
Rice Science ›› 2015, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (3): 108-115.DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60288-2
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yue Feng1, Rong-rong Zhai2, Ze-chuan Lin1, Li-yong Cao1, Xing-hua Wei1, Shi-hua Cheng1( )
)
Received:2014-10-27
Accepted:2015-01-13
Online:2015-05-28
Published:2015-03-27
Yue Feng, Rong-rong Zhai, Ze-chuan Lin, Li-yong Cao, Xing-hua Wei, Shi-hua Cheng. Quantitative Trait Locus Analysis for Rice Yield Traits under Two Nitrogen Levels[J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(3): 108-115.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.org/EN/10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60288-2
| Level | Trait | Parent | RIL population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xieqingzao B | Zhonghui 9308 | Mean | Range | Kurtosis | Skewness | |||
| Low N | Number of panicles per plant | 10.8 | 7.7 | 10 | 5.7-19.0 | 0.48 | 0.55 | |
| Panicle length (cm) | 19.3 | 25.3 | 20.4 | 15.2-29.7 | 0.53 | 0.55 | ||
| Number of spikelets per panicle | 74.6 | 193.2 | 111 | 51.8-242.8 | 0.72 | 0.89 | ||
| Number of filled grains per panicle | 62.8 | 168.5 | 90.4 | 19.2-218.8 | 0.57 | 0.7 | ||
| Seed-setting rate (%) | 84.2 | 87.2 | 80.7 | 41.2-94.5 | 1.69 | -1.21 | ||
| Grain density per panicle (grains/cm) | 3.9 | 7.6 | 5.4 | 3.0-9.3 | 0.08 | 0.61 | ||
| 1000-grain weight (g) | 26 | 21.6 | 23.3 | 19.4-29.6 | 0.09 | 0.59 | ||
| Grain yield per plant (g) | 17.6 | 27.4 | 19.6 | 4.8-37.9 | 0.61 | 0.53 | ||
| Normal N | Number of panicles per plant | 13.5 | 9.8 | 11.8 | 7.2-18.2 | -0.43 | 0.35 | |
| Panicle length (cm) | 20.7 | 26 | 20.6 | 15.5-29.2 | 0.86 | 0.6 | ||
| Number of spikelets per panicle | 106.5 | 168.3 | 112.4 | 55.7-229.1 | 0.46 | 0.79 | ||
| Number of filled grains per panicle | 90.9 | 135.6 | 91.4 | 29.7-198.0 | 0.43 | 0.65 | ||
| Seed-setting rate (%) | 85.4 | 80.6 | 81.1 | 51.4-94.2 | 1.86 | -1.28 | ||
| Grain density per panicle (grains/cm) | 5.1 | 6.5 | 5.4 | 3.0-9.0 | -0.1 | 0.55 | ||
| 1000-grain weight (g) | 26.4 | 21.5 | 23.2 | 14.5-29.4 | 0.69 | 0.15 | ||
| Grain yield per plant (g) | 25.9 | 29.8 | 23.7 | 5.6-45.3 | 0.86 | 0.13 | ||
Table 1 Phenotypic analysis of recombinant inbred line (RIL) population and the parents under low N and normal N levels.
| Level | Trait | Parent | RIL population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xieqingzao B | Zhonghui 9308 | Mean | Range | Kurtosis | Skewness | |||
| Low N | Number of panicles per plant | 10.8 | 7.7 | 10 | 5.7-19.0 | 0.48 | 0.55 | |
| Panicle length (cm) | 19.3 | 25.3 | 20.4 | 15.2-29.7 | 0.53 | 0.55 | ||
| Number of spikelets per panicle | 74.6 | 193.2 | 111 | 51.8-242.8 | 0.72 | 0.89 | ||
| Number of filled grains per panicle | 62.8 | 168.5 | 90.4 | 19.2-218.8 | 0.57 | 0.7 | ||
| Seed-setting rate (%) | 84.2 | 87.2 | 80.7 | 41.2-94.5 | 1.69 | -1.21 | ||
| Grain density per panicle (grains/cm) | 3.9 | 7.6 | 5.4 | 3.0-9.3 | 0.08 | 0.61 | ||
| 1000-grain weight (g) | 26 | 21.6 | 23.3 | 19.4-29.6 | 0.09 | 0.59 | ||
| Grain yield per plant (g) | 17.6 | 27.4 | 19.6 | 4.8-37.9 | 0.61 | 0.53 | ||
| Normal N | Number of panicles per plant | 13.5 | 9.8 | 11.8 | 7.2-18.2 | -0.43 | 0.35 | |
| Panicle length (cm) | 20.7 | 26 | 20.6 | 15.5-29.2 | 0.86 | 0.6 | ||
| Number of spikelets per panicle | 106.5 | 168.3 | 112.4 | 55.7-229.1 | 0.46 | 0.79 | ||
| Number of filled grains per panicle | 90.9 | 135.6 | 91.4 | 29.7-198.0 | 0.43 | 0.65 | ||
| Seed-setting rate (%) | 85.4 | 80.6 | 81.1 | 51.4-94.2 | 1.86 | -1.28 | ||
| Grain density per panicle (grains/cm) | 5.1 | 6.5 | 5.4 | 3.0-9.0 | -0.1 | 0.55 | ||
| 1000-grain weight (g) | 26.4 | 21.5 | 23.2 | 14.5-29.4 | 0.69 | 0.15 | ||
| Grain yield per plant (g) | 25.9 | 29.8 | 23.7 | 5.6-45.3 | 0.86 | 0.13 | ||
| Trait | QTL | Chromosome | Marker interval | LOD value | Additive effect a | Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNP | qPNP-1 | 1 | RM8147-RM10576 | 2.56 | -0.54 | 5.2 |
| qPNP-3a | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 3.86 | -0.88 | 13.62 | |
| qPNP-7a | 7 | RM5436-RM3670 | 2.5 | -0.61 | 6.09 | |
| qPNP-8 | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 3.29 | -0.68 | 8.11 | |
| PL (cm) | qPL-1a | 1 | RM8111-RM5359 | 2.62 | 0.65 | 5.03 |
| qPL-2 | 2 | RM3865-RM6247 | 2.54 | -0.64 | 5 | |
| qPL-6a | 6 | RM5754-RM136 | 5.4 | 1.11 | 15.58 | |
| qPL-7a | 7 | RM5436-RM3670 | 4.93 | 1.01 | 11.75 | |
| qPL-8a | 8 | RM8266-RM5556 | 3.38 | 0.76 | 7.06 | |
| SP | qSP-1a | 1 | RM1-RM3746 | 4.82 | 13.7 | 12.78 |
| qSP-2 | 2 | RM3865-RM6247 | 3.26 | -9.79 | 6.58 | |
| qSP-3a | 3 | RM282-RM6283 | 2.71 | 11.35 | 8.31 | |
| qSP-3b | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 7.62 | 17.07 | 18.75 | |
| qSP-6a | 6 | RM136-RM6302 | 3.55 | 10.45 | 6.4 | |
| qSP-6b | 6 | RM3207-RM7193 | 3.22 | 9.87 | 6.1 | |
| qSP-7a | 7 | RM5436-RM3670 | 2.99 | 8.99 | 5.42 | |
| qSP-8a | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 4.7 | 12.83 | 11.6 | |
| FGP | qFGP-1a | 1 | RM1-RM3746 | 3.47 | 12.2 | 11.21 |
| qFGP-2 | 2 | RM3865-RM6247 | 2.53 | -8.72 | 5.74 | |
| qFGP-3a | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 4.98 | 14.23 | 14.43 | |
| qFGP-8a | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 4.63 | 12.38 | 11.16 | |
| SSR (%) | qSSR-3 | 3 | RM6806-RM227 | 2.52 | -2.96 | 8.81 |
| GD (grains/cm) | qGD-1a | 1 | RM576-RM35 | 3.26 | 0.37 | 7.19 |
| qGD-3a | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 6.95 | 0.61 | 18.36 | |
| qGD-8 | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 3.98 | 0.41 | 8.93 | |
| TWG (g) | qTWG-3a | 3 | RM6283-RM7370 | 10.97 | -1.27 | 26.73 |
| qTWG-7 | 7 | RM320-RM182 | 2.51 | 0.49 | 4.93 | |
| GYP (g) | qGYP-4 | 4 | RM273-RM241 | 2.54 | 0.62 | 5.73 |
Table 2 QTL mapping of the traits of recombinant inbred line (RIL) population under low N level.
| Trait | QTL | Chromosome | Marker interval | LOD value | Additive effect a | Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNP | qPNP-1 | 1 | RM8147-RM10576 | 2.56 | -0.54 | 5.2 |
| qPNP-3a | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 3.86 | -0.88 | 13.62 | |
| qPNP-7a | 7 | RM5436-RM3670 | 2.5 | -0.61 | 6.09 | |
| qPNP-8 | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 3.29 | -0.68 | 8.11 | |
| PL (cm) | qPL-1a | 1 | RM8111-RM5359 | 2.62 | 0.65 | 5.03 |
| qPL-2 | 2 | RM3865-RM6247 | 2.54 | -0.64 | 5 | |
| qPL-6a | 6 | RM5754-RM136 | 5.4 | 1.11 | 15.58 | |
| qPL-7a | 7 | RM5436-RM3670 | 4.93 | 1.01 | 11.75 | |
| qPL-8a | 8 | RM8266-RM5556 | 3.38 | 0.76 | 7.06 | |
| SP | qSP-1a | 1 | RM1-RM3746 | 4.82 | 13.7 | 12.78 |
| qSP-2 | 2 | RM3865-RM6247 | 3.26 | -9.79 | 6.58 | |
| qSP-3a | 3 | RM282-RM6283 | 2.71 | 11.35 | 8.31 | |
| qSP-3b | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 7.62 | 17.07 | 18.75 | |
| qSP-6a | 6 | RM136-RM6302 | 3.55 | 10.45 | 6.4 | |
| qSP-6b | 6 | RM3207-RM7193 | 3.22 | 9.87 | 6.1 | |
| qSP-7a | 7 | RM5436-RM3670 | 2.99 | 8.99 | 5.42 | |
| qSP-8a | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 4.7 | 12.83 | 11.6 | |
| FGP | qFGP-1a | 1 | RM1-RM3746 | 3.47 | 12.2 | 11.21 |
| qFGP-2 | 2 | RM3865-RM6247 | 2.53 | -8.72 | 5.74 | |
| qFGP-3a | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 4.98 | 14.23 | 14.43 | |
| qFGP-8a | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 4.63 | 12.38 | 11.16 | |
| SSR (%) | qSSR-3 | 3 | RM6806-RM227 | 2.52 | -2.96 | 8.81 |
| GD (grains/cm) | qGD-1a | 1 | RM576-RM35 | 3.26 | 0.37 | 7.19 |
| qGD-3a | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 6.95 | 0.61 | 18.36 | |
| qGD-8 | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 3.98 | 0.41 | 8.93 | |
| TWG (g) | qTWG-3a | 3 | RM6283-RM7370 | 10.97 | -1.27 | 26.73 |
| qTWG-7 | 7 | RM320-RM182 | 2.51 | 0.49 | 4.93 | |
| GYP (g) | qGYP-4 | 4 | RM273-RM241 | 2.54 | 0.62 | 5.73 |
| Trait | QTL | Chromosome | Marker interval | LOD value | Additive effect a | Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNP | qPNP-3b | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 5.12 | -1.26 | 22.06 |
| qPNP-7b | 7 | RM5436-RM3670 | 3.5 | -0.81 | 9.03 | |
| PL (cm) | qPL-1b | 1 | RM3520-RM5310 | 3.49 | 0.71 | 7.81 |
| qPL-3 | 3 | RM148-RM85 | 4.4 | 0.73 | 9.48 | |
| qPL-6b | 6 | RM5754-RM136 | 5.22 | 0.87 | 13.77 | |
| qPL-7b | 7 | RM182-RM336 | 2.57 | 0.57 | 5.84 | |
| qPL-8b | 8 | RM8266-RM5556 | 3.04 | 0.59 | 5.74 | |
| SP | qSP-1b | 1 | RM35-RM8147 | 2.93 | 8.43 | 6.12 |
| qSP-1c | 1 | RM212-RM265 | 2.56 | 8.31 | 5.78 | |
| qSP-3c | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 6.25 | 14.08 | 15.82 | |
| qSP-7b | 7 | RM182-RM336 | 3.93 | 10.58 | 8.91 | |
| qSP-7c | 7 | RM234-RM118 | 3.38 | -10.67 | 8.43 | |
| qSP-8b | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 3.88 | 9.96 | 8.22 | |
| FGP | qFGP-1b | 1 | RM212-RM265 | 2.95 | 9.25 | 8.48 |
| qFGP-3b | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 6.54 | 13.53 | 17.73 | |
| qFGP-8b | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 3.8 | 9.31 | 8.52 | |
| SSR (%) | qSSR-1 | 1 | RM265-RM315 | 4.95 | 3.07 | 13.06 |
| qSSR-5 | 5 | RM159-RM1248 | 2.73 | -2.49 | 8.89 | |
| GD (grains/cm) | qGD-1b | 1 | RM576-RM35 | 2.73 | 0.34 | 6.04 |
| qGD-3b | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 6.11 | 0.66 | 21.93 | |
| qGD-6 | 6 | RM3430-RM494 | 2.56 | -0.4 | 7.96 | |
| TWG (g) | qTWG-3b | 3 | RM6283-RM7370 | 4.61 | -1.03 | 13.96 |
| GYP (g) | qGYP-1 | 1 | RM576-RM35 | 2.5 | 1.56 | 6.25 |
| qGYP-9 | 9 | RM1553-RM2144 | 2.78 | -1.62 | 6.8 |
Table 3 QTL mapping of the traits for recombinant inbred line (RIL) population under normal N level.
| Trait | QTL | Chromosome | Marker interval | LOD value | Additive effect a | Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNP | qPNP-3b | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 5.12 | -1.26 | 22.06 |
| qPNP-7b | 7 | RM5436-RM3670 | 3.5 | -0.81 | 9.03 | |
| PL (cm) | qPL-1b | 1 | RM3520-RM5310 | 3.49 | 0.71 | 7.81 |
| qPL-3 | 3 | RM148-RM85 | 4.4 | 0.73 | 9.48 | |
| qPL-6b | 6 | RM5754-RM136 | 5.22 | 0.87 | 13.77 | |
| qPL-7b | 7 | RM182-RM336 | 2.57 | 0.57 | 5.84 | |
| qPL-8b | 8 | RM8266-RM5556 | 3.04 | 0.59 | 5.74 | |
| SP | qSP-1b | 1 | RM35-RM8147 | 2.93 | 8.43 | 6.12 |
| qSP-1c | 1 | RM212-RM265 | 2.56 | 8.31 | 5.78 | |
| qSP-3c | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 6.25 | 14.08 | 15.82 | |
| qSP-7b | 7 | RM182-RM336 | 3.93 | 10.58 | 8.91 | |
| qSP-7c | 7 | RM234-RM118 | 3.38 | -10.67 | 8.43 | |
| qSP-8b | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 3.88 | 9.96 | 8.22 | |
| FGP | qFGP-1b | 1 | RM212-RM265 | 2.95 | 9.25 | 8.48 |
| qFGP-3b | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 6.54 | 13.53 | 17.73 | |
| qFGP-8b | 8 | RM5556-RM310 | 3.8 | 9.31 | 8.52 | |
| SSR (%) | qSSR-1 | 1 | RM265-RM315 | 4.95 | 3.07 | 13.06 |
| qSSR-5 | 5 | RM159-RM1248 | 2.73 | -2.49 | 8.89 | |
| GD (grains/cm) | qGD-1b | 1 | RM576-RM35 | 2.73 | 0.34 | 6.04 |
| qGD-3b | 3 | RM135-RM168 | 6.11 | 0.66 | 21.93 | |
| qGD-6 | 6 | RM3430-RM494 | 2.56 | -0.4 | 7.96 | |
| TWG (g) | qTWG-3b | 3 | RM6283-RM7370 | 4.61 | -1.03 | 13.96 |
| GYP (g) | qGYP-1 | 1 | RM576-RM35 | 2.5 | 1.56 | 6.25 |
| qGYP-9 | 9 | RM1553-RM2144 | 2.78 | -1.62 | 6.8 |
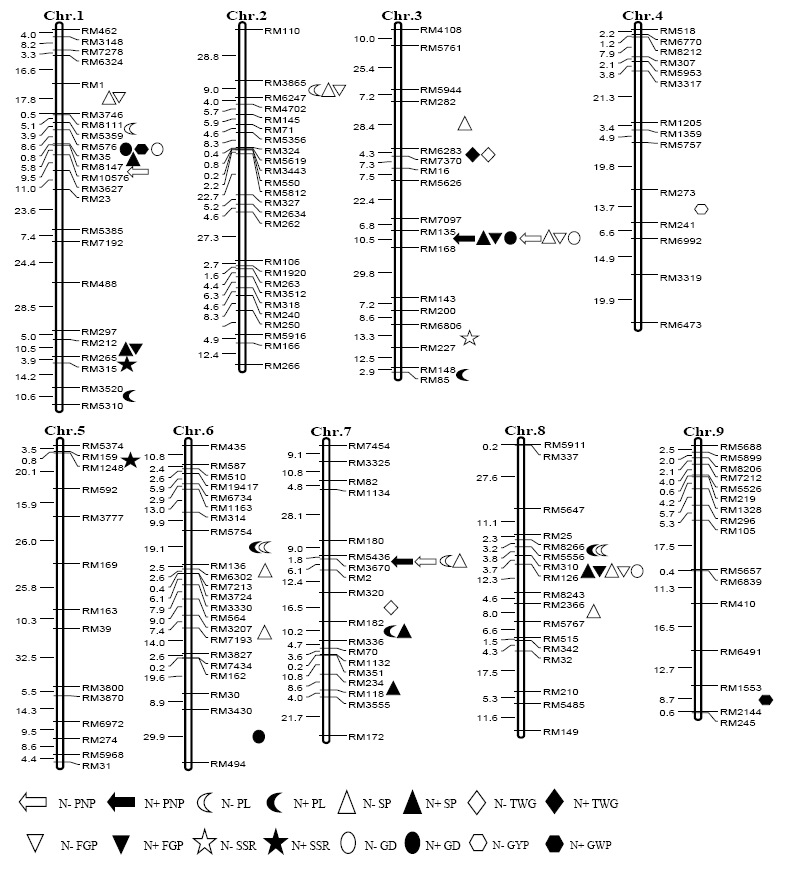
Fig. 1. Location of QTLs for rice yield component traits under low (N-) and normal (N+) N levels. PNP, Number of panicles per plant; PL, Panicle length; SP, Number of spikelets per panicle; FGP, Number of filled grains per panicle; SSR, Seed-setting rate; GD, Grain density per panicle; TWG, 1000-grain weight; GYP, Grain yield per plant.
| 1 | Cao G L, Zhang Y Y, Piao Z Z, Han L Z.2006. Evaluation of tolerance to low N-fertilized level for rice type.J Plant Genet Res, 7(3): 316-320. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 2 | Cheng J F, Dai T B, Jiang H Y, Pan X Y, Cao W X.2012. Characterization of leaf carbon and nitrogen assimilation in different rice genotypes at jointing stage and their relationships with nitrogen utilization efficiency.Chin J Rice Sci, 26(1): 101-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 | Cheng S H, Zhuang J Y, Cao L Y, Chen S G, Peng Y C, Fan Y Y, Zhan X D, Zheng K L.2004. Molecular breeding for super rice hybrids.Chin J Rice Sci, 18(5): 377-383. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 4 | Cho Y G, Kang H J, Lee J S, Lee Y T, Lim S J, Gauch H, Eun M Y, McCouch S R.2007. Identification of quantitative trait loci in rice for yield, yield components, and agronomic traits across years and locations.Crop Sci, 47: 2403-2417. |
| 5 | Cho Y, Jiang W Z, Chin J H, Piao Z Z, Cho Y G, McCouch S R, Koh H J.2007. Identification of QTLs associated with physiological nitrogen use efficiency in rice.Mol Cells, 23(1): 72-79. |
| 6 | Feng Y, Cao L Y, Wu W M, Shen X H, Zhan X D, Zhai R R, Chen D B, Cheng S H.2010a. Comparative analyses of QTLs for N-deficiency tolerance at different seedling stages in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 16(4): 880-886. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 7 | Feng Y, Cao L Y, Wu W M, Shen X H, Zhan X D, Zhai R R, Wang R C, Chen D B, Cheng S H.2010b. Mapping QTLs for nitrogen-deficiency tolerance at seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Plant Breeding, 129: 652-656. |
| 8 | Feng Y, Zhai R R, Cao L Y, Lin Z C, Wei X H, Cheng S H.2011. QTLs for plant height and heading date in rice under two nitrogen levels.Acta Agron Sin, 37(9): 1525-1532. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 9 | Hu S K, Zeng D L, Su Y, Shi Z Y, Ye W J, Dong G J, Zhu L, Hu J, Qian Q, Guo L B.2012. QTL analysis of nitrogen content of plant shoot under two nitrogen conditions in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Aust J Crop Sci, 6(12): 1737-1744. |
| 10 | Ishimaru K, Kobayashi N, Ono K, Yano M, Ohsugi R.2001. Are contents of rubisco, soluble protein and nitrogen in flag leaves of rice controlled by the same genetics?J Exp Bot, 52(362): 1827-1833. |
| 11 | Jiang L G, Dai T B, Wei S Q, Gan X Q, Xu J Y, Cao W X.2003. Genotypic differences and valuation in nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency in rice.Acta Phytoecol Sin, 27(4): 466-471. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 12 | Jiang Y H, Cai Z X, Xie W B, Long T, Yu H H, Zhang Q F.2012. Rice functional genomics research: Progress and implications for crop genetic improvement.Biotechnol Adv, 30: 1059-1070. |
| 13 | McCouch S R.2008. Gene nomenclature system for rice.Rice, 1(1): 72-84. |
| 14 | Obara M, Kajiura M, Fukuta Y, Yano M, Hayashi M, Yamaya T, Sato T.2001. Mapping of QTLs associated with cytosolic glutamine synthetase and NADH-glutamate synthase in rice (Oryza sativa L.).J Exp Bot, 52(359): 1209-1217. |
| 15 | Peng S B, Huang J L, Zhong X H, Yang J C, Wang G H, Zou Y B, Zhang F S, Zhu Q S, Roland B, Christian W.2002. Challenge and opportunity in improving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China.Sci Agric Sin, 1(7): 776-785. |
| 16 | Peng S B, Buresh R J, Huang J L, Yang J C, Zou Y B, Zhong X H, Wang G H, Zhang F S.2006. Strategies for overcoming low agronomic nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice system in China.Field Crops Res, 96(1): 37-47. |
| 17 | Piao Z Z, Han L Z, Koh H J.2003. Variations of nitrogen use efficiency by rice genotype.Chin J Rice Sci, 17(3): 233-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 18 | Senaratne R, Ratnasinghe D S.1995. Nitrogen fixation and beneficial effects of some grain legumes and green-manure crops on rice.Boil Fert Soils, 19(1): 49-54. |
| 19 | Senthilvel S, Vinod K K, Malarvizhi P, Maheswaran M.2008. QTL and QTL × environment effects on agronomic and nitrogen acquisition traits in rice.J Inter Plant Biol, 50(9): 1108-1117. |
| 20 | Shan Y H, Wang Y L, Pan X B.2005. Mapping of QTLs for nitrogen use efficiency and related traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Sci Agric Sin, 4(10): 721-727. |
| 21 | Shen X H, Chen S G, Cao L Y, Zhan X D, Chen D B, Wu W M, Cheng S H.2008. Construction of genetic linkage map based on a RIL population derived from super hybrid rice, XY9308.Mol Plant Breeding, 6(5): 861-866. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 22 | Tong H H, Mei H W, Yu X Q, Xu X Y, Li M S, Zhang S Q, Luo L J.2006. Identification of related QTLs at late developmental stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under two nitrogen levels.Acta Genet Sin, 33(5): 458-467. |
| 23 | Tong H H, Chen L, Li W P, Mei H W, Xiong Y Z, Yu X Q, Xu X Y, Zhang S Q, Luo L J.2011. Identification and characterization of quantitative trait loci for grain yield and its components under different nitrogen fertilization levels in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Mol Breeding, 28: 495-509. |
| 24 | Wei D, Cui K H, Pan J F, Wang Q, Wang K, Zhang X M, Xiang J, Nie L X, Huang J L.2011a. Identification of quantitative trait loci for grain yield and its components in response to low nitrogen application in rice.Aust J Crop Sci, 6(6): 986-994. |
| 25 | Wei D, Cui K H, Pan J F, Ye G Y, Xiang J, Nie L X, Huang J L.2011b. Genetic dissection of grain nitrogen use efficiency and grain yield and their relationship in rice.Field Crops Res, 124: 340-346. |
| 26 | Wei D, Cui K H, Yu G Y, Pan J F, Xiang J, Huang J L, Nie L X.2012. QTL mapping for nitrogen-use efficiency and nitrogen-deficiency tolerance traits in rice.Plant Soil, 359: 281-295. |
| 27 | Xing G X, Zhu Z L.2000. An assessment of N loss from agricultural fields to the environment in China.Nutr Cycl Agroecosys, 57(1): 67-73. |
| 28 | Yamaya T, Obara M, Nakajima H, Sasaki S, Hayakawa T, Sato T.2002. Genetic manipulation and quantitative-trait loci mapping for nitrogen recycling in rice.J Exp Bot, 53(370): 917-925. |
| 29 | Yin C Y, Wang S Y, Liu H M, Xue Y Z, Zhang X, Wang H L, Sun J Q, Hu X M, Li X J.2013. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on grain filling characteristics and rice quality of superior and inferior grains in super japonica rice Xindao 18.Chin J Rice Sci, 27(5): 503-510. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 30 | Zhan X D, Yu P, Lin Z C, Chen D B, Shen X H, Zhang Y X, Fu J L, Cheng S H, Cao L Y.2014. QTL mapping of heading date and yield -related traits in rice using a recombination inbred lines (RILs) population derived from BG1/XLJ.Chin J Rice Sci, 28(6): 570-580. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 31 | Zhang Q F.2007. Strategies for developing green super rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104(42): 16402-16409. |
| 32 | Zhuang J Y, Lin H X, Lu J, Qian H R, Hittalmani S, Huang N, Zheng K L.1997. Analysis of QTL × environment interaction for yield components and plant height in rice.Theor Appl Genet, 95: 799-808. |
| [1] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [2] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [3] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [4] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [5] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [6] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [7] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [8] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [9] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [10] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [14] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| [15] | Lu Xuedan, Li Fan, Xiao Yunhua, Wang Feng, Zhang Guilian, Deng Huabing, Tang Wenbang. Grain Shape Genes: Shaping the Future of Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 379-404. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||