
Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 552-565.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.06.004
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Li Qianlong2, Feng Qi1, Wang Heqin3, Kang Yunhai2, Zhang Conghe2,3, Du Ming2, Zhang Yunhu3, Wang Hui2,3, Chen Jinjie3, Han Bin1, Fang Yu2,3,4( ), Wang Ahong1(
), Wang Ahong1( )
)
Received:2023-02-07
Accepted:2023-06-30
Online:2023-11-28
Published:2023-08-10
Contact:
Wang Ahong (ahwang@ncgr.ac.cn);
Fang Yu (fy@zkwbreeding.com)
Li Qianlong, Feng Qi, Wang Heqin, Kang Yunhai, Zhang Conghe, Du Ming, Zhang Yunhu, Wang Hui, Chen Jinjie, Han Bin, Fang Yu, Wang Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages[J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 552-565.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
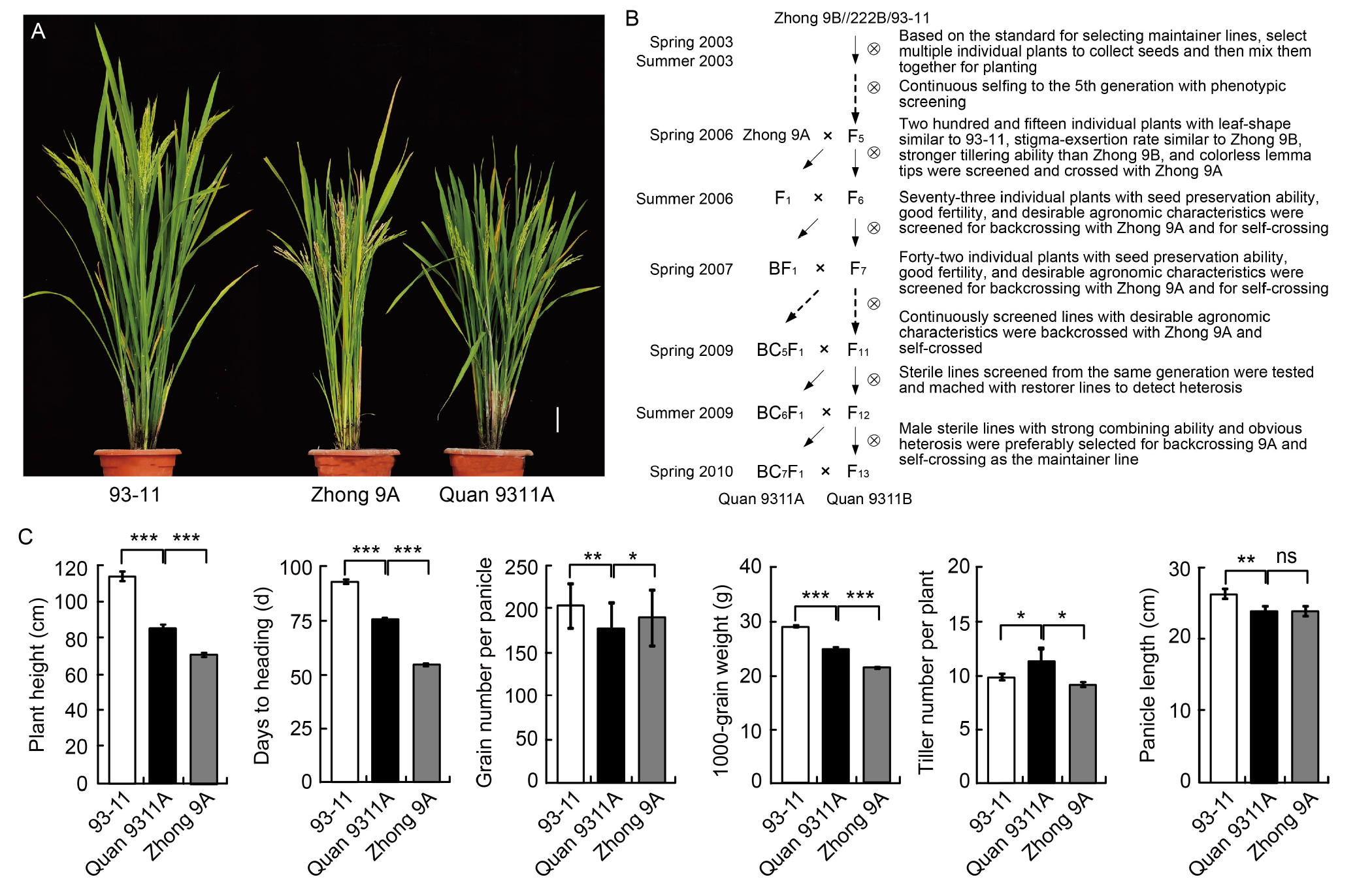
Fig. 1. Phenotypic characteristics and breeding process of Quan 9311A. A, Plant morphologies of 93-11, Zhong 9A, and Quan 9311A. Scale bar, 10 cm. B, Breeding pedigree of Quan 9311A/B. C, Phenotypes of 93-11, Quan 9311A, and Zhong 9A. The phenotypic values are Mean ± SD with 24 biological replicates. Student’s t-test significant difference: *, P?<?0.05; **, P?<?0.01; ***, P?<?0.001; ns, Not significant.
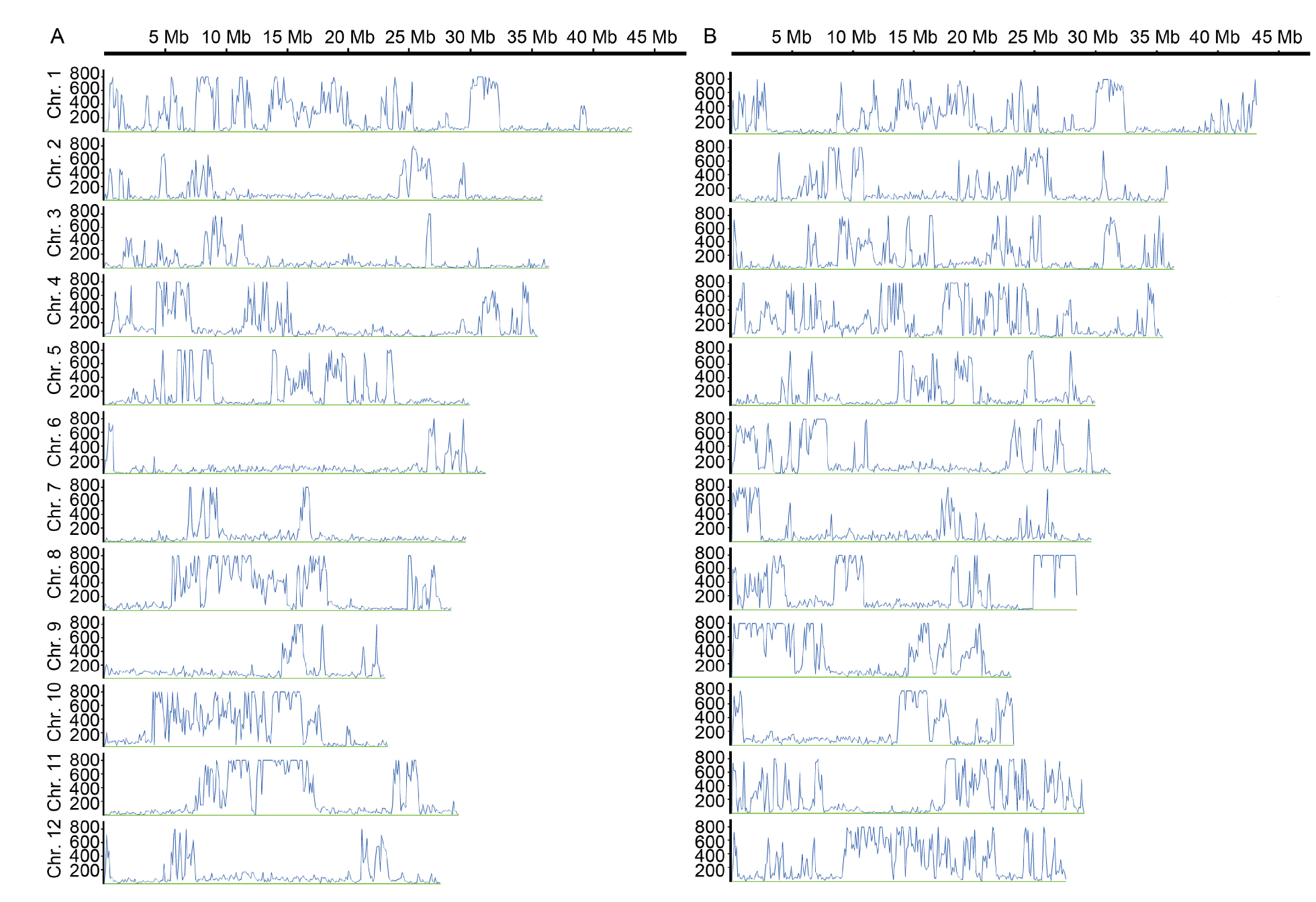
Fig. 2. Simple sequence polymorphism (SNP) discrepancy between two parents across entire genome. A, SNP distribution between Quan 9311A and 93-11. B, SNP distribution between Quan 9311A and Zhong 9A. The X-axis refers to the corresponding physical position of each chromosome. According to the physical division of an interval of 100 kb, 3 740 intervals are distributed on 12 chromosomes (Chr.) across the entire genome. The Y-axis is the number of SNPs in each interval. To make the image clearer to view, when the number of SNPs within an interval exceeds 800, only 800 will be displayed on the Y-axis.
| Trait | Chromosome | Gene | Alteration allele caused function a | 93-11 | Zhong 9A | Quan 9311A | WSSM | QYSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD | 1 | OsMADS51 | Delaying HD | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| YC | 2 | Rf2 | Fertility restoration | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| TQ | 6 | SSG6/OsACS6 | Controls starch grain size | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| TQ | 6 | Waxy/GBSSI | Changing amylose content | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| HD | 6 | Hd1 | Promoting HD under long days | √ | ○ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 6 | DLT/GS6 | Dwarf and low-tillering | √ | ○ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 7 | BG2/GE | Increasing grain size | √ | ○ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| OT | 7 | Sdr4 | Controlling seed dormancy | √ | ○ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 8 | GW8/OsSPL16 | Increasing grain width | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| ABS | 9 | Sub1A | Submergence tolerance | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| BS | 11 | STV11 | Increasing resistance to rice stripe virus | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| PA | 1 | D2/SMG11 | Decreasing plant height | ○ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 1 | Rf3/OsMADS3 | Fertility restoration | ○ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| OT | 3 | BOC1 | Callus browning | ○ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| BS | 4 | Xa1 | Increasing blight resistance | ○ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| HD | 7 | Ghd7/Hd4 | Promoting HD under long days | ○ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| BS | 11 | Xa3/Xa26 | Increasing blight resistance | ○ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 1 | NOG1 | Increasing grain number | √ | √ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| YC | 1 | LAX1 | Increasing grain number | √ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| BS | 4 | Pi21 | Increasing blast resistance | ○ | √ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| BS | 4 | Bph3 | Increasing brown planthopper resistance | √ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| YC | 5 | PTB1 | Increasing seed-setting rate | √ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| YC | 5 | GW5/GSE5 | Increasing grain width | ○ | ○ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| BS | 6 | Bph29 | Increasing brown planthopper resistance | √ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| BS | 6 | Pi9 | Increasing blast resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | √○ | √○ |
| HD | 7 | Ghd7.1 | Promoting HD under long days | √ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 8 | Ghd8 | Promoting HD under long days | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| PA | 8 | TIG1 | Smaller tiller angle | √ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| BS | 9 | Pi5 | Increasing blast resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| BS | 9 | Pi56 | Increasing blast resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| YC | 10 | Rf4 | Fertility restoration | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| YC | 10 | Rf1b | Fertility restoration | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| BS | 11 | Pi-ta | Increasing blast resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
Table 1. Summary of genes associated with crucial agronomic traits in Zhong 9A, 93-11, Quan 9311A, WSSM, and QYSM.
| Trait | Chromosome | Gene | Alteration allele caused function a | 93-11 | Zhong 9A | Quan 9311A | WSSM | QYSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD | 1 | OsMADS51 | Delaying HD | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| YC | 2 | Rf2 | Fertility restoration | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| TQ | 6 | SSG6/OsACS6 | Controls starch grain size | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| TQ | 6 | Waxy/GBSSI | Changing amylose content | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| HD | 6 | Hd1 | Promoting HD under long days | √ | ○ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 6 | DLT/GS6 | Dwarf and low-tillering | √ | ○ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 7 | BG2/GE | Increasing grain size | √ | ○ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| OT | 7 | Sdr4 | Controlling seed dormancy | √ | ○ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 8 | GW8/OsSPL16 | Increasing grain width | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| ABS | 9 | Sub1A | Submergence tolerance | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| BS | 11 | STV11 | Increasing resistance to rice stripe virus | √ | ○ | √ | √ | √ |
| PA | 1 | D2/SMG11 | Decreasing plant height | ○ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 1 | Rf3/OsMADS3 | Fertility restoration | ○ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| OT | 3 | BOC1 | Callus browning | ○ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| BS | 4 | Xa1 | Increasing blight resistance | ○ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| HD | 7 | Ghd7/Hd4 | Promoting HD under long days | ○ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| BS | 11 | Xa3/Xa26 | Increasing blight resistance | ○ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 1 | NOG1 | Increasing grain number | √ | √ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| YC | 1 | LAX1 | Increasing grain number | √ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| BS | 4 | Pi21 | Increasing blast resistance | ○ | √ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| BS | 4 | Bph3 | Increasing brown planthopper resistance | √ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| YC | 5 | PTB1 | Increasing seed-setting rate | √ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| YC | 5 | GW5/GSE5 | Increasing grain width | ○ | ○ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| BS | 6 | Bph29 | Increasing brown planthopper resistance | √ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| BS | 6 | Pi9 | Increasing blast resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | √○ | √○ |
| HD | 7 | Ghd7.1 | Promoting HD under long days | √ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| YC | 8 | Ghd8 | Promoting HD under long days | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| PA | 8 | TIG1 | Smaller tiller angle | √ | √ | √ | ○ | √○ |
| BS | 9 | Pi5 | Increasing blast resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| BS | 9 | Pi56 | Increasing blast resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| YC | 10 | Rf4 | Fertility restoration | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| YC | 10 | Rf1b | Fertility restoration | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
| BS | 11 | Pi-ta | Increasing blast resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | √ | √○ |
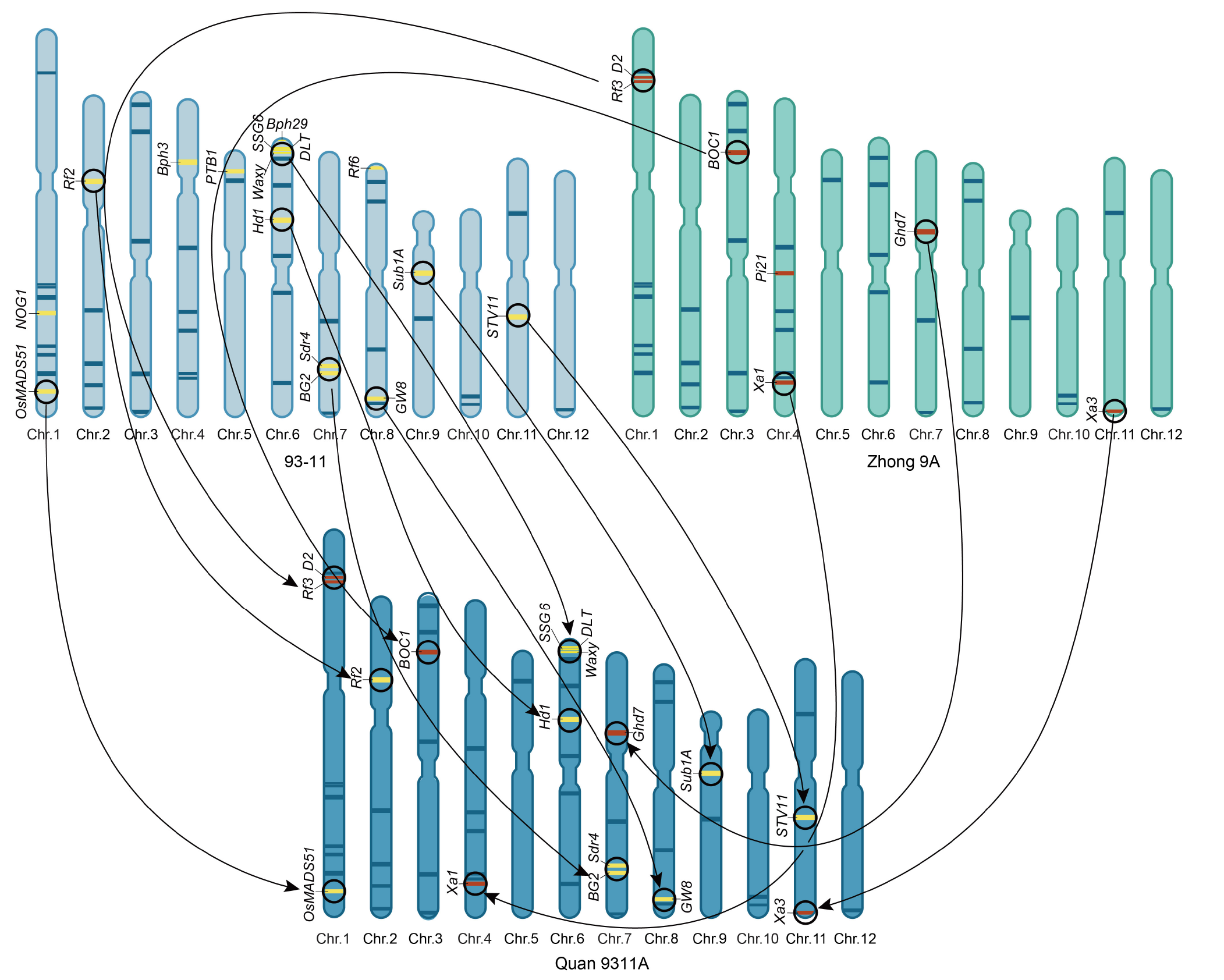
Fig. 3. Superior alleles inherited by Quan 9311A from both parents 93-11 and Zhong 9A. The unique genes in 93-11 and Zhong 9A are represented by yellow and brown bars, respectively. The genes with arrows in circles are inherited by Quan 9311A. Genes without circles and arrows are not inherited by Quan 9311A. Dark blue bars indicate superior genes simultaneously contained in the three cultivars, and each bar represents a superior gene. Chr., Chromosome.
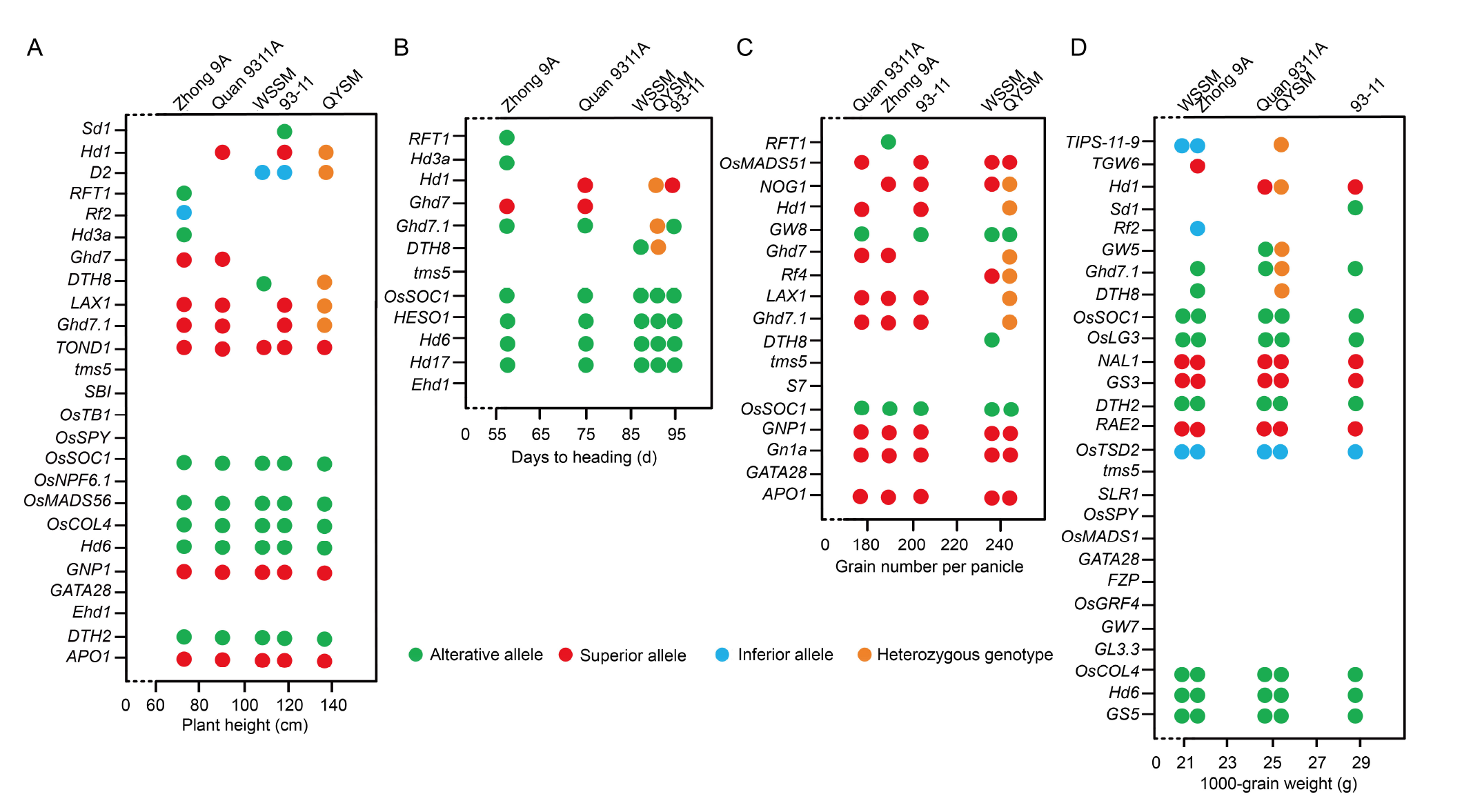
Fig. 4. Phenotypic characteristics and genetic loci in five cultivars. A?D, Plant height (A), days to heading (B), grain number per panicle (C), and 1000-grain weight (D). WSSM, Wushansimiao; QYSM, Quanyousimiao. The X-axis refers to the phenotypic data of each agronomic trait, and the five cultivar names are indicated at the positions of the corresponding phenotypic values. The Y-axis refers to genetic loci associated with important agronomic traits (Wei et al, 2020). Each dot represents the mutant genotype for each genetic locus. Genetic loci without marked dots are wild type genotypes. Alterative alleles can cause phenotypic changes. Superior alleles contribute to desirable agronomic traits, while inferior alleles do not.
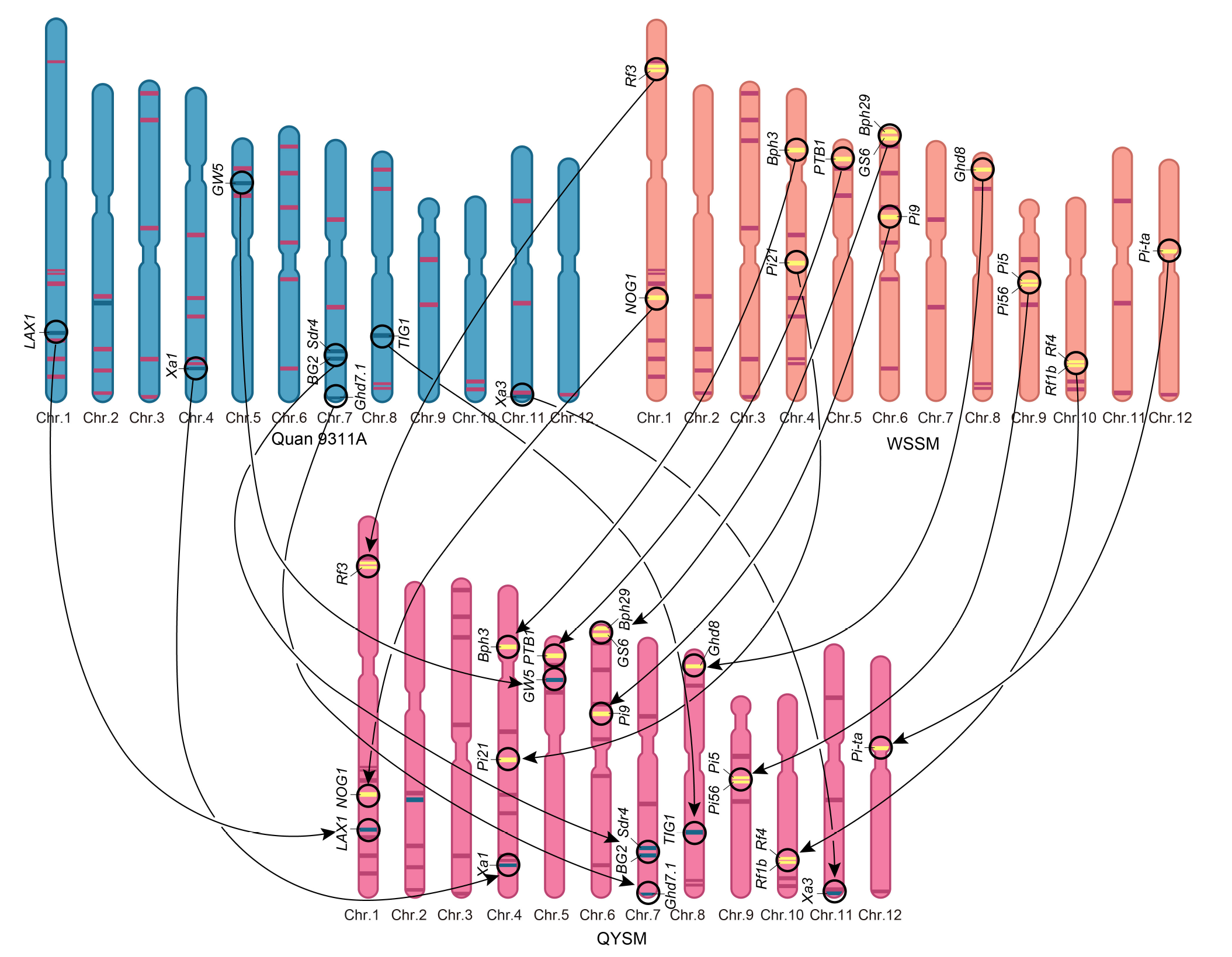
Fig. 5. Superior genes for Quanyousimiao (QYSM) aggregated from Quan 9311A and Wushansimiao (WSSM). The unique genes in Quan 9311A and WSSM are represented by blue and yellow bars, respectively. Purple bar indicates superior genes simultaneously contain in the three cultivars, and each bar represents a superior gene. Chr., Chromosome.
| Ecological growing region | Cultivar | Plot yield (kg) | Blast resistance | Bacterial blight resistance | White backed planthopper resistance | Brown planthopper resistance | Grain quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early-season indica in South China | Quanyousimiao | 10.77 ± 0.29 | 3.8 | 7 | 7 | / | II |
| Tianyouhuazhan | 10.49 ± 0.12 | 4.1 | 7 | 7 | / | NO | |
| Late-season indica in South China | Quanyousimiao | 9.35 ± 0.19* | 3.3* | 7 | 9 | / | II |
| Boyou 998 | 8.95 ± 0.10 | 7.1 | 7 | 9 | / | NO | |
| Mid-season indica in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River | Quanyousimiao | 12.75 ± 0.15 | 3.3* | / | / | 7 | II |
| F-You 498 | 12.55 ± 0.24 | 8.2 | / | / | 9 | NO | |
| Mid-season indica in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River | Quanyousimiao | 12.71 ± 0.04*** | 3.1*** | 5 | / | 7 | III |
| Fengliangyou 4 | 11.75 ± 0.15 | 7.2 | 9 | / | 9 | NO |
Table 2. Phenotypes of plot yield, blast resistance, bacterial blight resistance, planthopper resistance, and grain quality of Quanyousimiao and control cultivars.
| Ecological growing region | Cultivar | Plot yield (kg) | Blast resistance | Bacterial blight resistance | White backed planthopper resistance | Brown planthopper resistance | Grain quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early-season indica in South China | Quanyousimiao | 10.77 ± 0.29 | 3.8 | 7 | 7 | / | II |
| Tianyouhuazhan | 10.49 ± 0.12 | 4.1 | 7 | 7 | / | NO | |
| Late-season indica in South China | Quanyousimiao | 9.35 ± 0.19* | 3.3* | 7 | 9 | / | II |
| Boyou 998 | 8.95 ± 0.10 | 7.1 | 7 | 9 | / | NO | |
| Mid-season indica in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River | Quanyousimiao | 12.75 ± 0.15 | 3.3* | / | / | 7 | II |
| F-You 498 | 12.55 ± 0.24 | 8.2 | / | / | 9 | NO | |
| Mid-season indica in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River | Quanyousimiao | 12.71 ± 0.04*** | 3.1*** | 5 | / | 7 | III |
| Fengliangyou 4 | 11.75 ± 0.15 | 7.2 | 9 | / | 9 | NO |
| [1] | Bai S W, Yu H, Wang B, Li J Y. 2018. Retrospective and perspective of rice breeding in China. J Genet Genomics, 45(11): 603-612. |
| [2] | Cai J, Liao Q P, Dai Z J, Zhu H T, Zeng R Z, Zhang Z M, Zhang G Q. 2013. Allelic differentiations and effects of the Rf3 and Rf4 genes on fertility restoration in rice with wild abortive cytoplasmic male sterility. Biol Plant, 57(2): 274-280. |
| [3] | Chen R Z, Deng Y W, Ding Y L, Guo J X, Qiu J, Wang B, Wang C S, Xie Y Y, Zhang Z H, Chen J X, Chen L T, Chu C C, He G C, He Z H, Huang X H, Xing Y Z, Yang S H, Xie D X, Liu Y G, Li J Y. 2022. Rice functional genomics: Decades’ efforts and roads ahead. Sci China Life Sci, 65(1): 33-92. |
| [4] | Cheng S H, Zhuang J Y, Fan Y Y, Du J H, Cao L Y. 2007. Progress in research and development on hybrid rice: A super-domesticate in China. Ann Bot, 100(5): 959-966. |
| [5] | China National Institute of Standardization. 2020. Identification of plant varieties-MNP marker method: GB/T 38551-2020. Beijing, China: National Standard of China. (in Chinese) |
| [6] | Ding J H, Lu Q, Ouyang Y D, Mao H L, Zhang P B, Yao J L, Xu C G, Li X H, Xiao J H, Zhang Q F. 2012. A long noncoding RNA regulates photoperiod-sensitive male sterility, an essential component of hybrid rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109(7): 2654-2659. |
| [7] | Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Mao H L, Lu T T, Han B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F. 2006. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet, 112(6): 1164-1171. |
| [8] | Feng Q, Zhang Y J, Hao P, Wang S Y, Fu G, Huang Y C, Li Y, Zhu J J, Liu Y L, Hu X, Jia P X, Zhang Y, Zhao Q, Ying K, Yu S L, Tang Y S, Weng Q J, Zhang L, Lu Y, Mu J, Lu Y Q, Zhang L S, Yu Z, Fan D L, Liu X H, Lu T T, Li C, Wu Y R, Sun T G, Lei H Y, Li T, Hu H, Guan J P, Wu M, Zhang R Q, Zhou B, Chen Z H, Chen L, Jin Z Q, Wang R, Yin H F, Cai Z, Ren S X, Lv G, Gu W Y, Zhu G F, Tu Y F, Jia J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Kang H, Chen X Y, Shao C Y, Sun Y, Hu Q P, Zhang X L, Zhang W, Wang L J, Ding C W, Sheng H H, Gu J L, Chen S T, Ni L, Zhu F H, Chen W, Lan L F, Lai Y, Cheng Z K, Gu M H, Jiang J M, Li J Y, Hong G F, Xue Y B, Han B. 2002. Sequence and analysis of rice chromosome 4. Nature, 420: 316-320. |
| [9] | Fujino K. 2020. Days to heading, controlled by the heading date genes, Hd1 and DTH8, limits rice yield-related traits in Hokkaido, Japan. Breed Sci, 70(3): 277-282. |
| [10] | Gu Z, Zhu Z, Li Z, Zhan Q L, Feng Q, Zhou C C, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Peng X J, Dai B X, Sun R R, Li Y, Lu H Y, Zhang L, Huang T, Gong J Y, Lv D F, Huang X H, Han B. 2021. Cytoplasmic and nuclear genome variations of rice hybrids and their parents inform the trajectory and strategy of hybrid rice breeding. Mol Plant, 14(12): 2056-2071. |
| [11] | Guo T, Yu H, Qiu J, Li J Y, Han B, Lin H X. 2019. Advances in rice genetics and breeding by molecular design in China. Sci Sin Vitae, 49(10): 1185-1212. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Hickey L T, Hafeez A N, Robinson H, Jackson S A, Leal-Bertioli S C M, Tester M, Gao C X, Godwin I D, Hayes B J, Wulff B B H. 2019. Breeding crops to feed 10 billion. Nat Biotechnol, 37(7): 744-754. |
| [13] | Huang J Y, Hu J, Xu X, Li S Q, Yi P, Yang D C, Ren F G, Liu X Q, Zhu Y G. 2003. Fine mapping of the nuclear fertility restorer gene for HL cytoplasmic male sterility in rice. Bot Bull Acad Sin, 44(4): 285-289. |
| [14] | Huang W C, Yu C C, Hu J, Wang L L, Dan Z W, Zhou W, He C L, Zeng Y F, Yao G X, Qi J Z, Zhang Z H, Zhu R S, Chen X F, Zhu Y G. 2015. Pentatricopeptide-repeat family protein RF6 functions with hexokinase 6 to rescue rice cytoplasmic male sterility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 112(48): 14984-14989. |
| [15] | Huang X H, Yang S H, Gong J Y, Zhao Y, Feng Q, Gong H, Li W J, Zhan Q L, Cheng B Y, Xia J H, Chen N, Hao Z N, Liu K Y, Zhu C R, Huang T, Zhao Q, Zhang L, Fan D L, Zhou C C, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Wang Z X, Li J Y, Han B. 2015. Genomic analysis of hybrid rice varieties reveals numerous superior alleles that contribute to heterosis. Nat Commun, 6: 6258. |
| [16] | Huang X H, Yang S H, Gong J Y, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhan Q L, Zhao Y, Li W J, Cheng B Y, Xia J H, Chen N, Huang T, Zhang L, Fan D L, Chen J Y, Zhou C C, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Han B. 2016. Genomic architecture of heterosis for yield traits in rice. Nature, 537: 629-633. |
| [17] | Itabashi E, Iwata N, Fujii S, Kazama T, Toriyama K. 2011. The fertility restorer gene, Rf2, for lead rice-type cytoplasmic male sterility of rice encodes a mitochondrial glycine-rich protein. Plant J, 65(3): 359-367. |
| [18] | Li J M, Yuan L P. 2010. Hybrid rice: Genetics, breeding, and seed production. In: Janick J. Plant Breeding Reviews. Oxford, UK: John Wiley & Sons, 15-158. |
| [19] | Luan J, Liu T R, Luo W Q, Liu W, Peng M Q, Li W J, Dai X J, Liang M Z, Chen L B. 2013. Mitochondrial DNA genetic polymorphism in thirteen rice cytoplasmic male sterile lines. Plant Cell Rep, 32(4): 545-554. |
| [20] | Luo D P, Xu H, Liu Z L, Guo J X, Li H Y, Chen L T, Fang C, Zhang Q Y, Bai M, Yao N, Wu H, Wu H, Ji C H, Zheng H Q, Chen Y L, Ye S, Li X Y, Zhao X C, Li R Q, Liu Y G. 2013. A detrimental mitochondrial-nuclear interaction causes cytoplasmic male sterility in rice. Nat Genet, 45(5): 573-577. |
| [21] | Ngangkham U, Samantaray S, Yadav M K, Kumar A, Chidambaranathan P, Katara J L. 2018. Effect of multiple allelic combinations of genes on regulating grain size in rice. PLoS One, 13(1): e0190684. |
| [22] | Peng H F, Qiu Z G, Chen X H, Wan B H, Zhang G Q, Lu Y P. 2006. Pollen fertility and cytological observation of a thermosensitive genic male sterile line of non-pollen type XianS in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Ecol Sin, 26: 2322-2327. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Peng H F, Chen X H, Lu Y P, Peng Y F, Wan B H, Chen N D, Wu B, Xin S P, Zhang G Q. 2010. Fine mapping of a gene for non-pollen type thermosensitive genic male sterility in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 120(5): 1013-1020. |
| [24] | Qi F L, Jiang M S, Yuan S J, Yao F Y, Gao J, Li G X. 2008. Mapping of fertility-restoring gene Rf3 in wild-aborted cytoplasmic male sterility in rice. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 24(8): 114-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Qian Q, Guo L B, Smith S M, Li J Y. 2016. Breeding high-yield superior quality hybrid super rice by rational design. Natl Sci Rev, 3(3): 283-294. |
| [26] | Sasaki T. 1998. The rice genome project in Japan. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 95(5): 2027-2028. |
| [27] | Sasaki T, Burr B. 2000. International Rice Genome Sequencing Project: The effort to completely sequence the rice genome. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 3(2): 138-142. |
| [28] | Sattari M, Kathiresan A, Gregorio G B, Virmani S S. 2008. Comparative genetic analysis and molecular mapping of fertility restoration genes for WA, Dissi, and Gambiaca cytoplasmic male sterility systems in rice. Euphytica, 160(3): 305-315. |
| [29] | Shull G. H. 1952. Beginnings of the heterosis concept. In: Gowen J. Heterosis, a Record of Researches Directed toward Explaining and Utilizing the Vigor of Hybrids. Ames, USA: Iowa State College Press: 14-48. |
| [30] | Sun K L, Huang M H, Zong W B, Xiao D D, Lei C, Luo Y Q, Song Y G, Li S T, Hao Y, Luo W N, Xu B Q, Guo X T, Wei G L, Chen L T, Liu Y G, Guo J X. 2022. Hd1, Ghd7, and DTH8 synergistically determine the rice heading date and yield-related agronomic traits. J Genet Genomics, 49(5): 437-447. |
| [31] | Tang H W, Luo D P, Zhou D G, Zhang Q Y, Tian D S, Zheng X M, Chen L T, Liu Y G. 2014. The rice restorer Rf4 for wild-abortive cytoplasmic male sterility encodes a mitochondrial-localized PPR protein that functions in reduction of WA352 transcripts. Mol Plant, 7(9): 1497-1500. |
| [32] | Varshney R K, Bohra A, Roorkiwal M, Barmukh R, Cowling W A, Chitikineni A, Lam H M, Hickey L T, Croser J S, Bayer P E, Edwards D, Crossa J, Weckwerth W, Millar H, Kumar A, Bevan M W, Siddique K H M. 2021. Fast-forward breeding for a food-secure world. Trends Genet, 37(12): 1124-1136. |
| [33] | Wang H Q, Chen J J, Zhang Y H, Zhang C H, Yan Z, Liu X J, Chen L. 2013. Breeding of new quality indica CMS line Quan 9311A in rice. Hybrid Rice, 28(6): 10-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Wang H Q, Chen J J, Zhang C H, Zhang Y H, Yan Z, Chen L. 2016. Breeding and cultivation, seed production technology of high yield and good quality middle season indica hybrid rice combination Quanyousimiao. J Anhui Agric Sci, 44(20): 23-24/37. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [35] | Wang K, Gao F, Ji Y X, Liu Y, Dan Z W, Yang P F, Zhu Y G, Li S Q. 2013. ORFH79 impairs mitochondrial function via interaction with a subunit of electron transport chain complex III in Honglian cytoplasmic male sterile rice. New Phytol, 198(2): 408-418. |
| [36] | Wang S K, Wu K, Yuan Q B, Liu X Y, Liu Z B, Lin X Y, Zeng R Z, Zhu H T, Dong G J, Qian Q, Zhang G Q, Fu X D. 2012. Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet, 44(8): 950-954. |
| [37] | Wang Z H, Zou Y J, Li X Y, Zhang Q Y, Chen L T, Wu H, Su D H, Chen Y L, Guo J X, Luo D, Long Y M, Zhong Y, Liu Y G. 2006. Cytoplasmic male sterility of rice with boro II cytoplasm is caused by a cytotoxic peptide and is restored by two related PPR motif genes via distinct modes of mRNA silencing. Plant Cell, 18(3): 676-687. |
| [38] | Wei X, Qiu J, Yong K C, Fan J J, Zhang Q, Hua H, Liu J, Wang Q, Olsen K M, Han B, Huang X H. 2021. A quantitative genomics map of rice provides genetic insights and guides breeding. Nat Genet, 53(2): 243-253. |
| [39] | Yuan L P. 1994. Purification and production of foundation seed of rice PGMS and TGMS lines. Hybrid Rice, 6: 1-3. |
| [40] | Zhang H G, Che J L, Ge Y S, Pei Y, Zhang L J, Liu Q Q, Gu M H, Tang S Z. 2017. Ability of Rf5 and Rf6 to restore fertility of Chinsurah Boro II-type cytoplasmic male sterile Oryza sativa (ssp. japonica) lines. Rice, 10(1): 2. |
| [41] | Zhang Z H, Wang K, Guo L, Zhu Y J, Fan Y Y, Cheng S H, Zhuang J Y. 2012. Pleiotropism of the photoperiod-insensitive allele of Hd1 on heading date, plant height and yield traits in rice. PLoS One, 7(12): e52538. |
| [42] | Zhong H, Liu C, Kong W L, Zhang Y, Zhao G Q, Sun T, Li Y S. 2020. Effect of multi-allele combination on rice grain size based on prediction of regression equation model. Mol Genet Genomics, 295(2): 465-474. |
| [43] | Zhou H, Zhou M, Yang Y Z, Li J, Zhu L Y, Jiang D G, Dong J F, Liu Q J, Gu L F, Zhou L Y, Feng M J, Qin P, Hu X C, Song C L, Shi J F, Song X W, Ni E D, Wu X J, Deng Q Y, Liu Z L, Chen M S, Liu Y G, Cao X F, Zhuang C X. 2014. RNase ZS1 processes UbL40 mRNAs and controls thermosensitive genic male sterility in rice. Nat Commun, 5: 4884. |
| [44] | Zhou H, Li P B, Xie W B, Hussain S, Li Y B, Xia D, Zhao H, Sun S Y, Chen J X, Ye H, Hou J, Zhao D, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, Wang G W, Lian X M, Xiao J H, Yu S B, Li X H, He Y Q. 2017. Genome-wide association analyses reveal the genetic basis of stigma exsertion in rice. Mol Plant, 10(4): 634-644. |
| [1] | Liu Tingting, Zou Jinpeng, Yang Xi, Wang Kejian, Rao Yuchun, Wang Chun. Development and Application of Prime Editing in Plants [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 509-522. |
| [2] | Lu Xuedan, Li Fan, Xiao Yunhua, Wang Feng, Zhang Guilian, Deng Huabing, Tang Wenbang. Grain Shape Genes: Shaping the Future of Rice Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 379-404. |
| [3] | R. Abdul Fiyaz, D. Shivani, K. Chaithanya, K. Mounika, M. Chiranjeevi, G. S. Laha, B. C. Viraktamath, L. V. Subba Rao, R. M. Sundaram. Genetic Improvement of Rice for Bacterial Blight Resistance: Present Status and Future Prospects [J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(2): 118-132. |
| [4] | Muduli Lakesh, Kumar Pradhan Sukanta, Mishra Abinash, Nath Bastia Debendra, Chandra Samal Kailash, Kumar Agrawal Pawan, Dash Manasi. Understanding Brown Planthopper Resistance in Rice: Genetics, Biochemical and Molecular Breeding Approaches [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(6): 532-546. |
| [5] | Saichompoo Uthomphon, Narumol Possawat, Nakwilai Pawat, Thongyos Peeranut, Nanta Aekchupong, Tippunya Patompong, Ruengphayak Siriphat, Itthisoponkul Teerarat, Bueraheng Niranee, Cheabu Sulaiman, Malumpong Chanate. Breeding Novel Short Grain Rice for Tropical Region to Combine Important Agronomical Traits, Biotic Stress Resistance and Cooking Quality in Koshihikari Background [J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(5): 479-792. |
| [6] | Ning Xiao, Yunyu Wu, Aihong Li. Strategy for Use of Rice Blast Resistance Genes in Rice Molecular Breeding [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(4): 263-277. |
| [7] | B. ANGELES-SHIM Rosalyn, P. REYES Vincent, M. del VALLE Marilyn, S. LAPIS Ruby, SHIM Junghyun, SUNOHARA Hidehiko, K. JENA Kshirod, ASHIKARI Motoyuki, DOI Kazuyuki. Marker-Assisted Introgression of Quantitative Resistance Gene pi21 Confers Broad Spectrum Resistance to Rice Blast [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(2): 113-123. |
| [8] | Ngangkham Umakanta, Kumar Parida Swarup, Kumar Singh Ashok, Mohapatra Trilochan. Differential RNA Editing of Mitochondrial Genes in WA-Cytoplasmic Based Male Sterile Line Pusa 6A, and Its Maintainer and Restorer Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(5): 282-289. |
| [9] | Khlaimongkhon Sudthana, Chakhonkaen Sriprapai, Pitngam Keasinee, Ditthab Khanittha, Sangarwut Numphet, Panyawut Natjaree, Wasinanon Thiwawan, Mongkolsiriwatana Chareerat, Chunwongse Julapark, Muangprom Amorntip. Molecular Markers and Candidate Genes for Thermo-Sensitive Genic Male Sterile in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(3): 147-156. |
| [10] | P. M. Swamy B., Kaladhar K., Anuradha K., K. Batchu Anil, Longvah T., Sarla N.. QTL Analysis for Grain Iron and Zinc Concentrations in Two O. nivara Derived Backcross Populations [J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(4): 197-207. |
| [11] | Zhongkang Wang, Dongdong Zeng, Ran Qin, Jialin Liu, Chunhai Shi, Xiaoli Jin. A Novel and Pleiotropic Factor SLENDER GRAIN3 Is Involved in Regulating Grain Size in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2018, 25(3): 132-141. |
| [12] | Srivastava Deepti, Shamim Md, Kumar Mahesh, Mishra Anurag, Pandey Pramila, Kumar Deepak, Yadav Prashant, Harrish Siddiqui Mohammed, Narayan Singh Kapildeo. Current Status of Conventional and Molecular Interventions for Blast Resistance in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(6): 299-321. |
| [13] | Sakambari Mishra Swati, Panda Debabrata. Leaf Traits and Antioxidant Defense for Drought Tolerance During Early Growth Stage in Some Popular Traditional Rice Landraces from Koraput, India [J]. Rice Science, 2017, 24(4): 207-217. |
| [14] | Arunakumari K., V. Durgarani C., Satturu V., R. Sarikonda K., D. R. Chittoor P., Vutukuri B., S. Laha G., P. K. Nelli A., Gattu S., Jamal M., Prasadbabu A., Hajira S., M. Sundaram R.. Marker-Assisted Pyramiding of Genes Conferring Resistance Against Bacterial Blight and Blast Diseases into Indian Rice Variety MTU1010 [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(6): 306-316. |
| [15] | Hong-guang Xie, Jia-huang Jiang, Yan-mei Zheng, Yong-sheng Zhu, Fang-xi Wu, Xi Luo, Qiu-hua Cai, Jian-fu Zhang, Hua-an Xie. Development of Hybrid Rice Variety FY7206 with Blast Resistance Gene Pid3 and Cold Tolerance Gene Ctb1 [J]. Rice Science, 2016, 23(5): 266-273. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||