 19.83 ± 0.62 | 20.41 ± 0.40 | 19. 56 ± 1.20 | 18.75 ± 0.07 | 15.36 ± 0.22 * | ||
| Ca | 5.31 ± 0.60 | 3.28 ± 0.10 * | 4.60 ± 0.23 | 3.77 ± 0.13 | 3.39 ± 0.05 | 2.85 ± 0.02 | ||
| Mg | 6.77 ± 0.41 | 4.20 ± 0.14 * | 5.08 ± 0.19 | 4.19 ± 0.13 * | 3.19 ± 0.03 | 3.31 ± 0.08 | ||
| Mn | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.02 * | 0.67 ± 0.02 | 0.53 ± 0.02 * | 0.31 ± 0.00 | 0.24 ± 0.00 * | ||
| 1 | Arenhart R A, Lima J C D, Pedron M, Carvalho F E L, Silveira J A G D, Rosa S B, Caverzan A, Andrade C M B, Schünemann M, Margis R, Margis-pinheiro M.2013. Involvement of ASR genes in aluminum tolerance mechanisms in rice.Plant Cell Environ, 36(1): 52-67. |
| 2 | Chen Y H, Huang S H, Liu S H, Wang G P, Ding F, Shao Z C, Shen Z G.2006. Study of the heavy metal contamination in soils and vegetables in Nanjing area.Resour Environ Yangtze Basin, 15(3): 356-360. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 | Dally A M, Second G.1990. Chloroplast DNA diversity in wild and cultivated species of rice (Genus Oryza section Oryza): Cladistic-mutation and genetic-distance analysis.Theor Appl Genet, 80(2): 209-222. |
| 4 | Duan B L, Lu Y W, Yin C Y, Junttila Q, Li C Y.2005. Physiological responses to drought and shade in two contrasting picea asperata populations.Physiol Plant, 124(4): 476-484. |
| 5 | Famoso A N, Clark R T, Shaff J E, Craft E, McCouch S R, Kochian L V.2010. Development of a novel aluminum tolerance phenotyping platform used for comparisons of cereal aluminum tolerance and investigations into rice aluminum tolerance mechanisms.Plant Physiol, 153: 1678-1691. |
| 6 | Famoso A N, Zhao K, Clark R T, Tung C W, Wright M H, Carlos B, Kochian L V, McCouch S R.2011. Genetic architecture of aluminum tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) determined through genome-wide association analysis and QTL mapping.PLoS Genet, 7: e1002221. |
| 7 | Foy C D.1988. Plant adaptation to acid, aluminum-toxic soils.Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal, 19: 959-987. |
| 8 | Garris A J, Tai T H, Coburn J, Kresovich S, McCouch S.2005 Genetic structure and diversity in Oryza sativa L.Genetics, 169: 1631-1638. |
| 9 | Guo T R, Yao C P, Zhang Z D, Wang J J, Wang M.2013. Involvement of antioxidative defense system in rice seedlings exposed to aluminum toxicity and phosphorus deficiency.Chin J Rice Sci, 27(6): 653-657. (in Chinese with Englsih abstract) |
| 10 | Hoekenga O A, Vision T J, Shaff J E, Monforte A J, Lee G P, Howell S H, Kochian L V.2003. Identification and characterization of aluminum tolerance loci in Arabidopsis (Landsberg erecta × Columbia) by quantitative trait locus mapping: A physiologically simple but genetically complex trait.Plant Physiol, 132(2): 936-948. |
| 11 | Hu H, Mu J, Zhang H J, Tao Y Z, Han B.2006. Differentiation of a miniature inverted transposable element (MITE) system in Asian rice cultivars and its inference for a diphyletic origin of two sub-species of Asian cultivated rice.J Integ Plant Biol, 48(3): 260-267. |
| 12 | Huang W F, Chen X Y, Xing C H, Zheng Z S, Cai M Z, Zhao X L.2013. Effects of phosphorous on aluminum tolerance and cell wall polysaccharide components in rice root tips.Chin J Rice Sci, 27(2): 161-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 13 | Khatiwada S P, Senadhira Carpena A L, Zeigler R S, Fernandez P G.1996. Variability and genetics of tolerance for aluminum toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet, 93: 738-744. |
| 14 | Kikui S, Sasaki T, Maekawa M, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Matsumoto H, Yamamoto Y.2005. Physiological and genetic analyses of aluminum tolerance in rice, focusing on root growth during germination.J Inorg Biochem, 99: 1837-1844. |
| 15 | Kochian L V.1995. Cellular mechanisms of aluminum toxicity and resistance in plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 46: 237-260. |
| 16 | Kochian L V, Hoekenga O A, Pineros M A.2004. How do crop plants tolerate acid soils? Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance and phosphorous efficiency. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 55: 459-493. |
| 17 | Lin C H, Chen B S, Yu C W, Chiang S W.2001. A water-based triphenyltetrazolium chloride method for the evaluation of green plant tissue viability.Phytochem Anal, 12: 211-213. |
| 18 | Londo J P, Chiang Y C, Hung K H, Chiang T Y, Schaal B A.2006. Phylogeography of Asian wild rice, Oryza rufipogon, reveals multiple independent domestications of cultivated rice, Oryza sativa.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103: 9578-9583. |
| 19 | Ma J F.2000. Role of organic acids in detoxification of aluminum in higher plants.Plant Cell Physiol, 41(4): 383-390. |
| 20 | Ma J F, Ryan P R, Delhaize E.2001. Aluminum tolerance in plants and the complexing role of organic acids.Trends Plant Sci, 6(6): 273-278. |
| 21 | Ma J F, Shen R, Zhao Z, Wissuwa M, Takeuchi Y, Ebitani T, Yano M.2002. Response of rice to Al stress and identification of quantitative trait loci for Al tolerance.Plant Cell Physiol, 43: 652-659. |
| 22 | Narasimhamoorthy B, Blancaflor E B, Bouton J H, Payton M E, Sledge M K.2007. A comparison of hydroponics, soil, and root staining methods for evaluation of aluminum tolerance in Medicago truncatula (Barrel medic) germplasm.Crop Sci, 47: 321-328. |
| 23 | Pellet D M, Papernik L A, Kochian L V.1996. Multiple aluminum resistance mechanisms in wheat (roles of root apical phosphate and malate exudation).Plant Physiol, 112: 591-597. |
| 24 | Samac D A, Tesfaye M.2003. Plant improvement for tolerance to aluminum in acid soils: A review.Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult, 75: 189-207. |
| 25 | Shen R F, Ma J, Kyo M, Iwashita T.2002. Compartmentation of aluminum in leaves of an Al-accumulator, Fagopyrum esculentum Moench.Planta, 215: 394-398. |
| 26 | Silva J O C, Paiva E A S, Modolo L V, Nascentes C C, Franca M G C.2013. Removal of root apices enables study of dirent toxic effects of aluminum on rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaf cells.Envrion Exp Bot, 95: 41-49. |
| 27 | Taylor G J, Foy C D.1985. Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in Triticum aestivum L. (wheat): I. Differential pH induced by winter cultivars in nutrient solutions.Am J Bot, 72(5): 695-701. |
| 28 | Wang J P, Raman H, Read B, Zhou M, Mendham N J, Venkatanagappa S.2006. Validation of an Alt locus for aluminum tolerance scored with eriochrome cyanine R staining method in barley cultivar Honen (Hordeum vulgare L.).Aust J Agric Res, 57(1): 113-118. |
| 29 | Watanabe T, Okada K.2005. Interactive effects of Al, Ca and other cations on root elongation of rice cultivars under low pH.Ann Bot, 95: 379-385. |
| 30 | Wolt J.1994. Soil Solution Chemistry: Applications to Environmental Science and Agriculture. New York: John Wiley & Sons INC. |
| 31 | Wu P, Zhao B, Yan J, Luo A, Wu Y X, Senadihra D.1997. Genetic control of seedling tolerance to aluminum toxicity in rice.Euphytica, 97: 289-293. |
| 32 | Yang J L, Li Y Y, Zhang Y J, Zhang S S, Wu Y R, Wu P, Zheng S J.2008. Cell wall polysaccharides are specifically involved in the exclusion of aluminum from the rice root apex.Plant Physiol, 146: 602-611. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [13] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| [14] | Lu Xuedan, Li Fan, Xiao Yunhua, Wang Feng, Zhang Guilian, Deng Huabing, Tang Wenbang. Grain Shape Genes: Shaping the Future of Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 379-404. |
| [15] | Zhang Guomei, Li Han, Liu Shanshan, Zhou Xuming, Lu Mingyang, Tang Liang, Sun Lihua. Water Extract of Rice False Smut Balls Activates Nrf2/HO-1 and Apoptosis Pathways, Causing Liver Injury [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 473-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||