
Rice Science ›› 2015, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (1): 16-26.DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60277-8
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Md Iftekharuddaula Khandakar( ), Uddin Ahmed Helal, Ghosal Sharmistha, Rahman Moni Zakiah, Amin Al, Shamsher Ali Md
), Uddin Ahmed Helal, Ghosal Sharmistha, Rahman Moni Zakiah, Amin Al, Shamsher Ali Md
Received:2014-07-23
Accepted:2014-09-11
Online:2015-01-10
Published:2014-11-26
Md Iftekharuddaula Khandakar, Uddin Ahmed Helal, Ghosal Sharmistha, Rahman Moni Zakiah, Amin Al, Shamsher Ali Md. Development of New Submergence Tolerant Rice Variety for Bangladesh Using Marker-Assisted Backcrossing[J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(1): 16-26.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.org/EN/10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60277-8
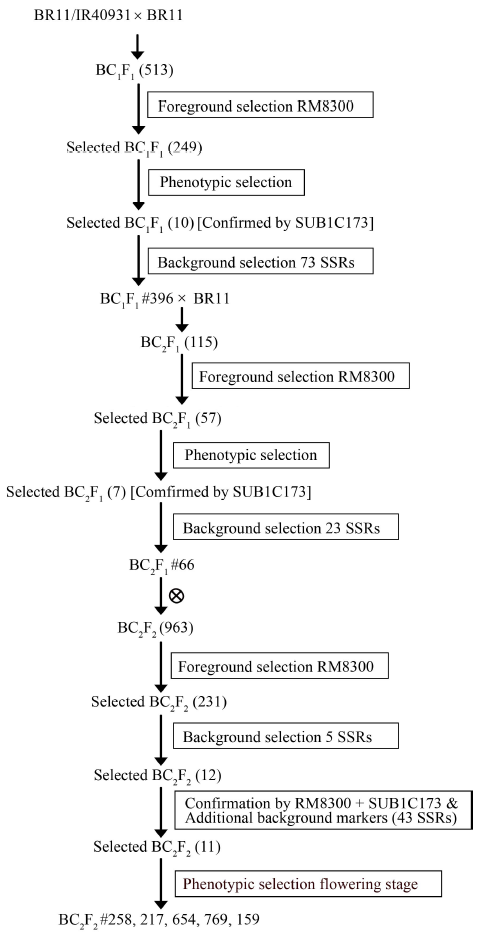
Fig. 1. Development of submergence tolerant backcross recombinant lines through marker-assisted backcrossing with details of markers used in each generation. The number in parentheses indicates the total number of plants whereas the number followed by # indicates the individual plant number.
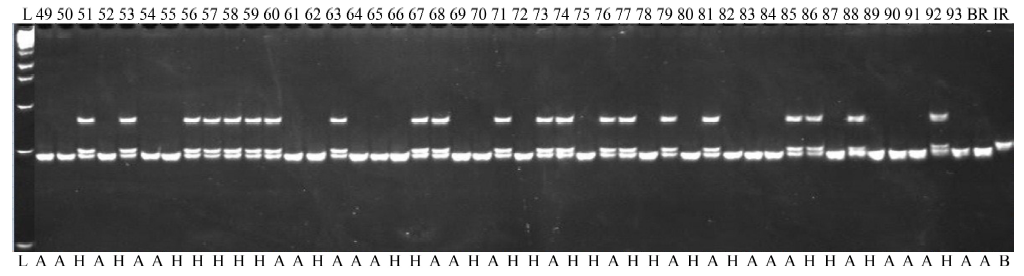
Fig. 2. Partial view of the gel picture of the foreground selection with the tightly linked marker RM8300, BC1F1 generation. L, 1 kb+ DNA ladder; BR, BR11, the recipient parent; IR, IR40931-33-1-3-2, the donor parent; A, Homozygous recipient allele; B, Homozygous donor allele; H, Heterozygous allele; 49-93, Plant number.
| Plant No. | A | H | B | Recipient allele (%) | Rank-background |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 46 | 26 | 0 | 81.9 | 2 |
| 59 | 26 | 46 | 0 | 68.1 | 7 |
| 73 | 23 | 41 | 8 | 60.4 | 9 |
| 86 | 29 | 43 | 0 | 70.1 | 5 |
| 145 | 34 | 38 | 0 | 73.6 | 4 |
| 235 | 18 | 43 | 11 | 54.9 | 10 |
| 248 | 26 | 46 | 0 | 68.1 | 8 |
| 396 | 48 | 24 | 0 | 83.3 | 1 |
| 445 | 44 | 28 | 0 | 80.6 | 3 |
| 496 | 27 | 45 | 0 | 68.8 | 6 |
| Average | 35 | 71 |
Table 1 Results of the background selection, BC1F1 generation.
| Plant No. | A | H | B | Recipient allele (%) | Rank-background |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 46 | 26 | 0 | 81.9 | 2 |
| 59 | 26 | 46 | 0 | 68.1 | 7 |
| 73 | 23 | 41 | 8 | 60.4 | 9 |
| 86 | 29 | 43 | 0 | 70.1 | 5 |
| 145 | 34 | 38 | 0 | 73.6 | 4 |
| 235 | 18 | 43 | 11 | 54.9 | 10 |
| 248 | 26 | 46 | 0 | 68.1 | 8 |
| 396 | 48 | 24 | 0 | 83.3 | 1 |
| 445 | 44 | 28 | 0 | 80.6 | 3 |
| 496 | 27 | 45 | 0 | 68.8 | 6 |
| Average | 35 | 71 |
| Plant No. | A | H | B | Recipient allele (%) | Rank-background |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 396-2 | 59 | 13 | 0 | 89.8 | 4 |
| 396-18 | 60 | 12 | 0 | 90.6 | 3 |
| 396-26 | 64 | 8 | 0 | 93.8 | 2 |
| 396-37 | 59 | 13 | 0 | 89.8 | 5 |
| 396-45 | 55 | 17 | 0 | 86.7 | 7 |
| 396-66 | 67 | 5 | 0 | 96.1 | 1 |
| 396-89 | 58 | 14 | 0 | 89.1 | 6 |
| Average | 12 | 90.8 |
Table 2 Results of the background selection, BC2F1 generation.
| Plant No. | A | H | B | Recipient allele (%) | Rank-background |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 396-2 | 59 | 13 | 0 | 89.8 | 4 |
| 396-18 | 60 | 12 | 0 | 90.6 | 3 |
| 396-26 | 64 | 8 | 0 | 93.8 | 2 |
| 396-37 | 59 | 13 | 0 | 89.8 | 5 |
| 396-45 | 55 | 17 | 0 | 86.7 | 7 |
| 396-66 | 67 | 5 | 0 | 96.1 | 1 |
| 396-89 | 58 | 14 | 0 | 89.1 | 6 |
| Average | 12 | 90.8 |
| Marker | Plant number | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 396-158 | 396-159 | 396-217 | 396-258 | 396-294 | 396-559 | 396-607 | 396-642 | 396-654 | 396-664 | 396-769 | 396-771 | |
| RM237 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| RM486 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| RM154 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| RM279 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| RM566 | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | H | B | B | H | B |
Table 3 Results of the background selection, BC2F2 generation.
| Marker | Plant number | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 396-158 | 396-159 | 396-217 | 396-258 | 396-294 | 396-559 | 396-607 | 396-642 | 396-654 | 396-664 | 396-769 | 396-771 | |
| RM237 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| RM486 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| RM154 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| RM279 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| RM566 | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | H | B | B | H | B |
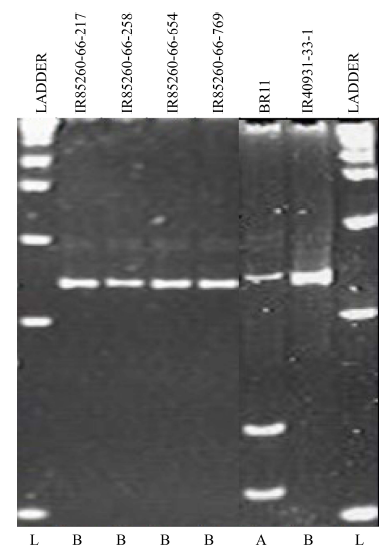
Fig. 3. Confirmation of SUB1 allele in four backcross recombinant lines derived from BR11/IR40931-33-1-3-2 by GnS2 marker. A, Homozygous recipient allele; B, Homozygous donor allele; L, 1 kb+ DNA ladder.

Fig. 4. Graphical genotype of plant number IR85260-66-654 of BC2F2 population. The red colored regions on the chromosomes indicate homozygous regions for the recipient genome while the blue colored regions indicate the heterozygous regions. The distances were represented in cM based on published map of Temnykh et al (2001)
| Designation | Days to maturity (d) | Plant height (cm) | No. of panicles per plant | Panicle length (cm) | No. of grains per m2 | Survival rate (%) | Grain yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t/hm2) | |||||||
| BR11-Sub1 | 152 | 123 | 14.4 | 26.1 | 25 044 | 79.6 | 5.67 |
| Swarna-Sub1 | 155 | 95 | 15.3 | 23.8 | 33 783 | 89.6 | 5.53 |
| Sambha Mahsuri-Sub1 | 151 | 93 | 14.1 | 23.6 | 32 424 | 89 | 4.4 |
| IR85260-66-217-Gaz2 | 153 | 127 | 11.8 | 25.7 | 27 303 | 90.8 | 5.8 |
| IR85260-66-654-Gaz2 (BRRI dhan52) | 152 | 127 | 11.8 | 26.5 | 26 909 | 93.4 | 6.13 |
| IR85620-66-769-Gaz2 | 151 | 127 | 11.7 | 26.1 | 24 461 | 94.4 | 5.54 |
| IR85620-391-217 | 152 | 116 | 10.6 | 25.7 | 25 402 | 88.2 | 5.17 |
| IR85260-391-1192 | 152 | 120 | 9.8 | 25.3 | 26 278 | 87.8 | 5.86 |
| IR85260-66-258-Gaz2 | 153 | 128 | 12.5 | 27.7 | 27 284 | 88.4 | 5.79 |
| IR64-Sub1 | 135 | 102 | 17.8 | 25.6 | 22 942 | 92.6 | 3.92 |
| Swarna (CK) | 164 | 90 | 22.4 | 24.5 | 18 075 | 24.8 | 2.15 |
| BR11 (CK) | 164 | 125 | 19.4 | 27.6 | 17 982 | 30.6 | 3.67 |
| LSD (0.05) | 2.4 | 3.7 | 6.53 | 1.53 | 5 942 | 15.1 | 1.37 |
Table 4 Performances of Sub1-lines under controlled submergence condition, T. Aman 2009, BRRI, Gazipur.
| Designation | Days to maturity (d) | Plant height (cm) | No. of panicles per plant | Panicle length (cm) | No. of grains per m2 | Survival rate (%) | Grain yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t/hm2) | |||||||
| BR11-Sub1 | 152 | 123 | 14.4 | 26.1 | 25 044 | 79.6 | 5.67 |
| Swarna-Sub1 | 155 | 95 | 15.3 | 23.8 | 33 783 | 89.6 | 5.53 |
| Sambha Mahsuri-Sub1 | 151 | 93 | 14.1 | 23.6 | 32 424 | 89 | 4.4 |
| IR85260-66-217-Gaz2 | 153 | 127 | 11.8 | 25.7 | 27 303 | 90.8 | 5.8 |
| IR85260-66-654-Gaz2 (BRRI dhan52) | 152 | 127 | 11.8 | 26.5 | 26 909 | 93.4 | 6.13 |
| IR85620-66-769-Gaz2 | 151 | 127 | 11.7 | 26.1 | 24 461 | 94.4 | 5.54 |
| IR85620-391-217 | 152 | 116 | 10.6 | 25.7 | 25 402 | 88.2 | 5.17 |
| IR85260-391-1192 | 152 | 120 | 9.8 | 25.3 | 26 278 | 87.8 | 5.86 |
| IR85260-66-258-Gaz2 | 153 | 128 | 12.5 | 27.7 | 27 284 | 88.4 | 5.79 |
| IR64-Sub1 | 135 | 102 | 17.8 | 25.6 | 22 942 | 92.6 | 3.92 |
| Swarna (CK) | 164 | 90 | 22.4 | 24.5 | 18 075 | 24.8 | 2.15 |
| BR11 (CK) | 164 | 125 | 19.4 | 27.6 | 17 982 | 30.6 | 3.67 |
| LSD (0.05) | 2.4 | 3.7 | 6.53 | 1.53 | 5 942 | 15.1 | 1.37 |
| Designation | Plant height (cm) | Survival rate (%) | Days to maturity (d) | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t/hm2) | ||||
| BRRI dhan52 | 100.7 | 94.9 | 159 | 4.9 |
| IR64-Sub1 | 84.9 | 96.8 | 138 | 3 |
| Samba Mahsuri-Sub1 | 89.2 | 93.2 | 153 | 3.9 |
| IR85260-66-1192 | 95.7 | 93.2 | 155 | 4.1 |
| BRRI dhan51 | 82.1 | 95.6 | 161 | 4.6 |
| IR85260-391-148 | 95.8 | 94.6 | 163 | 4.3 |
| BRRI dhan33 (CK) | 95.2 | 74.2 | 140 | 2.5 |
| BINA dhan7 (CK) | 91.7 | 88.4 | 141 | 2.8 |
| LSD (0.01) | 2.27 | 1.35 | 1.05 | 0.27 |
Table 5 Performances of Sub1-lines under natural flash flood condition, T. Aman in 2010, Borobari, Lalmonirhat.
| Designation | Plant height (cm) | Survival rate (%) | Days to maturity (d) | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t/hm2) | ||||
| BRRI dhan52 | 100.7 | 94.9 | 159 | 4.9 |
| IR64-Sub1 | 84.9 | 96.8 | 138 | 3 |
| Samba Mahsuri-Sub1 | 89.2 | 93.2 | 153 | 3.9 |
| IR85260-66-1192 | 95.7 | 93.2 | 155 | 4.1 |
| BRRI dhan51 | 82.1 | 95.6 | 161 | 4.6 |
| IR85260-391-148 | 95.8 | 94.6 | 163 | 4.3 |
| BRRI dhan33 (CK) | 95.2 | 74.2 | 140 | 2.5 |
| BINA dhan7 (CK) | 91.7 | 88.4 | 141 | 2.8 |
| LSD (0.01) | 2.27 | 1.35 | 1.05 | 0.27 |
| Designation | Plant height | Growth duration | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (d) | (t/hm2) | |
| BRRI dhan52 | 115 | 145 | 5.2 |
| IR64-Sub1 | 95 | 119 | 2.5 |
| BRRI dhan51 | 89 | 150 | 2.1 |
| BRRI dhan33 (CK) | 104 | 117 | 2.6 |
| LSD (0.01) | 2.52 | 0.94 | 0.46 |
Table 6 Performance of entries of phenotypic variations trial, T. Aman in 2011, Gadadhardangi, Faridpur.
| Designation | Plant height | Growth duration | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (d) | (t/hm2) | |
| BRRI dhan52 | 115 | 145 | 5.2 |
| IR64-Sub1 | 95 | 119 | 2.5 |
| BRRI dhan51 | 89 | 150 | 2.1 |
| BRRI dhan33 (CK) | 104 | 117 | 2.6 |
| LSD (0.01) | 2.52 | 0.94 | 0.46 |
| Designation | Plant height (cm) | Growth duration (d) | Yield (t/hm2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L2 | Ave | L1 | L2 | Ave | L1 | L2 | Ave | |
| IR09F147 | 123 | 121 | 122 | 137 | 134 | 136 | 3 | 3.1 | 3.1 |
| IR09F177 | 133 | 129 | 131 | 143 | 139 | 141 | 2.6 | 2.9 | 2.7 |
| IR09F189 | 124 | 105 | 114 | 139 | 135 | 137 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 3 |
| IR09F226 | 137 | 132 | 135 | 143 | 138 | 141 | 3 | 3.2 | 3.1 |
| IR09F236 | 136 | 121 | 128 | 140 | 137 | 138 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 2.8 |
| IR09F253 | 123 | 114 | 118 | 142 | 139 | 140 | 2.8 | 3 | 2.9 |
| BRRI dhan51 | 96 | 86 | 91 | 148 | 143 | 146 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 4.6 |
| BRRI dhan52 | 131 | 136 | 134 | 138 | 133 | 135 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| LSD (0.01) | 6.05 | 12.2 | 2.05 | 2.87 | 0.32 | 0.3 | |||
Table 7 Performance of entries of phenotypic variations trial in submergence prone farmers’ field, T. Aman in 2012.
| Designation | Plant height (cm) | Growth duration (d) | Yield (t/hm2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L2 | Ave | L1 | L2 | Ave | L1 | L2 | Ave | |
| IR09F147 | 123 | 121 | 122 | 137 | 134 | 136 | 3 | 3.1 | 3.1 |
| IR09F177 | 133 | 129 | 131 | 143 | 139 | 141 | 2.6 | 2.9 | 2.7 |
| IR09F189 | 124 | 105 | 114 | 139 | 135 | 137 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 3 |
| IR09F226 | 137 | 132 | 135 | 143 | 138 | 141 | 3 | 3.2 | 3.1 |
| IR09F236 | 136 | 121 | 128 | 140 | 137 | 138 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 2.8 |
| IR09F253 | 123 | 114 | 118 | 142 | 139 | 140 | 2.8 | 3 | 2.9 |
| BRRI dhan51 | 96 | 86 | 91 | 148 | 143 | 146 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 4.6 |
| BRRI dhan52 | 131 | 136 | 134 | 138 | 133 | 135 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| LSD (0.01) | 6.05 | 12.2 | 2.05 | 2.87 | 0.32 | 0.3 | |||
| 1 | Chen S, Lin X H, Xu C G, Zhang Q F.2000. Improvement of bacterial blight resistance of ‘Minghui 63’ an elite restorer line of hybrid rice, by molecular marker-assisted selection.Crop Sci, 40(1): 239-244. |
| 2 | Collard B C Y, Vera Cruz C M, McNally K L, Virk P S, Mackill D J.2008. Rice molecular breeding laboratories in the genomics era: Current status and future considerations.Int J Plant Genom, e524847. |
| 3 | Dey M M, Upadhyaya H K.1996. Yield loss due to drought, cold and submergence in Asia. In: Evenson R E, Herdt R W, Hossain M. Rice Research in Asia: Progress and Priorities. UK, CAB International Wallingford: 291-303. |
| 4 | Frisch M, Bohn M, Melchinger A E.1999. Minimum sample size and optimum positioning of flanking markers in marker-assisted backcrossing for transfer of a target gene.Crop Sci, 39(4): 967-975. |
| 5 | Grover A, Agarwal M, Katiyar-Agarwal S, Sahi C, Agarwal S.2000. Prospects of improving flooding tolerance in lowland rice varieties by conventional breeding and genetic engineering.Curr Sci, 78(2): 132-137. |
| 6 | Hospital F.2001. Size of donor chromosome segments around introgressed loci and reduction of linkage drag in marker- assisted backcross programs.Genetics, 158(3): 1363-1379. |
| 7 | Iftekharuddaula K M, Salam M A, Newaz M A, Haque M E.2005. Per Se performance, specific combining ability, heterosis and interrelationships among them for yield and yield components in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Bull Instit Trop Agric, Kyushu Univ, 27: 1-10. |
| 8 | Iftekharuddaula K M, Newaz M A, Salam M A, Ahmed H U, Mahbub M A A, Septiningsih E M, Collard B C Y, Sanchez D L, Pamplona A M, Mackill D J. 2009. Strategies to introgress qSUB1 through marker-assisted backcrossing into BR11, a mega variety of Bangladesh for rainfed lowland. In: Proceeding of the 14th Australasian Plant Breeding & 11th Sabrao Conference, Cairns, Tropical North Queensland, Australia, 10-14 August, 2009. |
| 9 | Iftekharuddaula K M, Newaz M A, Salam M A, Ahmed H U, Mahbub M A A, Septiningsih E M, Collard B C Y, Sanchez D L, Pamplona A M, Mackill D J.2011. Rapid and high-precision marker assisted backcrossing to introgress the SUB1 QTL into BR11, the rainfed lowland rice mega variety of Bangladesh.Euphytica, 178(1): 83-97. |
| 10 | Iftekharuddaula K M, Salam M A, Newaz M A, Ahmed H U, Collard B C Y, Septiningsih E M, Sanchez D L, Pamplona A M, Mackill D J.2012. Comparison of phenotypic versus marker- assisted background selection for the SUB1 QTL during backcrossing in rice.Breeding Sci, 62(3): 216-222. |
| 11 | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 2007. Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel in Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| 12 | IRGSP.2005. The map-based sequence of the rice genome.Nature, 436: 793-800. |
| 13 | Kabir W.2010. Development of rice in Bangladesh and role of IRRI. In: Proceedings on the Occasion of Celebration of 50th Anniversary of IRRI, Dhaka, 13-14 July, 2010. |
| 14 | Mackill D J.1986. Varietal improvement for rainfed lowland rice in South and Southeast Asia: Results of survey. In: Maclean J, Banta S J, Argosino G S. Progress in rainfed lowland rice. Los Banos, Laguna(Philippines): 115-144. |
| 15 | Mackill D J, Amante M M, Vergara B S, Sarkarung S.1993. Improved semidwarf rice lines with tolerance to submergence of seedlings.Crop Sci, 33(4): 749-753. |
| 16 | McCouch S R, Teytelman L, Xu Y B, Lobos K B, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B Y, Maghirang R, Li Z K, Xing Y Z, Zhang Q F, Kono I, Yano M, Fellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L.2002. Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.).DNA Res, 9(6): 199-207. |
| 17 | Seck P A, Diagne A, Mohanty S, Wopereis M C S.2012. Crops that feed the world 7: Rice.Food Secur, 4(1): 7-24. |
| 18 | Takeuchi Y, Ebitani T, Yamamoto T, Sato H, Ohta H, Hirabayashi H, Ohta H, Nemoto H, Imbe T, Yano M.2006. Development of isogenic lines of rice cultivar Koshihikari with early and late heading by marker-assisted selection.Breeding Sci, 56(4): 405-413. |
| 19 | Temnykh S, Clerck G D, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Carthinour S, McCouch S R.2001. Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (O. sativa L.): Frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential.Genome Res, 11(8): 1441-1452. |
| 20 | van Berloo R.2008. GGT 2.0: Versatile software for visualization and analysis of genetic data.J Hered, 99(2): 232-236. |
| 21 | Young N D, Tanksley S D.1989. RFLP analysis of the size of chromosomal segments retained around the Tm-2 locus of tomato during backcross breeding.Theor Appl Genet, 77(3): 353-359. |
| 22 | Zheng K L, Huang N, Bennett J, Khush G S.1995. PCR-based marker-assisted selection in rice breeding. IRRI Discussion Paper Series No. 12. Los Banos, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute: 1-4. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [14] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [15] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||