
Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 509-522.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.07.005
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Liu Tingting1,2,#, Zou Jinpeng1,#, Yang Xi1,3, Wang Kejian1, Rao Yuchun3( ), Wang Chun1(
), Wang Chun1( )
)
Received:2023-05-03
Accepted:2023-07-27
Online:2023-11-28
Published:2023-08-10
Contact:
Wang Chun (wangchun@caas.cn);
Rao Yuchun (ryc@zjnu.cn)
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
Liu Tingting, Zou Jinpeng, Yang Xi, Wang Kejian, Rao Yuchun, Wang Chun. Development and Application of Prime Editing in Plants[J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 509-522.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
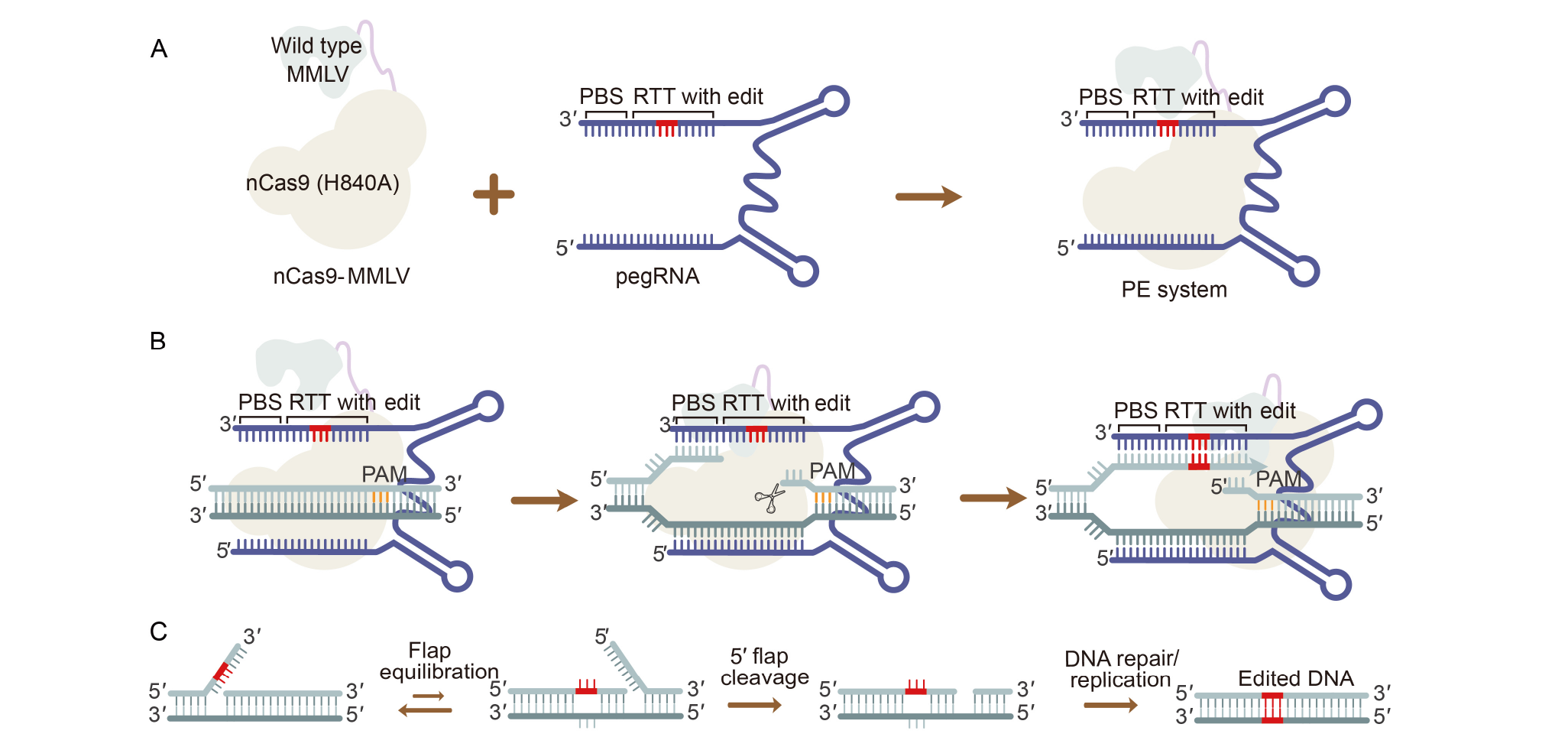
Fig. 1. Composition and mechanism of prime editing (PE) system. A, Composition of original PE system. The PE system is composed of two components: prime editor and pegRNA. The prime editor is a fusion protein formed by nCas9 and wild type MMLV reverse transcriptase. The pegRNA is an engineered sgRNA with an added PBS for directing prime editor to the genomic target site and a RTT for mediating the desired edit at the 3?-terminus of sgRNA. MMLV, Moloney murine leukaemia virus reverse transcriptase; nCas9 (H840A), Cas9 nickase; nCas9-MMLV, A fusion protein formed by nCas9 and MMLV; pegRNA, Prime editing guide RNA; PBS, Primer binding site; RTT, Reverse transcriptase template; sgRNA, Single-guide RNA. B, Mechanism of PE system. PE system uses a prime editor with a pegRNA to nick the PAM-containing strand and template the synthesis of an edited DNA flap. The resulting 3?-end hybridizes to the PBS, then primes reverse transcription of new DNA containing the desired edit using the RTT of the pegRNA. PAM, Protospacer adjacent motif. C, Overview of DNA repair process. The edited 3?-flap is processed by endogenous cellular pathways, and after initial synthesis of the edited strand, the 5?-flap is excised leaving a DNA heteroduplex containing one edited strand and one non-edited strand. Mismatch repair resolves the heteroduplex by permanently copying the edited sequence to the non-edited strand.
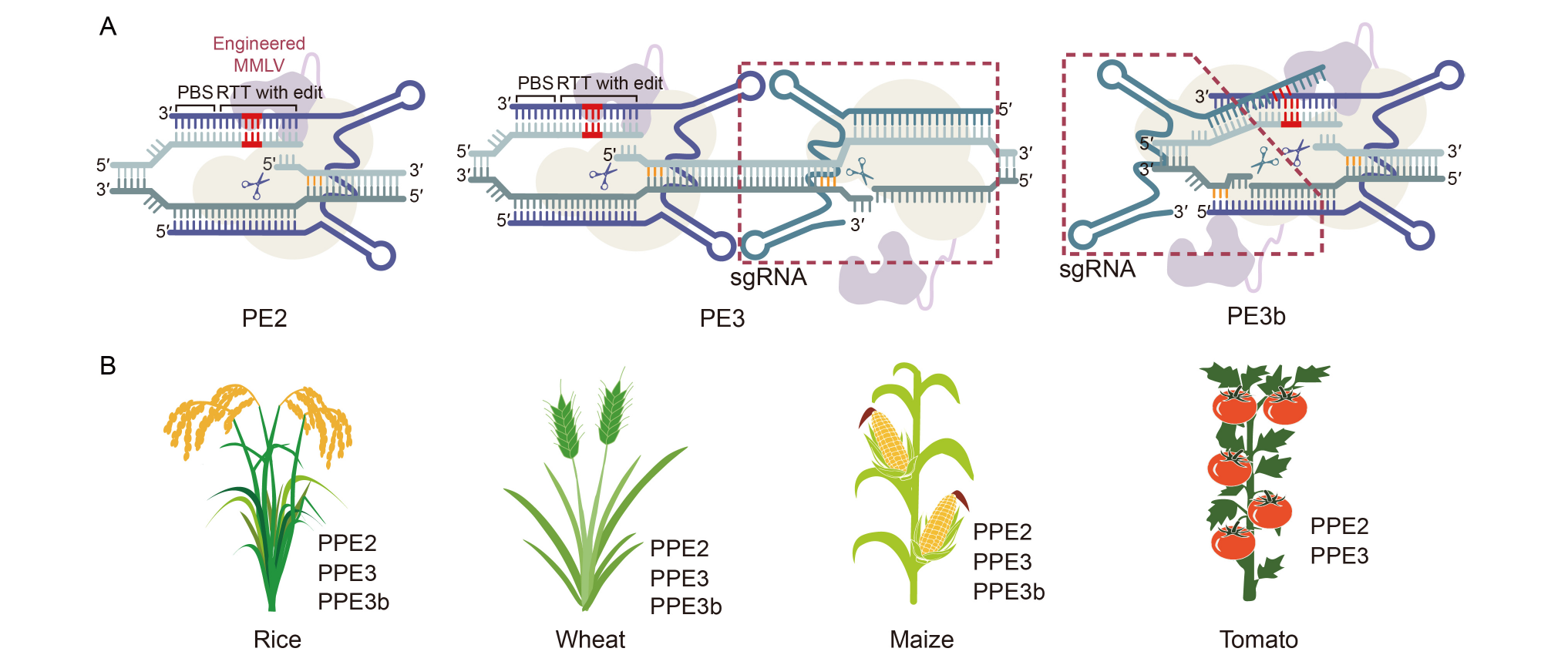
Fig. 2. Emergence and development of prime editing (PE) systems in plants. A, Emergence of plant PE (PPE) systems. PE2 prime editor uses an engineered MMLV with improved efficiency and stability. Building upon PE2 system, PE3 system uses an additional sgRNA to nick the non-edited strand and stimulate replacement of the non-edited strand, which enhances permanent incorporation of the edited sequence. The sgRNA of PE3b matches the edited strand, mismatches the unedited allele, and only cleaves and repairs after the edited strand has been edited. MMLV, Moloney murine leukaemia virus reverse transcriptase; PBS, Primer binding site; RTT, Reverse transcriptase template; sgRNA, Single-guide RNA. B, Development of PE in various plants. PEs were performed in rice, wheat, maize, and tomato with endogenous gene editing.

Fig. 3. Overview of prime editor (PE) system optimization in plants. A, Various types of prime editors. PPE1 is the original PE system, and PPE2 is updated to engineering MMLV. On the basis of PPE2, PPEmax is changed to nCas9 variant and a c-Myc NLS is added. ePPE is updated to MMLV-△RHase H and an NC protein is added between nCas9 and MMLV. PPEmax-MLH1dn has one more individually expressed MLH1dn protein than PPEmax. PPE-T5 adds a T5 exonuclease prior to nCas9. PrimeRoot adds an integrase (Cre/FLP) and a nucleoplasmin NLS than ePPE at the end. PPE-SpG is updated to nSpG. NC, A viral protein with nucleic acid chaperone activity that affects a variety of functions related to reverse transcription; NLS, Nuclear localization signal; PPE, Plant prime editing system; Pro, Promoter; nCas9, Cas9 nickase; MMLV, Moloney murine leukaemia virus reverse transcriptase; MMLV-△RHase H, A MMLV variant with deletion ribonuclease H (RNase H) domain; MLH1dn, A dominant negative variant of MLH1 protein; nSpG, An nCas9 variant with NGN (N = A, T, C, G) protospacer adjacent motif. B, Various types of pegRNA. The original pegRNAs are optimized for complex promoter-driven or motif-added pegRNAs to improve PPE efficiency. OsU3, Rice U3 promoter; CaMV35S-CmYLCV-U6, Composite promoter of the CaMV 35S enhancer, CmYLCV promoter, and shortened U6 promoter; evopreQ1, A structured RNA pseudoknot that protects 3?-extension from degradation by exonucleases; MS2, A hairpin that facilitates its recruitment to reverse transcriptase by binding a fused MS2 coat protein. C, Various types of twinPE strategies. The dual-pegRNA and GRAND mediated precise insertion or deletion of DNA fragments. The edited or insertion (or deletion) is labeled in red. PBS, Primer binding site; RTT, Reverse transcriptase template with edit; pegRNA, Prime editing guide RNA; GRAND, An editing strategy, genome editing by RTTs partially aligned to each other but nonhomologous to target sequences within dual-pegRNA.
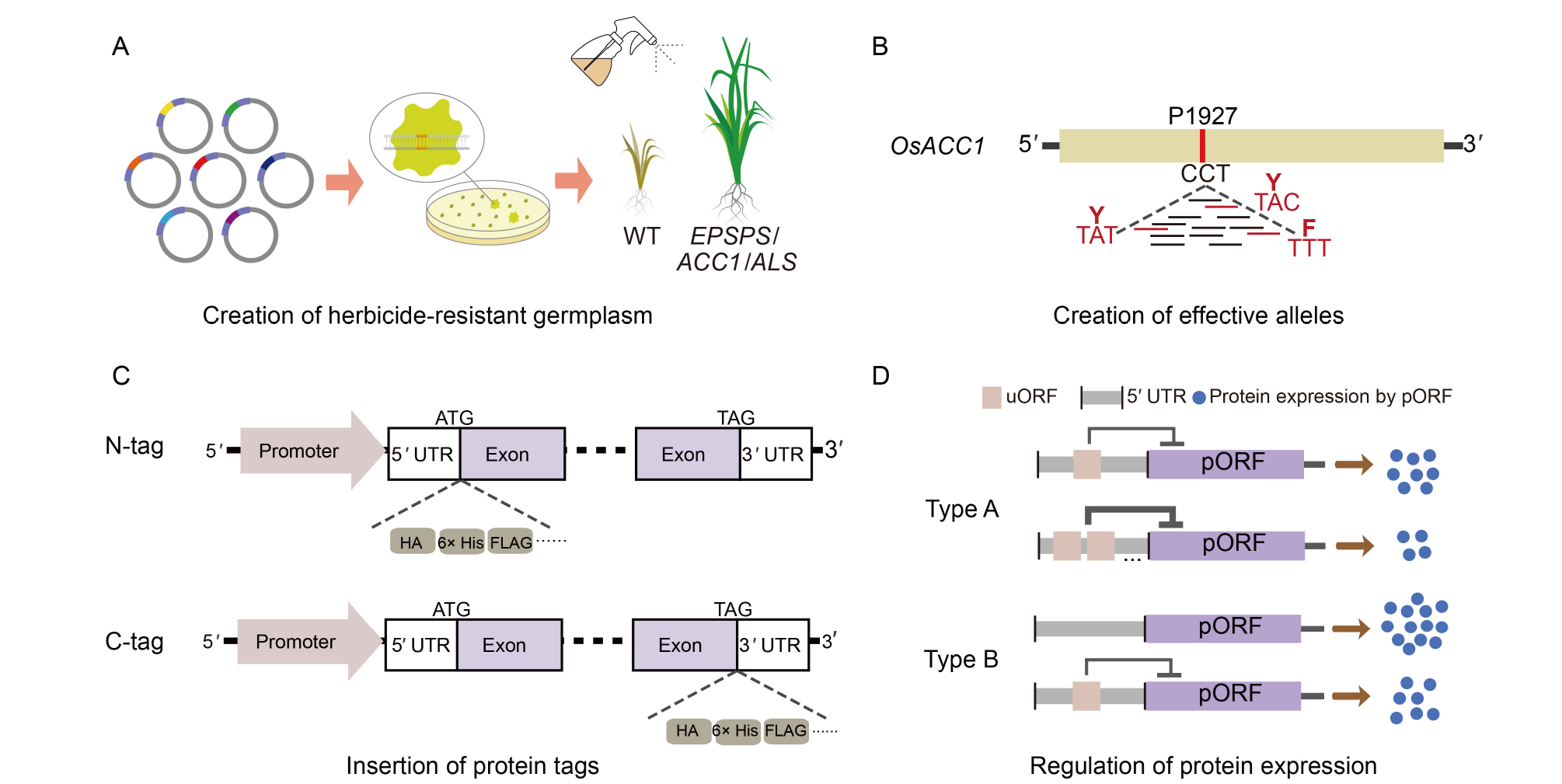
Fig. 4. Applications of prime editing systems in plants. A, Creation of herbicide-resistant germplasms. The EPSPS, ACC1, and ALS genes are mainly modified to enhance herbicide resistance. B, Creation of effective alleles. The saturation mutation of P1927 in the OsACC1 yields three mutation types, which are indicated by red horizontal lines in the figure. P, Proline; Y, Tyrosine; F, Phenylalanine. C, Insertion of protein tags. Insert different tags at the N-terminus (N-tag) and C-terminus (C-tag), such as 6× His, HA and FLAG. D, Regulation of protein expression. Down-regulation of downstream target protein expression by expanding endogenous uORFs (Type A) and generating de novo uORFs (Type B) strategies. WT, Wild type; UTR, Untranslated region; 6× His, Polyhistidine tag; HA, Hemagglutinin tag; uORF, Upstream open reading frame; pORF, Primary open reading frame.
| [1] | Al-Zain A M, Symington L S. 2021. The dark side of homology- directed repair. DNA Repair, 106: 103181. |
| [2] | Anzalone A V, Randolph P B, Davis J R, Sousa A A, Koblan L W, Levy J M, Chen P J, Wilson C, Newby G A, Raguram A, Liu D R. 2019. Search-and-replace genome editing without double- strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature, 576(7785): 149-157. |
| [3] | Anzalone A V, Gao X D, Podracky C J, Nelson A T, Koblan L W, Raguram A, Levy J M, Mercer J A M, Liu D R. 2022. Programmable deletion, replacement, integration and inversion of large DNA sequences with twin prime editing. Nat Biotechnol, 40(5): 731-740. |
| [4] | Beale R C L, Petersen-Mahrt S K, Watt I N, Harris R S, Rada C, Neuberger M S. 2004. Comparison of the differential context- dependence of DNA deamination by APOBEC enzymes: Correlation with mutation spectra in vivo. J Mol Biol, 337(3): 585-596. |
| [5] | Bibikova M, Beumer K, Trautman J K, Carroll D. 2003. Enhancing gene targeting with designed zinc finger nucleases. Science, 300(5620): 764. |
| [6] | Boch J, Scholze H, Schornack S, Landgraf A, Hahn S, Kay S, Lahaye T, Nickstadt A, Bonas U. 2009. Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors. Science, 326: 1509-1512. |
| [7] | Bochtler M. 2016. Indirect DNA sequence readout by LAGLIDADG homing endonucleases. Structure, 24(6): 839-840. |
| [8] | Butt H, Rao G S, Sedeek K, Aman R, Kamel R, Mahfouz M. 2020. Engineering herbicide resistance via prime editing in rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 18(12): 2370-2372. |
| [9] | Chai Y P, Jiang Y Y, Wang J Y, Qiao D X, Zhang Y, Xin C P, Zhou Y, Wang X C, Chen Q J. 2021. MS2 RNA aptamer enhances prime editing in rice. bioRxiv, DOI: 10.1101/2021.10.20.465209. |
| [10] | Chen P J, Liu D R. 2023. Prime editing for precise and highly versatile genome manipulation. Nat Rev Genet, 24(3): 161-177. |
| [11] | Chen P J, Hussmann J A, Yan J, Knipping F, Ravisankar P, Chen P F, Chen C D, Nelson J W, Newby G A, Sahin M, Osborn M J, Weissman J S, Adamson B, Liu D R. 2021. Enhanced prime editing systems by manipulating cellular determinants of editing outcomes. Cell, 184(22): 5635-5652. |
| [12] | Chen R H, Cao Y, Liu Y J, Zhao D D, Li J, Cheng Z H, Bi C H, Zhang X L. 2023. Enhancement of a prime editing system via optimal recruitment of the pioneer transcription factor P65. Nat Commun, 14: 257. |
| [13] | Chevalier B S, Stoddard B L. 2001. Homing endonucleases: Structural and functional insight into the catalysts of intron/ intein mobility. Nucleic Acids Res, 29(18): 3757-3774. |
| [14] | Choi J, Chen W, Suiter C C, Lee C, Chardon F M, Yang W, Leith A, Daza R M, Martin B, Shendure J. 2022. Precise genomic deletions using paired prime editing. Nat Biotechnol, 40(2): 218-226. |
| [15] | Chow R D, Chen J S, Shen J, Chen S D. 2021. A web tool for the design of prime-editing guide RNAs. Nat Biomed Eng, 5(2): 190-194. |
| [16] | Cong L, Ran F A, Cox D, Lin S L, Barretto R, Habib N, Hsu P D, Wu X B, Jiang W Y, Marraffini L A, Zhang F. 2013. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science, 339: 819-823. |
| [17] | Conticello S G. 2008. The AID/APOBEC family of nucleic acid mutators. Genome Biol, 9(6): 229. |
| [18] | Cullot G, Boutin J, Toutain J, Prat F, Pennamen P, Rooryck C, Teichmann M, Rousseau E, Lamrissi-Garcia I, Guyonnet-Duperat V, Bibeyran A, Lalanne M, Prouzet-Mauléon V, Turcq B, Ged C, Blouin J M, Richard E, Dabernat S, Moreau-Gaudry F, Bedel A. 2019. CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing induces megabase-scale chromosomal truncations. Nat Commun, 10(1): 1136. |
| [19] | Endo M, Osakabe K, Ono K, Handa H, Shimizu T, Toki S. 2007. Molecular breeding of a novel herbicide-tolerant rice by gene targeting. Plant J, 52(1): 157-166. |
| [20] | Gao C X. 2021. Genome engineering for crop improvement and future agriculture. Cell, 184(6): 1621-1635. |
| [21] | Gaudelli N M, Komor A C, Rees H A, Packer M S, Badran A H, Bryson D I, Liu D R. 2017. Programmable base editing of A∙T to G∙C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage. Nature, 551: 464-471. |
| [22] | Grünewald J, Zhou R H, Garcia S P, Iyer S, Lareau C A, Aryee M J, Joung J K. 2019. Transcriptome-wide off-target RNA editing induced by CRISPR-guided DNA base editors. Nature, 569: 433-437. |
| [23] | Gupta A, Liu B, Chen Q J, Yang B. 2023. High-efficiency prime editing enables new strategies for broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight of rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 21(7): 1454-1464. |
| [24] | Han H P, Yu Q, Purba E, Li M, Walsh M, Friesen S, Powles S B. 2012. A novel amino acid substitution Ala-122-Tyr in ALS confers high-level and broad resistance across ALS-inhibiting herbicides. Pest Manag Sci, 68(8): 1164-1170. |
| [25] | Hao L J, Pu X D, Song J Y. 2021. Introduction of mutations in plants with prime editing. Methods, 194: 83-93. |
| [26] | Hsu J Y, Grünewald J, Szalay R, Shih J, Anzalone A V, Lam K C, Shen M W, Petri K, Liu D R, Joung J K, Pinello L. 2021. PrimeDesign software for rapid and simplified design of prime editing guide RNAs. Nat Commun, 12(1): 1034. |
| [27] | Hu X X, Wang C, Liu Q, Fu Y P, Wang K J. 2017. Targeted mutagenesis in rice using CRISPR-Cpf1 system. J Genet Genomics, 44(1): 71-73. |
| [28] | Hua K, Jiang Y W, Tao X P, Zhu J K. 2020. Precision genome engineering in rice using prime editing system. Plant Biotechnol J, 18(11): 2167-2169. |
| [29] | Ira G, Pellicioli A, Balijja A, Wang X, Fiorani S, Carotenuto W, Liberi G, Bressan D, Wan L H, Hollingsworth N M, Haber J E, Foiani M. 2004. DNA end resection, homologous recombination and DNA damage checkpoint activation require CDK1. Nature, 431: 1011-1017. |
| [30] | Jang S, Marjanovic J, Gornicki P. 2013. Resistance to herbicides caused by single amino acid mutations in acetyl-CoA carboxylase in resistant populations of grassy weeds. New Phytol, 197(4): 1110-1116. |
| [31] | Jiang T T, Zhang X O, Weng Z P, Xue W. 2022. Deletion and replacement of long genomic sequences using prime editing. Nat Biotechnol, 40(2): 227-234. |
| [32] | Jiang Y Y, Chai Y P, Lu M H, Han X L, Lin Q P, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Zhou Y, Wang X C, Gao C X, Chen Q J. 2020. Prime editing efficiently generates W542L and S621I double mutations in two ALS genes in maize. Genome Biol, 21(1): 257. |
| [33] | Jiang Y Y, Chai Y P, Qiao D X, Wang J Y, Xin C P, Sun W, Cao Z H, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Wang X C, Chen Q J. 2022. Optimized prime editing efficiently generates glyphosate-resistant rice plants carrying homozygous TAP-IVS mutation in EPSPS. Mol Plant, 15(11): 1646-1649. |
| [34] | Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna J A, Charpentier E. 2012. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science, 337: 816-821. |
| [35] | Kawai K, Kaku K, Izawa N, Shimizu T, Fukuda A, Tanaka Y. 2007. A novel mutant acetolactate synthase gene from rice cells, which confers resistance to ALS-inhibiting herbicides. J Pestic Sci, 32(2): 89-98. |
| [36] | Kosicki M, Tomberg K, Bradley A. 2018. Repair of double-strand breaks induced by CRISPR-Cas9 leads to large deletions and complex rearrangements. Nat Biotechnol, 36(8): 765-771. |
| [37] | Kurt I C, Zhou R H, Iyer S, Garcia S P, Miller B R, Langner L M, Grünewald J, Joung J K. 2021. CRISPR C-to-G base editors for inducing targeted DNA transversions in human cells. Nat Biotechnol, 39(1): 41-46. |
| [38] | Kweon J, Yoon J K, Jang A H, Shin H R, See J E, Jang G, Kim J I, Kim Y. 2021. Engineered prime editors with PAM flexibility. Mol Ther, 29(6): 2001-2007. |
| [39] | Li C, Zhang R, Meng X B, Chen S, Zong Y, Lu C J, Qiu J L, Chen Y H, Li J Y, Gao C X. 2020. Targeted, random mutagenesis of plant genes with dual cytosine and adenine base editors. Nat Biotechnol, 38(7): 875-882. |
| [40] | Li H Y, Li J Y, Chen J L, Yan L, Xia L Q. 2020. Precise modifications of both exogenous and endogenous genes in rice by prime editing. Mol Plant, 13(5): 671-674. |
| [41] | Li H Y, Zhu Z W, Li S Y, Li J Y, Yan L, Zhang C, Ma Y Z, Xia L Q. 2022. Multiplex precision gene editing by a surrogate prime editor in rice. Mol Plant, 15(7): 1077-1080. |
| [42] | Li J, Chen L K, Liang J, Xu R F, Jiang Y L, Li Y Z, Ding J, Li M, Qin R Y, Wei P C. 2022. Development of a highly efficient prime editor 2 system in plants. Genome Biol, 23(1): 161. |
| [43] | Li J, Ding J, Zhu J Y, Xu R F, Gu D F, Liu X S, Liang J, Qiu C H, Wang H H, Li M, Qin R Y, Wei P C. 2023. Prime editing- mediated precise knockin of protein tag sequences in the rice genome. Plant Commun, 4(3): 100572. |
| [44] | Li X Y, Wang X, Sun W J, Huang S S, Zhong M T, Yao Y, Ji Q J, Huang X X. 2022. Enhancing prime editing efficiency by modified pegRNA with RNA G-quadruplexes. J Mol Cell Biol, 14(4): mjac022. |
| [45] | Liang Z, Wu Y Q, Guo Y J, Wei S. 2023. Addition of the T5 exonuclease increases the prime editing efficiency in plants. J Genet Genomics, 50(8): 582-588. |
| [46] | Lin Q P, Zong Y, Xue C X, Wang S X, Jin S, Zhu Z X, Wang Y P, Anzalone A V, Raguram A, Doman J L, Liu D R, Gao C X. 2020. Prime genome editing in rice and wheat. Nat Biotechnol, 38(5): 582-585. |
| [47] | Lin Q P, Jin S, Zong Y, Yu H, Zhu Z X, Liu G W, Kou L Q, Wang Y P, Qiu J L, Li J Y, Gao C X. 2021. High-efficiency prime editing with optimized, paired pegRNAs in plants. Nat Biotechnol, 39(8): 923-927. |
| [48] | Ling X Y, Chang L Y, Chen H Q, Gao X Q, Yin J H, Zuo Y, Huang Y J, Zhang B, Hu J Z, Liu T. 2021. Improving the efficiency of CRISPR-Cas12a-based genome editing with site-specific covalent Cas12a-crRNA conjugates. Mol Cell, 81(22): 4747-4756. |
| [49] | Liu B, Dong X L, Cheng H Y, Zheng C W, Chen Z X, Rodríguez T C, Liang S Q, Xue W, Sontheimer E J. 2022. A split prime editor with untethered reverse transcriptase and circular RNA template. Nat Biotechnol, 40(9): 1388-1393. |
| [50] | Lu Y M, Tian Y F, Shen R D, Yao Q, Zhong D T, Zhang X N, Zhu J K. 2021. Precise genome modification in tomato using an improved prime editing system. Plant Biotechnol J, 19(3): 415-417. |
| [51] | Mali P, Yang L H, Esvelt K M, Aach J, Guell M, DiCarlo J E, Norville J E, Church G M. 2013. RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science, 339: 823-826. |
| [52] | Moscou M J, Bogdanove A J. 2009. A simple cipher governs DNA recognition by TAL effectors. Science, 326: 1501. |
| [53] | Nelson J W, Randolph P B, Shen S P, Everette K A, Chen P J, Anzalone A V, An M R, Newby G A, Chen J C, Hsu A, Liu D R. 2022. Engineered pegRNAs improve prime editing efficiency. Nat Biotechnol, 40(3): 402-410. |
| [54] | Okuzaki A, Shimizu T, Kaku K, Kawai K, Toriyama K. 2007. A novel mutated acetolactate synthase gene conferring specific resistance to pyrimidinyl carboxy herbicides in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 64: 219-224. |
| [55] | Oliva R, Ji C H, Atienza-Grande G, Huguet-Tapia J C, Perez- Quintero A, Li T, Eom J S, Li C H, Nguyen H, Liu B, Auguy F, Sciallano C, Luu V T, Dossa G S, Cunnac S, Schmidt S M, Slamet-Loedin I H, Cruz C V, Szurek B, Frommer W B, White F F, Yang B. 2019. Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing. Nat Biotechnol, 37(11): 1344-1350. |
| [56] | Perotti V E, Larran A S, Palmieri V E, Martinatto A K, Alvarez C E, Tuesca D, Permingeat H R. 2019. A novel triple amino acid substitution in the EPSPS found in a high-level glyphosate- resistant Amaranthus hybridus population from Argentina. Pest Manag Sci, 75(5): 1242-1251. |
| [57] | Powles S B, Yu Q. 2010. Evolution in action: Plants resistant to herbicides. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 61: 317-347. |
| [58] | Rukmini M, Wei Z, Joshi R K, Zhao K J. 2021. Genome editing strategies towards enhancement of rice disease resistance. Rice Sci, 28(2): 133-145. |
| [59] | Qiao D X, Wang J Y, Lu M H, Xin C P, Chai Y P, Jiang Y Y, Sun W, Cao Z H, Guo S Y, Wang X C, Chen Q J. 2023. Optimized prime editing efficiently generates heritable mutations in maize. J Integr Plant Biol, 65(4): 900-906. |
| [60] | Siegner S M, Karasu M E, Schröder M S, Kontarakis Z, Corn J E. 2021. PnB Designer: A web application to design prime and base editor guide RNAs for animals and plants. BMC Bioinformatics, 22(1): 101. |
| [61] | Song M, Lim J M, Min S, Oh J S, Kim D Y, Woo J S, Nishimasu H, Cho S R, Yoon S, Kim H H. 2021. Generation of a more efficient prime editor 2 by addition of the Rad51 DNA-binding domain. Nat Commun, 12: 5617. |
| [62] | Srivastava A K, Lu Y M, Zinta G, Lang Z B, Zhu J K. 2018. UTR- dependent control of gene expression in plants. Trends Plant Sci, 23(3): 248-259. |
| [63] | Standage-Beier K, Tekel S J, Brafman D A, Wang X. 2021. Prime editing guide RNA design automation using PINE-CONE. ACS Synth Biol, 10(2): 422-427. |
| [64] | Sun C, Lei Y, Li B S, Gao Q, Li Y J, Cao W, Yang C, Li H C, Wang Z W, Li Y, Wang Y P, Liu J, Zhao K T, Gao C X. 2023. Precise integration of large DNA sequences in plant genomes using PrimeRoot editors. Nat Biotechnol, DOI: 10.1038/s41587-023-01769-w. |
| [65] | Tang X, Sretenovic S, Ren Q R, Jia X Y, Li M K, Fan T T, Yin D S, Xiang S Y, Guo Y C, Liu L, Zheng X L, Qi Y P, Zhang Y. 2020. Plant prime editors enable precise gene editing in rice cells. Mol Plant, 13(5): 667-670. |
| [66] | Tao R, Wang Y H, Jiao Y G, Hu Y, Li L, Jiang L R, Zhou L F, Qu J Y, Chen Q, Yao S H. 2022. Bi-PE: Bi-directional priming improves CRISPR/Cas9 prime editing in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res, 50(11): 6423-6434. |
| [67] | Tian Y F, Shen R D, Li Z R, Yao Q, Zhang X N, Zhong D T, Tan X H, Song M L, Han H, Zhu J K, Lu Y M. 2022. Efficient C-to-G editing in rice using an optimized base editor. Plant Biotechnol J, 20(7): 1238-1240. |
| [68] | Távora F T P K, Meunier A C, Vernet A, Portefaix M, Joëlle Milazzo J, Adreit H, Tharreau D, Franco O L, Mehta A. 2022. CRISPR/Cas9-targeted knockout of rice susceptibility genes OsDjA2 and OsERF104 reveals alternative sources of resistance to Pyricularia oryzae. Rice Sci, 29(6): 535-544. |
| [69] | Velimirovic M, Zanetti L C, Shen M W, Fife J D, Lin L, Cha M S, Akinci E, Barnum D, Yu T, Sherwood R I. 2022. Peptide fusion improves prime editing efficiency. Nat Commun, 13: 3512. |
| [70] | Wang C L, Zhang X P, Fan Y L, Gao Y, Zhu Q L, Zheng C K, Qin T F, Li Y Q, Che J Y, Zhang M W, Yang B, Liu Y G, Zhao K J. 2014. XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad- spectrum disease resistance in rice. Mol Plant, 8(2): 290-302. |
| [71] | Wang J J, Meng X B, Hu X X, Sun T T, Li J Y, Wang K J, Yu H. 2019. xCas9 expands the scope of genome editing with reduced efficiency in rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 17(4): 709-711. |
| [72] | Wang J L, He Z, Wang G Q, Zhang R W, Duan J Y, Gao P, Lei X L, Qiu H Y, Zhang C P, Zhang Y, Yin H. 2022. Efficient targeted insertion of large DNA fragments without DNA donors. Nat Methods, 19(3): 331-340. |
| [73] | Xu R F, Li J, Liu X S, Shan T F, Qin R Y, Wei P C. 2020. Development of plant prime-editing systems for precise genome editing. Plant Commun, 1(3): 100043. |
| [74] | Xu R F, Liu X S, Li J, Qin R Y, Wei P C. 2021. Identification of herbicide resistance OsACC1 mutations via in planta prime- editing-library screening in rice. Nat Plants, 7(7): 888-892. |
| [75] | Xu W, Zhang C W, Yang Y X, Zhao S, Kang G T, He X Q, Song J L, Yang J X. 2020. Versatile nucleotides substitution in plant using an improved prime editing system. Mol Plant, 13(5): 675-678. |
| [76] | Xu W, Yang Y X, Yang B Y, Krueger C J, Xiao Q L, Zhao S, Zhang L, Kang G T, Wang F P, Yi H M, Ren W, Li L, He X Q, Zhang C M, Zhang B, Zhao J R, Yang J X. 2022. A design optimized prime editor with expanded scope and capability in plants. Nat Plants, 8(1): 45-52. |
| [77] | Xu Y B, Meng X B, Wang J J, Qin B X, Wang K J, Li J Y, Wang C, Yu H. 2020. ScCas9 recognizes NNG protospacer adjacent motif in genome editing of rice. Sci China Life Sci, 63(3): 450-452. |
| [78] | Xue C X, Qiu F T, Wang Y X, Li B S, Zhao K T, Chen K L, Gao C X. 2023. Tuning plant phenotypes by precise, graded downregulation of gene expression. Nat Biotechnol, DOI: 10.1038/s41587-023-01707-w. |
| [79] | Yarnall M T N, Ioannidi E I, Schmitt-Ulms C, Krajeski R N, Lim J, Villiger L, Zhou W Y, Jiang K Y, Garushyants S K, Roberts N, Zhang L Y, Vakulskas C A, Walker J A, Kadina A P, Zepeda A E, Holden K, Ma H, Xie J, Gao G P, Foquet L, Bial G, Donnelly S K, Miyata Y, Radiloff D R, Henderson J M, Ujita A, Abudayyeh O O, Gootenberg J S. 2023. Drag-and-drop genome insertion of large sequences without double-strand DNA cleavage using CRISPR-directed integrases. Nat Biotechnol, 41(4): 500-512. |
| [80] | Yu S Y, Birkenshaw A, Thomson T, Carlaw T, Zhang L H, Ross C J D. 2022. Increasing the targeting scope of CRISPR base editing system beyond NGG. CRISPR J, 5(2): 187-202. |
| [81] | Zhang G Q, Liu Y, Huang S S, Qu S Y, Cheng D L, Yao Y, Ji Q J, Wang X L, Huang X X, Liu J H. 2022. Enhancement of prime editing via xrRNA motif-joined pegRNA. Nat Commun, 13(1): 1856. |
| [82] | Zhang H, Dou S Q, He F, Luo J J, Wei L P, Lu J. 2018. Genome- wide maps of ribosomal occupancy provide insights into adaptive evolution and regulatory roles of uORFs during Drosophila development. PLoS Biol, 16(7): e2003903. |
| [83] | Zhang T, Wu A Q, Yue Y P, Zhao Y. 2020. uORFs: Important cis-regulatory elements in plants. Int J Mol Sci, 21(17): 6238. |
| [84] | Zhu H C, Li C, Gao C X. 2020. Applications of CRISPR-Cas in agriculture and plant biotechnology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 21(11): 661-677. |
| [85] | Zong Y, Liu Y J, Xue C X, Li B S, Li X Y, Wang Y P, Li J, Liu G W, Huang X X, Cao X F, Gao C X. 2022. An engineered prime editor with enhanced editing efficiency in plants. Nat Biotechnol, 40(9): 1394-1402. |
| [86] | Zou J P, Meng X B, Liu Q, Shang M Q, Wang K J, Li J Y, Yu H, Wang C. 2022. Improving the efficiency of prime editing with epegRNAs and high-temperature treatment in rice. Sci China Life Sci, 65(11): 2328-2331. |
| [87] | Zuo E W, Sun Y D, Wei W, Yuan T L, Ying W Q, Sun H, Yuan L Y, Steinmetz L M, Li Y X, Yang H. 2019. Cytosine base editor generates substantial off-target single-nucleotide variants in mouse embryos. Science, 364: 289-292. |
| [1] | Mishra Rukmini, Zheng Wei, Kumar Joshi Raj, Kaijun Zhao. Genome Editing Strategies Towards Enhancement of Rice Disease Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(2): 133-145. |
| [2] | Yuyu Chen, Aike Zhu, Pao Xue, Xiaoxia Wen, Yongrun Cao, Beifang Wang, Yue Zhang, Liaqat Shah, Shihua Cheng, Liyong Cao, Yingxin Zhang. Effects of GS3 and GL3.1 for Grain Size Editing by CRISPR/Cas9 in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(5): 405-413. |
| [3] | Srivastava Deepti, Shamim Md, Kumar Mahesh, Mishra Anurag, Pandey Pramila, Kumar Deepak, Yadav Prashant, Harrish Siddiqui Mohammed, Narayan Singh Kapildeo. Current Status of Conventional and Molecular Interventions for Blast Resistance in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(6): 299-321. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||