
Rice Science ›› 2015, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (1): 1-8.DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60275-4
• Orginal Article • Next Articles
Ming Huang, Ya-hui Wu, Xing-xing Tao, Yong-zhu Liu, Gui-li Yang, Zhi-qiang Chen( )
)
Received:2014-06-22
Accepted:2014-08-16
Online:2015-01-10
Published:2014-11-26
About author:# These authors contributed equally to this work
Ming Huang, Ya-hui Wu, Xing-xing Tao, Yong-zhu Liu, Gui-li Yang, Zhi-qiang Chen. Genetic Diversity of Main Inbred Indica Rice Varieties Applied in Guangdong Province as Revealed by Molecular Marker[J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(1): 1-8.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.org/EN/10.1016/S1672-6308(14)60275-4
| Marker | Chr | Na | Nr | PIC | Marker | Chr | Na | Nr | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ILP marker | RM212 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0.46 | ||||
| RI02341 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.5 | RM489 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.05 |
| RI04587 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM279 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0.25 |
| RI00945 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.06 | RM240 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0.07 |
| RI00301 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0.47 | RM251 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0.3 |
| RI05751 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0.35 | RM168 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0.49 |
| RI01085 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0.49 | RM401 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0.53 |
| RI01614 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0.5 | RM437 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0.1 |
| RI02821 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0.03 | RM584 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0.64 |
| RI04246 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0.36 | RM564 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 0.42 |
| RI03949 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0.09 | RM214 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0.03 |
| RI05815 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM321 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0.45 |
| RI04107 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM21 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0.47 |
| RI03187 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM224 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0.2 |
| RI00213 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0.04 | RM1337 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 0.53 |
| RI02123 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 0.02 | RM499 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 0.09 |
| RI01540 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 0.38 | RM246 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 0.66 |
| RI05818 | 11 | 2 | 0 | 0.5 | RM341 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0.58 |
| RI05618 | 11 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM280 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 0.34 |
| RI05373 | 12 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM481 | 9 | 4 | 0 | 0.67 |
| RI03123 | 12 | 4 | 2 | 0.49 | RM248 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 0.54 |
| SSR marker | RM531 | 10 | 4 | 0 | 0.68 | ||||
| RM1395 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.24 | RM566 | 10 | 4 | 0 | 0.45 |
| RM274 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.27 | RM3808 | 11 | 4 | 0 | 0.41 |
| RM30 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.22 | RM474 | 11 | 4 | 1 | 0.39 |
| RM271 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.03 | RM80 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 0.63 |
| RM277 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.04 | RM518 | 12 | 5 | 2 | 0.65 |
| RM5479 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0.5 | RM440 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 0.6 |
| Average of ILPs | 2.2 | 0.7 | 0.22 | ||||||
| Average of SSRs | 3.3 | 0.7 | 0.38 | ||||||
| Average of ILP and SSR combinations | 3.4 | 0.7 | 0.32 | ||||||
Table 1 Genetic diversity information revealed by intron length polymorphism (ILP) and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for the 299 indica rice.
| Marker | Chr | Na | Nr | PIC | Marker | Chr | Na | Nr | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ILP marker | RM212 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0.46 | ||||
| RI02341 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.5 | RM489 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.05 |
| RI04587 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM279 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0.25 |
| RI00945 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.06 | RM240 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0.07 |
| RI00301 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0.47 | RM251 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0.3 |
| RI05751 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0.35 | RM168 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0.49 |
| RI01085 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0.49 | RM401 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0.53 |
| RI01614 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0.5 | RM437 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0.1 |
| RI02821 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0.03 | RM584 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0.64 |
| RI04246 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0.36 | RM564 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 0.42 |
| RI03949 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0.09 | RM214 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0.03 |
| RI05815 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM321 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0.45 |
| RI04107 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM21 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0.47 |
| RI03187 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM224 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0.2 |
| RI00213 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0.04 | RM1337 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 0.53 |
| RI02123 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 0.02 | RM499 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 0.09 |
| RI01540 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 0.38 | RM246 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 0.66 |
| RI05818 | 11 | 2 | 0 | 0.5 | RM341 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0.58 |
| RI05618 | 11 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM280 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 0.34 |
| RI05373 | 12 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | RM481 | 9 | 4 | 0 | 0.67 |
| RI03123 | 12 | 4 | 2 | 0.49 | RM248 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 0.54 |
| SSR marker | RM531 | 10 | 4 | 0 | 0.68 | ||||
| RM1395 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.24 | RM566 | 10 | 4 | 0 | 0.45 |
| RM274 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.27 | RM3808 | 11 | 4 | 0 | 0.41 |
| RM30 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.22 | RM474 | 11 | 4 | 1 | 0.39 |
| RM271 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.03 | RM80 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 0.63 |
| RM277 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.04 | RM518 | 12 | 5 | 2 | 0.65 |
| RM5479 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0.5 | RM440 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 0.6 |
| Average of ILPs | 2.2 | 0.7 | 0.22 | ||||||
| Average of SSRs | 3.3 | 0.7 | 0.38 | ||||||
| Average of ILP and SSR combinations | 3.4 | 0.7 | 0.32 | ||||||
| Region / | No. of varieties | Na | Ne | He |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | ||||
| Introduced | 33 | 1.67 ± 0.06 | 1.34 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| Local | 266 | 1.92 ± 0.03 | 1.33 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| Group I | 15 | 1.35 ± 0.07 | 1.27 ± 0.03 | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| Group II | 131 | 1.84 ± 0.04 | 1.34 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| Group III | 153 | 1.84 ± 0.04 | 1.32 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.01 |
| Total | 299 | 1.93 ± 0.03 | 1.34 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
Table 2 Estimated no. of alleles (Na), no. of effective alleles (Ne), expected heterozygosity (He) for each clustering group and region.
| Region / | No. of varieties | Na | Ne | He |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | ||||
| Introduced | 33 | 1.67 ± 0.06 | 1.34 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| Local | 266 | 1.92 ± 0.03 | 1.33 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| Group I | 15 | 1.35 ± 0.07 | 1.27 ± 0.03 | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| Group II | 131 | 1.84 ± 0.04 | 1.34 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| Group III | 153 | 1.84 ± 0.04 | 1.32 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.01 |
| Total | 299 | 1.93 ± 0.03 | 1.34 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
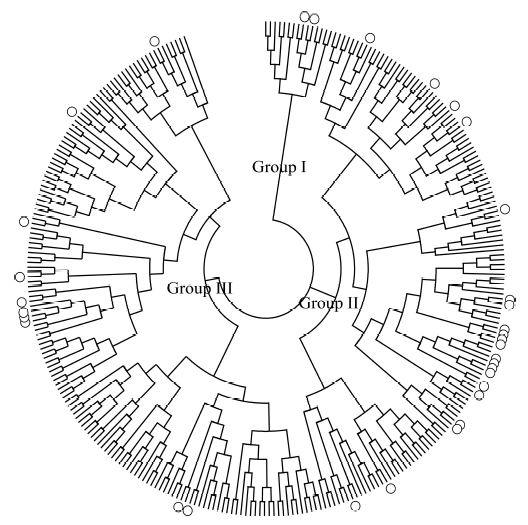
Fig. 1. Neighbor-joining tree of 299 varieties revealed by intron length ploymorphism and simple sequence repeat markers. ‘○’ indicates the varieties introduced outside Guangdong Province.
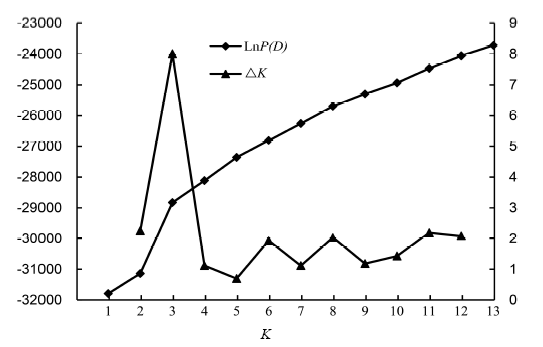
Fig. 2. Mean values of LnP(D) and ΔK over five repeated runs of Structure simulations, respectively, for 299 rice varieties using combined markers. LnP(D) with K = 1 to 13, ΔK with K = 2 to 12.
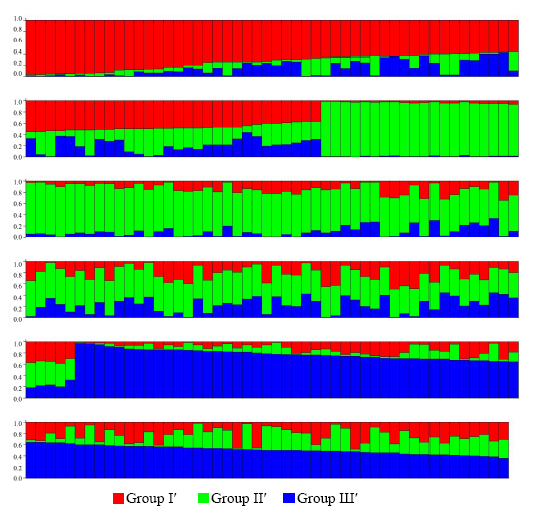
Fig. 3. Model-based ancestry for each variety revealed by combined markers using Structure. Each variety is presented by a single vertical line broken into K (K = 3) colored segments, with lengths proportional to each of the K inferred clusters. Different color within group indicates the proportion of shared ancestry with other group which has the same color with the admixture.
| Source of variationa | df | SS | MS | Estimated variance | Variance (%) | P- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | ||||||
| ILP | ||||||
| Among Regions | 1 | 27.048 | 27.048 | 0.385 | 2.1 | 0.001 |
| Among Pops | 2 | 83.027 | 41.514 | 0.458 | 7.7 | |
| Within Pops | 295 | 1233.959 | 4.183 | 4.049 | 90.2 | |
| Total | 298 | 1344.033 | 4.893 | 100 | ||
| SSR | ||||||
| Among Regions | 1 | 54.904 | 54.904 | 0.692 | 4.6 | 0.001 |
| Among Pops | 2 | 163.565 | 81.782 | 0.834 | 5.6 | |
| Within Pops | 295 | 4077.531 | 13.822 | 14.456 | 89.7 | |
| Total | 298 | 4296 | 15.982 | 100 | ||
| ILP + SSR | ||||||
| Among Regions | 1 | 81.951 | 81.951 | 1.077 | 5.4 | 0.001 |
| Among Pops | 2 | 246.592 | 123.296 | 1.293 | 6.6 | |
| Within Pops | 295 | 5311.49 | 18.005 | 18.403 | 89.5 | |
| Total | 298 | 5640.033 | 20.772 | 100 |
Table 3 Analysis of molecular variance for 299 inbred indica rice varieties in Guangdong Province of China.
| Source of variationa | df | SS | MS | Estimated variance | Variance (%) | P- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | ||||||
| ILP | ||||||
| Among Regions | 1 | 27.048 | 27.048 | 0.385 | 2.1 | 0.001 |
| Among Pops | 2 | 83.027 | 41.514 | 0.458 | 7.7 | |
| Within Pops | 295 | 1233.959 | 4.183 | 4.049 | 90.2 | |
| Total | 298 | 1344.033 | 4.893 | 100 | ||
| SSR | ||||||
| Among Regions | 1 | 54.904 | 54.904 | 0.692 | 4.6 | 0.001 |
| Among Pops | 2 | 163.565 | 81.782 | 0.834 | 5.6 | |
| Within Pops | 295 | 4077.531 | 13.822 | 14.456 | 89.7 | |
| Total | 298 | 4296 | 15.982 | 100 | ||
| ILP + SSR | ||||||
| Among Regions | 1 | 81.951 | 81.951 | 1.077 | 5.4 | 0.001 |
| Among Pops | 2 | 246.592 | 123.296 | 1.293 | 6.6 | |
| Within Pops | 295 | 5311.49 | 18.005 | 18.403 | 89.5 | |
| Total | 298 | 5640.033 | 20.772 | 100 |
| 1 | Agrama H A, Eizenga G C.2008. Molecular diversity and genome-wide linkage disequilibrium patterns in a worldwide collection of Oryza sativa and its wild relatives.Euphytica, 160(3): 339-355. |
| 2 | Agrama H A, Yan W G, Lee F, Fjellstrom R, Chen M H, Jia M, McClung A.2009. Genetic assessment of a mini-core developed from the USDA rice genebank.Crop Sci, 49(6): 2413. |
| 3 | Bao J S, Corke H, Sun M.2006. Analysis of genetic diversity and relationships in waxy rice (Oryza sativa L.) using AFLP and ISSR markers.Genet Resour Crop Evol, 53(2): 323-330. |
| 4 | Belaj A, Satovic Z, Cipriani G, Baldoni L, Testolin R, Rallo L, Trujillo I.2003. Comparative study of the discriminating capacity of RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers and of their effectiveness in establishing genetic relationships in olive.Theor Appl Genet, 107(4): 736-744. |
| 5 | Budak H, Shearman R C, Parmaksiz I, Dweikat I.2004. Comparative analysis of seeded and vegetative biotype buffalograsses based on phylogenetic relationship using ISSRs, SSRs, RAPDs, and SRAPs.Theor Appl Genet, 109(2): 280-288. |
| 6 | Chakanda R, van Treuren R, Visser B, van den Berg R.2013. Analysis of genetic diversity in farmers’ rice varieties in Sierra Leone using morphological and AFLP markers.Genet Resour Crop Evol, 60(4): 1237-1250. |
| 7 | Chao Z, Xiang Z L, Zhong W, Wei F, Feng W.2010. Analysis of the current development of Guangdong rice industry in 2009.Guangdong Agric Sci, (3): 231-232. (in Chinese) |
| 8 | Corbellini M, Perenzin M, Accerbi M, Vaccino P, Borghi B.2002. Genetic diversity in bread wheat, as revealed by coefficient of parentage and molecular markers, and its relationship to hybrid performance.Euphytica, 123(2): 273-285. |
| 9 | de Souza S G H, Carpentieri-Pipolo V, Ruas C D, Carvalho V D P, Ruas P M, Gerage A C.2008. Comparative analysis of genetic diversity among the maize inbred lines (Zea mays L.) obtained by RAPD and SSR markers.Braz Arch Biol Technol, 51(1): 183-192. |
| 10 | Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J.2005. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study.Mol Ecol, 14(8): 2611-2620. |
| 11 | Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard J K.2007. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: Dominant markers and null alleles.Mol Ecol Notes, 7(4): 574-578. |
| 12 | Garcia A A F, Benchimol L L, Barbosa A M M, Geraldi I O, Souza C L, de Souza A P.2004. Comparison of RAPD, RFLP, AFLP and SSR markers for diversity studies in tropical maize inbred lines.Genet Mol Biol, 27(4): 579-588. |
| 13 | He Z Z, Xie F M, Chen L Y, DELA PAZ. M A.2012. Genetic diversity of tropical hybrid rice germplasm measured by molecular markers.Rice Sci, 19(3):193-201. |
| 14 | Huang M, Xie F M, Chen L Y, Zhao X Q, Jojee L, Madonna D.2010. Comparative analysis of genetic diversity and structure in rice using ILP and SSR markers.Rice Sci, 17(4): 257-268. |
| 15 | Jeong I S, Yoon U H, Lee G S, Ji H S, Lee H J, Han C D, Hahn J H, An G, Kim T H.2013. SNP-based analysis of genetic diversity in anther-derived rice by whole genome sequencing.Rice, 6: 6. |
| 16 | Kiula B A, Lyimo N G, Botha A M.2008. Association between AFLP-based genetic distance and hybrid performance in tropical maize.Plant Breeding, 127(2): 140-144. |
| 17 | Liu K, Muse S V.2005. PowerMarker: An integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis.Bioinformatics, 21(9): 2128-2129. |
| 18 | Mantel N.1967. The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach.Cancer Res, 27(2): 209-220. |
| 19 | Murray M G, Thompson W F.1980. Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA.Nucleic Acids Res, 8(19): 4321-4325. |
| 20 | Naghavi M R, Mardi M, Pirseyedi S M, Kazemi M, Potki P, Ghaffari M R.2007. Comparison of genetic variation among accessions of Aegilops tauschii using AFLP and SSR markers.Genet Resour Crop Evol, 54(2): 237-240. |
| 21 | Nei M.1973. Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 70(12): 3321-3323. |
| 22 | Nei M, Li W H.1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 76(10): 5269-5273. |
| 23 | Patzak J.2001. Comparison of RAPD, STS, ISSR and AFLP molecular methods used for assessment of genetic diversity in hop (Humulus lupulus L.).Euphytica, 121(1): 9-18. |
| 24 | Peakall R, Smouse P E.2006. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research.Mol Ecol Notes, 6(1): 288-295. |
| 25 | Pritchard J K, Stephens M, Donnelly P.2000. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data.Genetics, 155(2): 945-959. |
| 26 | Qi Y W, Zhang D L, Zhang H L, Wang M X, Sun J L, Wei X H, Qiu Z G, Tang S X, Cao Y S, Wang X K, Li Z C.2006. Genetic diversity of rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.) in China and the temporal trends in recent fifty years.Chin Sci Bull, 51(6): 681-688. |
| 27 | Rabbani M A, Pervaiz Z H, Masood M S.2008. Genetic diversity analysis of traditional and improved cultivars of Pakistani rice (Oryza sativa L.) using RAPD markers.Electron J Biotechn, 11(3): 52-61. |
| 28 | Ravi M, Geethanjali S, Sameeyafarheen F, Maheswaran M.2003. Molecular marker based genetic diversity analysis in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using RAPD and SSR markers.Euphytica, 133(2): 243-252. |
| 29 | Scariot V, de Keyser E, Handa T, de Riek J.2007. Comparative study of the discriminating capacity and effectiveness of AFLP, STMS and EST markers in assessing genetic relationships among evergreen azaleas.Plant Breeding, 126(2): 207-212. |
| 30 | Sharma R K, Gupta P, Sharma V, Sood A, Mohapatra T, Ahuja P S.2008. Evaluation of rice and sugarcane SSR markers for phylogenetic and genetic diversity analyses in bamboo.Genome, 51(2): 91-103. |
| 31 | Shu A P, Hwan K J, Zhang S Y, Cao G L, Nan Z H, Seong L K, Lu Q, Han L Z.2009. Analysis on genetic similarity of japonica cice variety from different origins of geography in the world.Agric Sci China, 8(5): 513-520. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 32 | Singh N, Choudhury D R, Singh A K, Kumar S, Srinivasan K, Tyagi R K, Singh N K, Singh R.2013. Comparison of SSR and SNP markers in estimation of genetic diversity and population structure of Indian rice varieties.PLoS One, 8(12): e84136. |
| 33 | Sun C Q, Wang X K, Li Z C, Yoshimura A, Iwata N.2001. Comparison of the genetic diversity of common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) and cultivated rice (O. sativa L.) using RFLP markers.Theor Appl Genet, 101(1): 157-162. |
| 34 | Sun X Y, Kang S, Zhang Y J, Tan X Q, Yu Y F, He H Y, Zhang X Y, Liu Y F, Wang S, Sun W X, Cai L, Li S J.2013. Genetic diversity and population structure of rice pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in China.PLoS One, 8(9): 559-564. |
| 35 | Tam S M, Mhiri C, Vogelaar A, Kerkveld M, Pearce S R, Grandbastien M A.2005. Comparative analyses of genetic diversities within tomato and pepper collections detected by retrotransposon-based SSAP, AFLP and SSR.Theor Appl Genet, 110(5): 819-831. |
| 36 | Upadhyay A, Saboji M D, Reddy S, Deokar K, Karibasappa G S.2007. AFLP and SSR marker analysis of grape rootstocks in Indian grape germplasm.Sci Hort, 112(2): 176-183. |
| 37 | Upadhyay P, Neeraja C N, Kole C, Singh V K.2012. Population structure and genetic diversity in popular rice varieties of India as evidenced from SSR analysis.Biochem Genet, 50(9-10): 770-783. |
| 38 | Wan Z, Zhang C, Fang W.2010. Development situation of Guangdong rice industry and countermeasures in first half of 2010.Guangdong Agric Sci, (9): 232-233. (in Chinese) |
| 39 | Wan Z, Zhang C, Fang W.2011a. Development situation of Guangdong rice industry and countermeasures in first half of 2011.Guangdong Agric Sci, (19): 13-14. (in Chinese) |
| 40 | Wan Z, Zhang C, Fang W.2011b. Retrospect and prospect of the development of Guangdong rice industry in 2010.Guangdong Agric Sci, (6): 179-180. (in Chinese) |
| 41 | Wan Z, Kang Y Z, Fang W.2012. Development situation of Guangdong rice industry and countermeasures in first half of 2012.Guangdong Agric Sci, (18): 3-5. (in Chinese) |
| 42 | Wan Z, Zheng S F, Fang W, Kang Y Z.2013. Development situation and countermeasures of Guangdong rice industry in 2012.Guangdong Agric Sci, (12): 1-3. (in Chinese) |
| 43 | Wang S, Lu Z.2006. Genetic diversity among parental lines of Indica hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) in China based on coefficient of parentage.Plant Breeding, 125(6): 606-612. |
| 44 | Wang S J, Lu Z M, Wan J M.2006. Genetic diversity among parents of hybrid rice based on cluster analysis of morphological traits and simple sequence repeat markers.Rice Sci, 13(3): 155-160. |
| 45 | Wang X Q, Kwon S W, Park Y J.2013. Evaluation of genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium in Korean-bred rice varieties using SSR markers.Electron J Biotechnol, 16(5): 11-20. |
| 46 | Xu Q, Chen H, Wang C H, Yu H Y, Yuan X P, Wang Y P, Feng Y, Tang S X, Wei X H.2012. Genetic diversity and structure of new inbred ricecultivars in China.J Integr Agric, 11(10): 1567-1573. |
| 47 | Xu W J, Virmani S S, Hernandez J E, Sebastian L S, Redona E D, Li Z K.2002. Genetic diversity in the parental lines and heterosis of the tropical rice hybrids.Euphytica, 127(1): 139-148. |
| 48 | Yuan X P, Wei X H, Hua L, Yu H Y, Wang Y P, Xu Q, Tang S X.2007. A comparative stydy of SSR diversity in Chinese major rice varieties planted in 1950s and in the recent ten years (1995-2004).Rice Sci, 14(2): 78-84. |
| 49 | Zeng X H, Fang W, Kang Y Z, Wan Z.2014. Development situation and countermeasures of Guangdong rice industry in 2013.Guangdong Agric Sci, (4): 1-4. (in Chinese) |
| 50 | Zhang D L, Wang M X, Qi Y W, Sun J L, Wang F M, Li J J, Zhang H L, Li Z C.2012. Genetic structure and eco-geographical differentiation of cultivated Keng rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp japonica) in China revealed by microsatellites.J Integr Agric, 11(11): 1755-1766. |
| 51 | Zhang D L, Zhang H L, Qi Y W, Wang M X, Sun J L, Ding L, Li Z C.2013. Genetic structure and eco-geographical differentiation of cultivated Hsien rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp indica) in China revealed by microsatellites.Chin Sci Bull, 58(3): 344-352. |
| 52 | Zhang G X, Wang Z G, Chen W S, Wu C X, Han X, Chang H, Zan L S, Li R L, Wang J H, Song W T, Xu G F, Yang H J, Luo Y F.2007. Genetic diversity and population structure of indigenous yellow cattle breeds of China using 30 microsatellite markers.Animal Genet, 38(6): 550-559. |
| 53 | Zhang P, Li J Q, Li X L, Liu X D, Zhao X J, Lu Y G.2011. Population structure and genetic diversity in a rice core collection (Oryza sativa L.) investigated with SSR markers.PLoS One, 6(12): e27565. |
| 54 | Zhao W G, Chung J W, Ma K H, Kim T S, Kim S M, Shin D I, Kim C H, Koo H M, Park Y J.2009. Analysis of genetic diversity and population structure of rice cultivars from Korea, China and Japan using SSR markers.Genes Genom, 31(4): 283-292. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [14] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [15] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||