
Rice Science ›› 2015, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (3): 99-107.DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60287-0
• Orginal Article • Next Articles
D. Kumbhar Shailesh1,2, L. Kulwal Pawan1( ), V. Patil Jagannath1,3, D. Sarawate Chandrakant2, P. Gaikwad Anil4, S. Jadhav Ashok1
), V. Patil Jagannath1,3, D. Sarawate Chandrakant2, P. Gaikwad Anil4, S. Jadhav Ashok1
Received:2014-10-05
Accepted:2015-02-11
Online:2015-05-28
Published:2015-03-27
D. Kumbhar Shailesh, L. Kulwal Pawan, V. Patil Jagannath, D. Sarawate Chandrakant, P. Gaikwad Anil, S. Jadhav Ashok. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure in Landraces and Improved Rice Varieties from India[J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(3): 99-107.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.org/EN/10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60287-0
| Genotype | Parentage/detail |
|---|---|
| Heera | CR404-48 × CR289-1208 |
| Halvi Sal 17 | Local selection from Kolhapur (MS) |
| RDN185-2 | Halvi Sal 17 × TN1 |
| Phule Radha | TN1 × Kolamba 540 |
| RTN1 | IR8 × RTN24 |
| Ratna | TKM6 × IR8 |
| Phule Samruddhi | Indrayani × Sonsali |
| Jaya | TN1 × T141 |
| Phule Maval | Pawana × Indrayani |
| Pawana | Pusa 33 × IR28 |
| Indrayani | Ambemohar 157 × IR8 |
| Bhogavati | Selection from Basmati composite |
| Pusa Basmati 1 | Pusa 150 × Karnal Local |
| Ghansal | Local selection from Kolhapur (MS) |
| Kalajirga | Local selection from Kolhapur (MS) |
| Vivek Dhan 82 | VL221 × UPR82-1-7 |
| Badshabhog | Local type/landrace from Orissa |
| Kothimbire | Landrace from Kolhapur (MS) |
| BPT5204 | (GEB24 × TN1) × Mahsuri |
| RDN98-2-3-5-14 | Halvi Sal 17 × TN1 |
| RDN01-2-10-9 | Ambemohar 157 × IR8 |
| KJT2 | RP6-17 × RP4-14 |
| EK70 | Landrace from Igatpuri, Nasik (MS) |
| Patni | Landrace from Sindhudurg (MS) |
| Diwani | Landrace from Uttar Pradesh |
| Shyam Jeer | Landrace from Bihar |
| Kasturi | Basmati 370 × CRR88-17-1-5 |
| SD17 | Pusa Basmati 1 × IET12603 |
| Sugandhamati | Pusa Basmati 1 × IET12603 |
| Basmati 386 | Selection from Pak Basmati |
| MC4 | Selection from Karnal Local |
| Haryana Basmati | Local selection from Haryana |
| Mahisugandha | BK79 × Basmati 370 |
| Khalibagh | Landrace from Sindhudurg (MS) |
| Vikram | Landrace from Sindhudurg (MS) |
| Tulshi tall | Landrace from Kolhapur (MS) |
| Champakali | Landrace from Kolhapur (MS) |
| Siddhagiri | Landrace from Kolhapur (MS) |
| RDN97-2 | TN1 × IR64 |
| RDN99-12 | Selection from Phule Maval |
| RDN99-14 | Bhogavati × RTN24 |
| RTN purple | Local selection from Ratnagiri (MS) |
| Taraori Basmati | Pureline selection from NBC19 |
| RDN02-80 | Indrayani × Pusa Basmati 1 |
| Pavsal | Landrace from Pune (MS) |
| Antersal | Landrace from Pune (MS) |
| Nalabhat | Landrace from Pune (MS) |
| Sonsali | Landrace from Pune (MS) |
| LK248 | Local selection from Nasik (MS) |
| Pomendi Local | Landrace from Ratnagiri (MS) |
Table 1 List of rice genotypes along with their pedigree.
| Genotype | Parentage/detail |
|---|---|
| Heera | CR404-48 × CR289-1208 |
| Halvi Sal 17 | Local selection from Kolhapur (MS) |
| RDN185-2 | Halvi Sal 17 × TN1 |
| Phule Radha | TN1 × Kolamba 540 |
| RTN1 | IR8 × RTN24 |
| Ratna | TKM6 × IR8 |
| Phule Samruddhi | Indrayani × Sonsali |
| Jaya | TN1 × T141 |
| Phule Maval | Pawana × Indrayani |
| Pawana | Pusa 33 × IR28 |
| Indrayani | Ambemohar 157 × IR8 |
| Bhogavati | Selection from Basmati composite |
| Pusa Basmati 1 | Pusa 150 × Karnal Local |
| Ghansal | Local selection from Kolhapur (MS) |
| Kalajirga | Local selection from Kolhapur (MS) |
| Vivek Dhan 82 | VL221 × UPR82-1-7 |
| Badshabhog | Local type/landrace from Orissa |
| Kothimbire | Landrace from Kolhapur (MS) |
| BPT5204 | (GEB24 × TN1) × Mahsuri |
| RDN98-2-3-5-14 | Halvi Sal 17 × TN1 |
| RDN01-2-10-9 | Ambemohar 157 × IR8 |
| KJT2 | RP6-17 × RP4-14 |
| EK70 | Landrace from Igatpuri, Nasik (MS) |
| Patni | Landrace from Sindhudurg (MS) |
| Diwani | Landrace from Uttar Pradesh |
| Shyam Jeer | Landrace from Bihar |
| Kasturi | Basmati 370 × CRR88-17-1-5 |
| SD17 | Pusa Basmati 1 × IET12603 |
| Sugandhamati | Pusa Basmati 1 × IET12603 |
| Basmati 386 | Selection from Pak Basmati |
| MC4 | Selection from Karnal Local |
| Haryana Basmati | Local selection from Haryana |
| Mahisugandha | BK79 × Basmati 370 |
| Khalibagh | Landrace from Sindhudurg (MS) |
| Vikram | Landrace from Sindhudurg (MS) |
| Tulshi tall | Landrace from Kolhapur (MS) |
| Champakali | Landrace from Kolhapur (MS) |
| Siddhagiri | Landrace from Kolhapur (MS) |
| RDN97-2 | TN1 × IR64 |
| RDN99-12 | Selection from Phule Maval |
| RDN99-14 | Bhogavati × RTN24 |
| RTN purple | Local selection from Ratnagiri (MS) |
| Taraori Basmati | Pureline selection from NBC19 |
| RDN02-80 | Indrayani × Pusa Basmati 1 |
| Pavsal | Landrace from Pune (MS) |
| Antersal | Landrace from Pune (MS) |
| Nalabhat | Landrace from Pune (MS) |
| Sonsali | Landrace from Pune (MS) |
| LK248 | Local selection from Nasik (MS) |
| Pomendi Local | Landrace from Ratnagiri (MS) |
| Marker | Total no. of alleles | No. of monomorphic alleles | No. of unique alleles | Polymorphism (%) | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM11 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.461 |
| RM21 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.663 |
| RM44 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.91 |
| RM72 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.765 |
| RM162 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 0.765 |
| RM204 | 23 | 0 | 2 | 100 | 0.928 |
| RM209 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.811 |
| RM215 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 0.607 |
| RM224 | 15 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 0.901 |
| RM241 | 17 | 0 | 2 | 100 | 0.923 |
| RM246 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.917 |
| RM259 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.963 |
| RM307 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.523 |
| TRS26 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.893 |
| TRS33 | 19 | 0 | 2 | 100 | 0.902 |
| ISSR808 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 66.7 | 0.105 |
| ISSR809 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.818 |
| ISSR810 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.867 |
| ISSR811 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.866 |
| ISSR812 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 90 | 0.85 |
| ISSR813 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.851 |
| ISSR814 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.65 |
| ISSR815 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.91 |
| ISSR818 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.648 |
| ISSR821 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.793 |
| ISSR823 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 91.7 | 0.913 |
| ISSR826 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.197 |
| ISSR827 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.989 |
Table 2 Polymorphism patterns obtained using simple sequence repeat (SSR) and inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) primers
| Marker | Total no. of alleles | No. of monomorphic alleles | No. of unique alleles | Polymorphism (%) | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM11 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.461 |
| RM21 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.663 |
| RM44 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.91 |
| RM72 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.765 |
| RM162 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 0.765 |
| RM204 | 23 | 0 | 2 | 100 | 0.928 |
| RM209 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.811 |
| RM215 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 0.607 |
| RM224 | 15 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 0.901 |
| RM241 | 17 | 0 | 2 | 100 | 0.923 |
| RM246 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.917 |
| RM259 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.963 |
| RM307 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.523 |
| TRS26 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.893 |
| TRS33 | 19 | 0 | 2 | 100 | 0.902 |
| ISSR808 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 66.7 | 0.105 |
| ISSR809 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.818 |
| ISSR810 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.867 |
| ISSR811 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.866 |
| ISSR812 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 90 | 0.85 |
| ISSR813 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.851 |
| ISSR814 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.65 |
| ISSR815 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.91 |
| ISSR818 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.648 |
| ISSR821 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.793 |
| ISSR823 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 91.7 | 0.913 |
| ISSR826 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.197 |
| ISSR827 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.989 |
| Cluster | Sub-cluster | No. of genotypes | Genotype | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | A | 4 | Heera, SD17, Sugandhamati, MC4 | Basmati line Karnal Local as parent or in ancestry, except Heera |
| B | 1 | RDN02-80 | Basmati line Karnal Local as parent or in ancestry, except Heera | |
| II | A | 7 | Halvi Sal 17, EK70, Patni, Siddhagiri, RDN97-2, Khalibagh, Sonsali | Non-scented, landraces or local selections, except RDN97-2 |
| B | 3 | Kalajirga, Kasturi, Champakali | Scented landraces except Kasturi | |
| III | A | 14 | RDN185-2, Phule Radha, RTN1, Pawana, Jaya, Ratna, Phule Samruddhi, Phule Maval, Indrayani, Bhogavati, RDN01-2-10-9, KJT2, BPT5204, RDN98-2-3-5-14 | All improved varieties with dwarf plant type, IR8 or TN1 as parent or in ancestry |
| B | 5 | RDN99-12, RDN99-14, RTN purple, LK248, Pomendi Local | Dwarf plant type, midlate to late maturity, medium slender grain type | |
| C | 2 | Nalabhat, Taroari Basmati | Landraces, long-slender grain type, late maturity | |
| D | 3 | Vivek Dhan 82, Haryana Basmati, Antersal | Tall plant type | |
| IV | 2 | Vikram, Tulshi tall | Landraces | |
| V | A | 4 | Pusa Basmati 1, Ghansal, Badshabhog, Pavsal | Scented Basmati or non-Basmati genotypes; mostly landraces |
| B | 5 | Kothimbire, Diwani, Shyam Jeer, | Scented Basmati or non-Basmati genotypes; mostly landraces | |
| Basmati 386, Mahisugandha |
Table 3 Distribution of rice genotypes into different clusters based on simple sequence repeat (SSR) and inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers.
| Cluster | Sub-cluster | No. of genotypes | Genotype | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | A | 4 | Heera, SD17, Sugandhamati, MC4 | Basmati line Karnal Local as parent or in ancestry, except Heera |
| B | 1 | RDN02-80 | Basmati line Karnal Local as parent or in ancestry, except Heera | |
| II | A | 7 | Halvi Sal 17, EK70, Patni, Siddhagiri, RDN97-2, Khalibagh, Sonsali | Non-scented, landraces or local selections, except RDN97-2 |
| B | 3 | Kalajirga, Kasturi, Champakali | Scented landraces except Kasturi | |
| III | A | 14 | RDN185-2, Phule Radha, RTN1, Pawana, Jaya, Ratna, Phule Samruddhi, Phule Maval, Indrayani, Bhogavati, RDN01-2-10-9, KJT2, BPT5204, RDN98-2-3-5-14 | All improved varieties with dwarf plant type, IR8 or TN1 as parent or in ancestry |
| B | 5 | RDN99-12, RDN99-14, RTN purple, LK248, Pomendi Local | Dwarf plant type, midlate to late maturity, medium slender grain type | |
| C | 2 | Nalabhat, Taroari Basmati | Landraces, long-slender grain type, late maturity | |
| D | 3 | Vivek Dhan 82, Haryana Basmati, Antersal | Tall plant type | |
| IV | 2 | Vikram, Tulshi tall | Landraces | |
| V | A | 4 | Pusa Basmati 1, Ghansal, Badshabhog, Pavsal | Scented Basmati or non-Basmati genotypes; mostly landraces |
| B | 5 | Kothimbire, Diwani, Shyam Jeer, | Scented Basmati or non-Basmati genotypes; mostly landraces | |
| Basmati 386, Mahisugandha |
| Sub-population | No. of genotypes | Genotype | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19 | Phule Maval, RTN1, Indrayani, Bhogavati, | Almost all improved varieties (except Antersal and Kalajirga) with dwarf plant type; Most of the genotypes have IR8 or TN1 in their parentage/ancestry. |
| RDN01-2-10-9, KJT2, Pawana, Phule Samruddhi, Ratna, Antersal, RDN185-2, Phule Radha, | |||
| RDN99-12, Vivek Dhan 82, Jaya, BPT5204, RDN98-2-3-5-14, Kalajirga, Kasturi | |||
| 2 | 9 | Pomendi Local, LK248, Vikram, RDN99-14, | Almost all are landraces or selections from local types (except RDN99-14) |
| RTN purple, Taroari Basmati, Nalabhat, Sonsali, MC4 | |||
| 3 | 8 | Siddhagiri, Patni, RDN97-2, EK70, Halvi Sal 17, RDN02-80, Champakali, Haryana Basmati | Almost all are landraces or selections from local types (except RDN97-2 and RDN02-80) |
| 4 | 7 | Shyam Jeer, Basmati 386, Kothimbire, Mahisugandha, Diwani, Tulshi tall, Khalibagh | Mostly landraces; Basmati 386 and Mahisugandha have Pakistan Basmati in parentage/ancestry |
| 5 | 7 | Pusa Basmati 1, Ghansal, Badshabhog, Sugandhamati, Pavsal, SD17, Heera | Landraces and improved Basmati types; Pusa Basmati 1, SD17 and Sugandhamati have Karnal Local in the parentage/ancestry |
Table 4 Distribution of rice genotypes into different sub-populations based on population structure analysis.
| Sub-population | No. of genotypes | Genotype | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19 | Phule Maval, RTN1, Indrayani, Bhogavati, | Almost all improved varieties (except Antersal and Kalajirga) with dwarf plant type; Most of the genotypes have IR8 or TN1 in their parentage/ancestry. |
| RDN01-2-10-9, KJT2, Pawana, Phule Samruddhi, Ratna, Antersal, RDN185-2, Phule Radha, | |||
| RDN99-12, Vivek Dhan 82, Jaya, BPT5204, RDN98-2-3-5-14, Kalajirga, Kasturi | |||
| 2 | 9 | Pomendi Local, LK248, Vikram, RDN99-14, | Almost all are landraces or selections from local types (except RDN99-14) |
| RTN purple, Taroari Basmati, Nalabhat, Sonsali, MC4 | |||
| 3 | 8 | Siddhagiri, Patni, RDN97-2, EK70, Halvi Sal 17, RDN02-80, Champakali, Haryana Basmati | Almost all are landraces or selections from local types (except RDN97-2 and RDN02-80) |
| 4 | 7 | Shyam Jeer, Basmati 386, Kothimbire, Mahisugandha, Diwani, Tulshi tall, Khalibagh | Mostly landraces; Basmati 386 and Mahisugandha have Pakistan Basmati in parentage/ancestry |
| 5 | 7 | Pusa Basmati 1, Ghansal, Badshabhog, Sugandhamati, Pavsal, SD17, Heera | Landraces and improved Basmati types; Pusa Basmati 1, SD17 and Sugandhamati have Karnal Local in the parentage/ancestry |
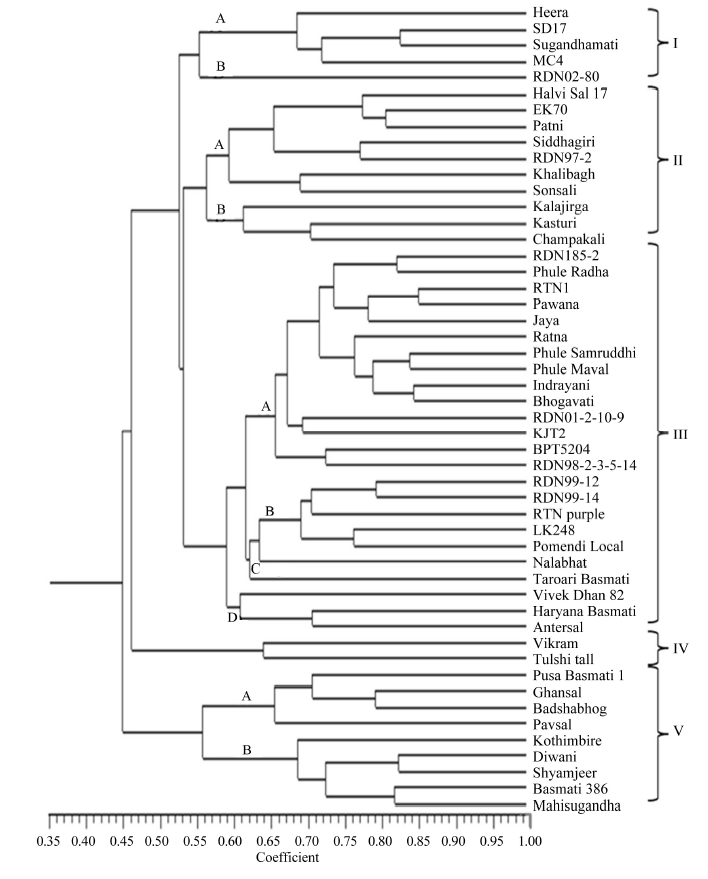
Fig. 1. Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) based dendrogram of rice genotypes using pooled data of inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers.
| 1 | Chang T T.1976. The origin, evolution, cultivation, dissemination, and diversification of Asian and African rices.Euphytica, 25(1): 425-441. |
| 2 | Davierwala A P, Chowdari K V, Kumar S, Reddy A P K, Ranjekar P K, Gupta V S.2000. Use of three different marker systems to estimate genetic diversity of Indian elite rice varieties.Genetica, 108(3): 269-284. |
| 3 | Das B, Sengupta S, Parida S K, Roy B, Ghosh M, Prasad M, Ghose T K.2013. Genetic diversity and population structure of rice landraces from Eastern and North Eastern States of India.BMC Genet, 14: 71. |
| 4 | Doyle J J, Doyle J L.1990. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue.Focus, 12: 13-15. |
| 5 | Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J.2005. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study.Mol Ecol, 14(8): 2611-2620. |
| 6 | Ghaley B B, Christiansen J L, Andersen S B.2012. Genetic diversity for blast resistance of Bhutan rice landraces.Euphytica, 184(1): 119-130. |
| 7 | Hashimoto Z, Mori N, Kawamural M, Ishii T, Yoshida S, Ikegami M, Takumi S, Nakamural C.2004. Genetic diversity and phylogeny of Japanese sake-brewing rice as revealed by AFLP and nuclear and chloroplast SSR markers.Theor Appl Genet, 109(8): 1586-1596. |
| 8 | Jain S, Jain R K, McCouch S R.2004. Genetic analysis of Indian aromatic and quality rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm using panels of fluorescently-labeled microsatellite markers.Theor Appl Genet, 109(5): 965-977. |
| 9 | Joshi S P, Gupta V S, Aggarwal R K, Ranjekar P K, Brar D S.2000. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship as revealed by inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism in the genus Oryza.Theor Appl Genet, 100(8): 1311-1320. |
| 10 | Kanawapee N, Sanitchon J, Srihaban P, Theerakulpisut P.2011. Genetic diversity analysis of rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.) differing in salinity tolerance based on RAPD and SSR markers.Elect J Biotech, 14(6): e1379. |
| 11 | Lapitan V C, Brar D S, Abe T, Redofia E D.2007. Assessment of genetic diversity of Philippine rice cultivars carrying good quality traits with SSR markers.Breeding Sci, 57(4): 263-270. |
| 12 | McCouch S R, Teytelman L, Xu Y B, Lobos K B, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B Y, Maghirang R, Li Z K, Xing Y Z, Zhang Q F, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L.2002. Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.).DNA Res, 9(6): 199-207. |
| 13 | Murthy B R, Arunachalam V.1966. The nature of divergence in relation to breeding systems in some crop plants.Ind J Genet Plant Breeding, 26: 188-198. |
| 14 | Nagaraju J, Kathirvel M, Ramesh Kumar R, Siddiq E A, Hasnain S E.2002. Genetic analysis of traditional and evolved Basmati and non-Basmati rice varieties by using fluorescence-based ISSR-PCR and SSR markers.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99(9): 5836-5841. |
| 15 | O’Neill R, Snowdon R, Kohler W.2003. Population genetics: Aspects of biodiversity.Progr Bot, 64: 115-137. |
| 16 | Pervaiz Z H, Rabbani M A, Khaliq I, Pearce S R, Malik S A.2010. Genetic diversity associated with agronomic traits using microsatellite markers in Pakistani rice landraces.Electr J Biotech, 13(3): 1-12. |
| 17 | Powell W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey M, Vogel J, Tingey S, Rafalski A.1996. The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis.Mol Breeding, 2(3): 225-238. |
| 18 | Pritchard J K, Stephens M, Donnelly P.2000. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data.Genetics, 155: 945-959. |
| 19 | Rabbani M A, Pervaiz Z H, Masood M S.2008. Genetic diversity analysis of traditional and improved cultivars of Pakistani rice (Oryza sativa L.) using RAPD markers.Electr J Biotech, 11(3): 1-10. |
| 20 | Reed P W, Davies J L, Copeman J B, Bennett S T, Palmer S M, Pritchard L E, Gough S C L, Kawaguchi Y, Cordell H J, Balfour K M, Jenkins S C, Powell E E, Vignal A, Todd J A.1994. Chromosome-specific microsatellite sets for fluorescence-based, semi-automated genome mapping.Nat Genet, 7: 390-395. |
| 21 | Saini N, Jain N, Jain S, Jain R K.2004. Assessment of genetic diversity within and among Basmati and non-Basmati rice varieties using AFLP, ISSR and SSR markers.Euphytica, 140(3): 133-146. |
| 22 | Shivapriya M, Hittalmani S.2006. Detection of genotype-specific fingerprints and molecular diversity of selected Indian locals and landraces of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using DNA markers.Ind J Genet Plant Breeding, 66(1): 1-5. |
| 23 | Singh B, Singh S P, Kumar J.2011. Assessment of genetic diversity in aromatic rices (Oryza sativa L.) using morphological, physiological and SSR markers.Ind J Genet Plant Breeding, 71(3): 214-222. |
| 24 | Sivaranjani A K P, Pandey M K, Sudharshan I, Kumar G R, Madhav M S, Sundaram R M, Varaprasad G S, Shobha Rani N.2010. Assessment of genetic diversity among basmati and non-basmati aromatic rices of India using SSR markers.Curr Sci, 99(2): 221-226. |
| 25 | Smith J S C, Smith O S.1992. Fingerprinting crop varieties.Adv Agron, 47: 85-140. |
| 26 | Smith S.1997. Cultivar identification and varietal protection. In: Caetano-Anollés G, Gresshoff P M. DNA Markers: Protocols, Applications, and Overviews. New York: Wiley-VCH: 283. |
| 27 | Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S.2001. Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Frequency, length variation, transposon association and genetic marker potential.Genom Res, 11(8): 1441-1452. |
| 28 | Vanaja T, Babu L C.2004. Heterosis for yield and yield components in rice (Oryza sativa L.).J Trop Agric, 42(1/2): 43-44. |
| 29 | Vanniarajan C, Vinod K K, Pereira A.2012. Molecular evaluation of genetic diversity and association studies in rice (Oryza sativa L.).J Genet, 91(1): 9-19. |
| 30 | Yadav S, Singh A, Singh M R, Goel N, Vinod K K, Mohapatra T, Singh A K.2013. Assessment of genetic diversity in Indian rice germplasm (Oryza sativa L.): Use of random versus trait-linked microsatellite markers.J Genet, 92(3): 545-557. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [13] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| [14] | Lu Xuedan, Li Fan, Xiao Yunhua, Wang Feng, Zhang Guilian, Deng Huabing, Tang Wenbang. Grain Shape Genes: Shaping the Future of Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 379-404. |
| [15] | Zhang Guomei, Li Han, Liu Shanshan, Zhou Xuming, Lu Mingyang, Tang Liang, Sun Lihua. Water Extract of Rice False Smut Balls Activates Nrf2/HO-1 and Apoptosis Pathways, Causing Liver Injury [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 473-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||