
Rice Science ›› 2020, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 81-85.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2019.04.006
• • 下一篇
收稿日期:2019-01-29
接受日期:2019-04-26
出版日期:2020-03-28
发布日期:2019-11-28
. [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(2): 81-85.
| Trait | WT | M12 | M13 |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of days to heading (d) | 52.7 ± 0.9 a | 53.5 ± 1.4 a | 52.5 ± 1.0 a |
| No. of tillers per plant | 22.7 ± 2.2 a | 22.9 ± 2.0 a | 22.5 ± 1.8 a |
| Plant height (cm) | 61.3 ± 1.9 a | 60.3 ± 1.0 a | 60.2 ± 0.9 a |
| Panicle length (cm) | 11.5 ± 0.3 a | 11.4 ± 0.4 a | 11.6 ± 0.3 a |
| NPBP | 5.4 ± 0.8 a | 5.5 ± 0.8 a | 5.7 ± 0.9 a |
| NSBP | 4.2 ± 0.6 a | 3.9 ± 0.7 a | 4.0 ± 0.8 a |
| Seed-setting rate (%) | 88.3 ± 4.2 a | 86.6 ± 8.5 a | 70.1 ± 7.9 b |
Supplemental Table 1. Comparison of agronomic traits among wild type (WT), mutants M12 and M13 plants.
| Trait | WT | M12 | M13 |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of days to heading (d) | 52.7 ± 0.9 a | 53.5 ± 1.4 a | 52.5 ± 1.0 a |
| No. of tillers per plant | 22.7 ± 2.2 a | 22.9 ± 2.0 a | 22.5 ± 1.8 a |
| Plant height (cm) | 61.3 ± 1.9 a | 60.3 ± 1.0 a | 60.2 ± 0.9 a |
| Panicle length (cm) | 11.5 ± 0.3 a | 11.4 ± 0.4 a | 11.6 ± 0.3 a |
| NPBP | 5.4 ± 0.8 a | 5.5 ± 0.8 a | 5.7 ± 0.9 a |
| NSBP | 4.2 ± 0.6 a | 3.9 ± 0.7 a | 4.0 ± 0.8 a |
| Seed-setting rate (%) | 88.3 ± 4.2 a | 86.6 ± 8.5 a | 70.1 ± 7.9 b |
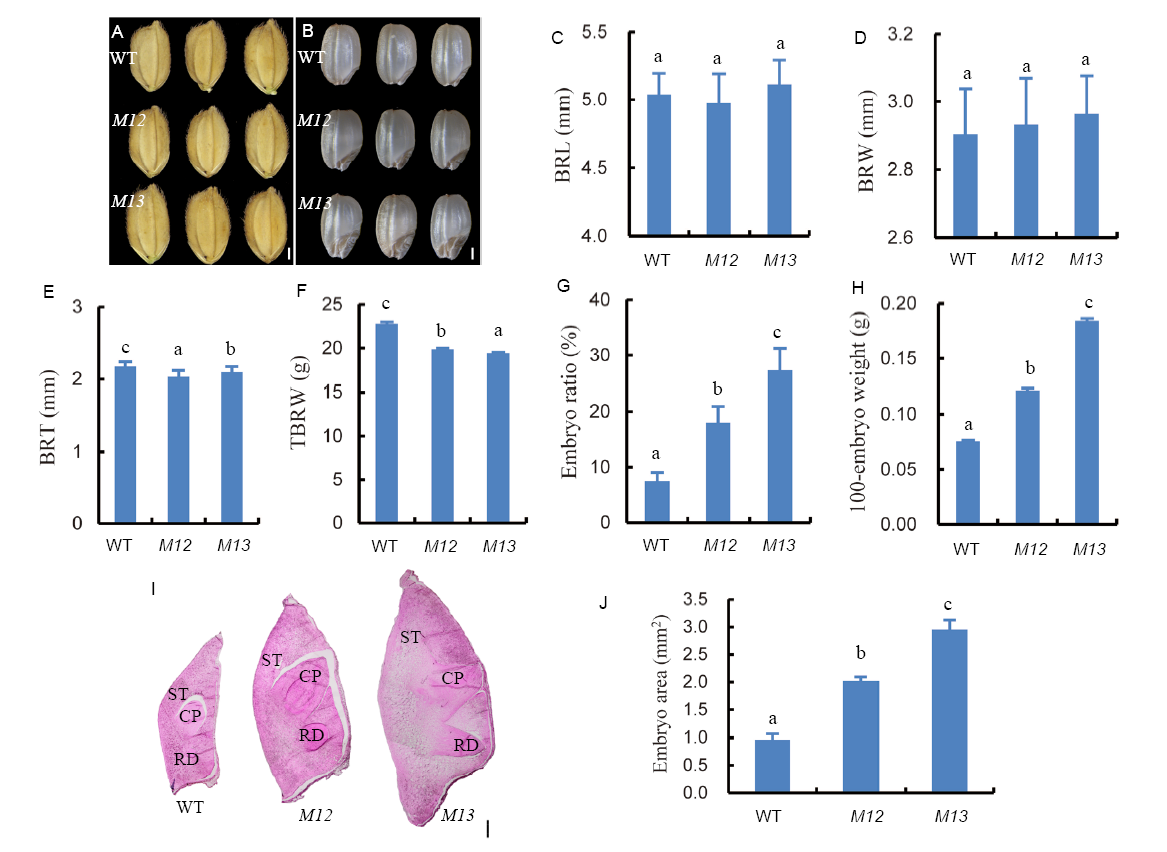
Fig. 1. Phenotypic analyses of giant embryo mutants M12 and M13.A, Morphologies of grains. Bar = 1 mm. B, Morphologies of brown rice. Bar = 1 mm. C, Quantification of brown rice length (BRL) (n = 20). D, Quantification of brown rice width (BRW) (n = 20). E, Quantification of brown rice thickness (BRT) (n = 20). F, 1000-brown rice weight (TBRW) (n = 3). G, The ratio of embryo size and seed size (n = 30). H, Weight of 100-embryo (n = 3). I, Longitudinal sections of the embryo of wild type (WT) and two mutants. CP, Coleoptile; RD, Radicle; ST, Scutellum. Bar = 0.2 mm. J, Embryo area of WT and two mutant seeds (n = 3). Data represent Mean ± SD. Different letters indicate a significant difference (P < 0.05).
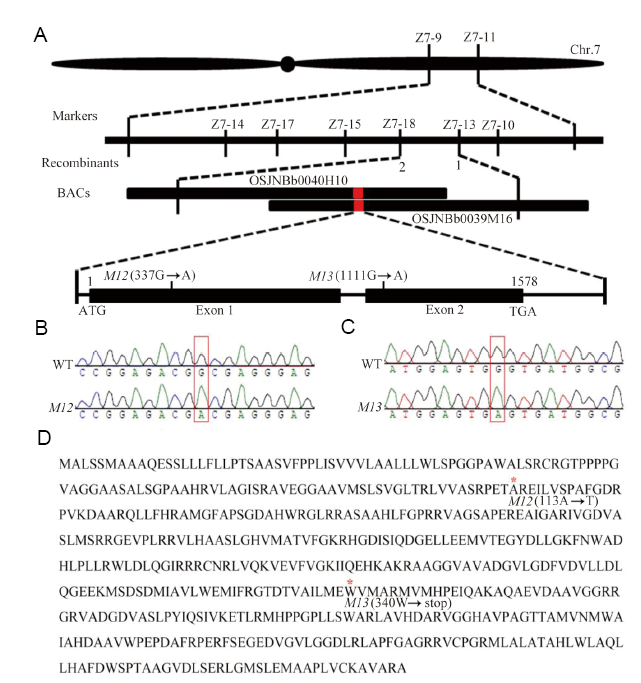
Fig. 2. Map-based cloning of the M12 and M13 mutation. A, Map-based cloning and identification of the mutation locus. The mutation locus was mapped to a 84.3 kb region between markers Z7-13 and Z7-18 on chromosome 7. A single nucleotide substitution of guanine to adenine occurred in the exon 1 and exon 2 in M12 and M13, respectively. B, Sequence chromatogram of M12. C, Sequence chromatogram of M13 mutation. The mutation site is noted with red box. D, Amino acid sequence of GE gene in M12 and M13. The two point mutations create Ala-113 replacement by Thr and a premature stop codon of Trp-340 in M12 and M13, respectively.
| Number | Locus name | Gene product name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | LOC_Os07g41230 | esterase, putative, expressed |
| 2 | LOC_Os07g41240 | cytochrome P450, putative, expressed |
| 3 | LOC_Os07g41250 | peptide transporter PTR2, putative |
| 4 | LOC_Os07g41260 | PPR repeat domain containing protein, putative |
| 5 | LOC_Os07g41270 | retrotransposon protein, putative, unclassified |
| 6 | LOC_Os07g41280 | 6-phosphogluconolactonase, putative |
| 7 | LOC_Os07g41290 | DEFL13-Defensin and Defensin-like DEFL family |
| 8 | LOC_Os07g41300 | respiratory-chain NADH dehydrogenase |
| 9 | LOC_Os07g41310 | COBRA, putative, expressed |
| 10 | LOC_Os07g41320 | COBRA-like protein precursor, putative, expressed |
| 11 | LOC_Os07g41330 | mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit Tim17 |
| 12 | LOC_Os07g41340 | B12D protein, putative, expressed |
| 13 | LOC_Os07g41350 | B12D protein, putative, expressed |
| 14 | LOC_Os07g41360 | alpha-1,4-glucan-protein synthase, putative, expressed |
Supplemental Table 2. Fine mapping region contained 14 predicted genes.
| Number | Locus name | Gene product name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | LOC_Os07g41230 | esterase, putative, expressed |
| 2 | LOC_Os07g41240 | cytochrome P450, putative, expressed |
| 3 | LOC_Os07g41250 | peptide transporter PTR2, putative |
| 4 | LOC_Os07g41260 | PPR repeat domain containing protein, putative |
| 5 | LOC_Os07g41270 | retrotransposon protein, putative, unclassified |
| 6 | LOC_Os07g41280 | 6-phosphogluconolactonase, putative |
| 7 | LOC_Os07g41290 | DEFL13-Defensin and Defensin-like DEFL family |
| 8 | LOC_Os07g41300 | respiratory-chain NADH dehydrogenase |
| 9 | LOC_Os07g41310 | COBRA, putative, expressed |
| 10 | LOC_Os07g41320 | COBRA-like protein precursor, putative, expressed |
| 11 | LOC_Os07g41330 | mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit Tim17 |
| 12 | LOC_Os07g41340 | B12D protein, putative, expressed |
| 13 | LOC_Os07g41350 | B12D protein, putative, expressed |
| 14 | LOC_Os07g41360 | alpha-1,4-glucan-protein synthase, putative, expressed |
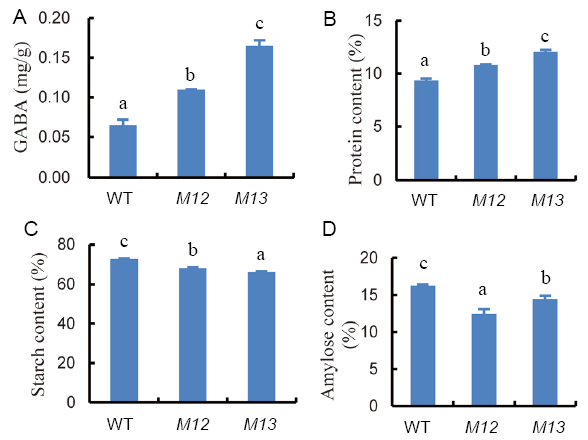
Fig. 3. Contents of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (A), protein (B), starch (C) and amylose (D) in brown rice flour of wild type (WT) and two mutants (M12 and M13). Different letters indicate a significant difference (n = 3, P < 0.05).
| Amino acid | WT | M12 | M13 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glutamic acid | 0.144 ± 0.002 a | 0.173 ± 0.000 b | 0.171 ± 0.002 b |
| Aspartic acid | 0.076 ± 0.001 a | 0.092 ± 0.001 b | 0.090 ± 0.001 b |
| Serine | 0.044 ± 0.001 a | 0.052 ± 0.001 b | 0.051 ± 0.001 b |
| Threonine | 0.031 ± 0.000 a | 0.037 ± 0.001 b | 0.036 ± 0.000 b |
| Glycine | 0.040 ± 0.001 a | 0.047 ± 0.001 b | 0.047 ± 0.001 b |
| Alanine | 0.048 ± 0.001 a | 0.057 ± 0.001 b | 0.058 ± 0.001 b |
| Cysteine | 0.016 ± 0.000 a | 0.018 ± 0.001 b | 0.017 ± 0.000 ab |
| Valine | 0.046 ± 0.000 a | 0.054 ± 0.000 b | 0.054 ± 0.001 b |
| Methionine | 0.015 ± 0.000 a | 0.017 ± 0.000 b | 0.017 ± 0.000 b |
| Isoleucine | 0.033 ± 0.000 a | 0.039 ± 0.000 b | 0.039 ± 0.001 b |
| Leucine | 0.068 ± 0.000 a | 0.080 ± 0.000 b | 0.079 ± 0.001 b |
| Tyrosine | 0.033 ± 0.001 a | 0.038 ± 0.000 b | 0.038 ± 0.000 b |
| Phenylalanin | 0.045 ± 0.000 a | 0.053 ± 0.000 b | 0.053 ± 0.001 b |
| Lysine | 0.034 ± 0.000 a | 0.041 ± 0.000 b | 0.041 ± 0.000 b |
| Histidine | 0.020 ± 0.000 a | 0.025 ± 0.000 b | 0.025 ± 0.000 b |
| Arginine | 0.068 ± 0.001 a | 0.081 ± 0.001 b | 0.083 ± 0.001 b |
| Proline | 0.033 ± 0.000 a | 0.038 ± 0.000 b | 0.039 ± 0.000 b |
| Total amino acid | 0.790 ± 0.007 a | 0.941 ± 0.006 b | 0.936 ± 0.012 b |
| Essential amino acid | 0.304 ± 0.002 a | 0.358 ± 0.001 b | 0.356 ± 0.004 b |
Table 1 Amino acid contents in brown rice. mg/g
| Amino acid | WT | M12 | M13 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glutamic acid | 0.144 ± 0.002 a | 0.173 ± 0.000 b | 0.171 ± 0.002 b |
| Aspartic acid | 0.076 ± 0.001 a | 0.092 ± 0.001 b | 0.090 ± 0.001 b |
| Serine | 0.044 ± 0.001 a | 0.052 ± 0.001 b | 0.051 ± 0.001 b |
| Threonine | 0.031 ± 0.000 a | 0.037 ± 0.001 b | 0.036 ± 0.000 b |
| Glycine | 0.040 ± 0.001 a | 0.047 ± 0.001 b | 0.047 ± 0.001 b |
| Alanine | 0.048 ± 0.001 a | 0.057 ± 0.001 b | 0.058 ± 0.001 b |
| Cysteine | 0.016 ± 0.000 a | 0.018 ± 0.001 b | 0.017 ± 0.000 ab |
| Valine | 0.046 ± 0.000 a | 0.054 ± 0.000 b | 0.054 ± 0.001 b |
| Methionine | 0.015 ± 0.000 a | 0.017 ± 0.000 b | 0.017 ± 0.000 b |
| Isoleucine | 0.033 ± 0.000 a | 0.039 ± 0.000 b | 0.039 ± 0.001 b |
| Leucine | 0.068 ± 0.000 a | 0.080 ± 0.000 b | 0.079 ± 0.001 b |
| Tyrosine | 0.033 ± 0.001 a | 0.038 ± 0.000 b | 0.038 ± 0.000 b |
| Phenylalanin | 0.045 ± 0.000 a | 0.053 ± 0.000 b | 0.053 ± 0.001 b |
| Lysine | 0.034 ± 0.000 a | 0.041 ± 0.000 b | 0.041 ± 0.000 b |
| Histidine | 0.020 ± 0.000 a | 0.025 ± 0.000 b | 0.025 ± 0.000 b |
| Arginine | 0.068 ± 0.001 a | 0.081 ± 0.001 b | 0.083 ± 0.001 b |
| Proline | 0.033 ± 0.000 a | 0.038 ± 0.000 b | 0.039 ± 0.000 b |
| Total amino acid | 0.790 ± 0.007 a | 0.941 ± 0.006 b | 0.936 ± 0.012 b |
| Essential amino acid | 0.304 ± 0.002 a | 0.358 ± 0.001 b | 0.356 ± 0.004 b |
| Material | To (ºC) | Tp (ºC) | Tc (ºC) | ΔH (J/g) | PV (MPa/s) | HV (MPa/s) | BV (MPa/s) | FV (MPa/s) | SV (MPa/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 61.9 ± 0.1 b | 70.0 ± 0.0 c | 77.2 ± 0.1 b | 4.8 ± 0.2 a | 1 314 ± 38 c | 955 ± 44 c | 359 ± 6 b | 2 002 ± 67 c | 1 047 ± 23 b |
| M12 | 60.3 ± 0.4 a | 68.4 ± 0.2 a | 75.7 ± 0.2 a | 4.7 ± 0.1 a | 1 104 ± 83 b | 709 ± 11 b | 395 ± 72 b | 1 529 ± 50 b | 820 ± 39 a |
| M13 | 60.8 ± 0.3 a | 69.0 ± 0.0 b | 76.2 ± 0.1 a | 4.7 ± 0.1 a | 684 ± 6 a | 461 ± 23 a | 223 ± 16 a | 1 239 ± 13 a | 778 ± 10 a |
Table 2 Thermal properties and pasting properties of brown rice flour.
| Material | To (ºC) | Tp (ºC) | Tc (ºC) | ΔH (J/g) | PV (MPa/s) | HV (MPa/s) | BV (MPa/s) | FV (MPa/s) | SV (MPa/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 61.9 ± 0.1 b | 70.0 ± 0.0 c | 77.2 ± 0.1 b | 4.8 ± 0.2 a | 1 314 ± 38 c | 955 ± 44 c | 359 ± 6 b | 2 002 ± 67 c | 1 047 ± 23 b |
| M12 | 60.3 ± 0.4 a | 68.4 ± 0.2 a | 75.7 ± 0.2 a | 4.7 ± 0.1 a | 1 104 ± 83 b | 709 ± 11 b | 395 ± 72 b | 1 529 ± 50 b | 820 ± 39 a |
| M13 | 60.8 ± 0.3 a | 69.0 ± 0.0 b | 76.2 ± 0.1 a | 4.7 ± 0.1 a | 684 ± 6 a | 461 ± 23 a | 223 ± 16 a | 1 239 ± 13 a | 778 ± 10 a |
| Primer name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Z7-9 | TCTCCTCTTCCCCCGATC | ATAGCGGGCGAGGCTTAG |
| Z7-10 | ACAGTATCCAAGGCCCTGG | CACGTGAGACAAAGACGGAG |
| Z7-11 | GCCCACCTGTCATTGAGAGTA | GTTTTTGCGCTTTTGTTGCT |
| Z7-13 | GGAGTATTTTAGTAGGCTATTA | TAAAGTTCAAAGATACAAGAAAT |
| Z7-14 | TGCTTGCTTCGATCTGATC | GTTGTGACTTGTGAAGAAGG |
| Z7-15 | AAGAGCTTCTTGACGAGGTA | ATGGATGGATATGAACAGTGC |
| Z7-17 | CTCGGAGAAATTGCCGTTC | GTCACCTCACCACCTTCTCC |
| Z7-18 | AACACCTTGAATCTTTCCACGT | GAATTTGAACCATATTAGCTA |
Supplemental Table 3. Primers used in mapping GE gene
| Primer name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Z7-9 | TCTCCTCTTCCCCCGATC | ATAGCGGGCGAGGCTTAG |
| Z7-10 | ACAGTATCCAAGGCCCTGG | CACGTGAGACAAAGACGGAG |
| Z7-11 | GCCCACCTGTCATTGAGAGTA | GTTTTTGCGCTTTTGTTGCT |
| Z7-13 | GGAGTATTTTAGTAGGCTATTA | TAAAGTTCAAAGATACAAGAAAT |
| Z7-14 | TGCTTGCTTCGATCTGATC | GTTGTGACTTGTGAAGAAGG |
| Z7-15 | AAGAGCTTCTTGACGAGGTA | ATGGATGGATATGAACAGTGC |
| Z7-17 | CTCGGAGAAATTGCCGTTC | GTCACCTCACCACCTTCTCC |
| Z7-18 | AACACCTTGAATCTTTCCACGT | GAATTTGAACCATATTAGCTA |
| [1] | Chen Y L, Liu L L, Shen Y Y, Liu S J, Huang J X, Long Q Z, Wu W, Yang C Y, Chen H, Guo X P, Cheng Z J, Jiang L, Wan J M. 2014. Loss of function of the cytochrome P450 gene CYP78B5 causes giant embryos in rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep, 33(1): 69-83. |
| [2] | Choi I, Kim D, Son J, Yang C, Chun J, Kim K. 2006. Physico- chemical properties of giant embryo brown rice (Keunnunbyeo). J Appl Biol Chem, 49(3): 95-100. |
| [3] | Chung S I, Lee S C, Kang M Y. 2017. Physicochemical properties of giant embryo rice Seonong 17 and Keunnunjami. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 81(5): 972-978. |
| [4] | Du Y M, Pan T, Tian Y L, Liu S J, Liu X, Jiang L, Zhang W W, Wang Y H, Wan J M. 2019. Phenotypic analysis and gene cloning of rice floury endosperm mutant fse4. Chin J Rice Sci, 33(6): 499-512. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Kaur A, Ghumman A, Singh N, Kaur S, Virdi A S, Riar G S, Mahajan G. 2016. Effect of different doses of nitrogen on protein profiling, pasting and quality attributes of rice from different cultivars. J Food Sci Technol, 53(5): 2452-2462. |
| [6] | Kim J Y, Seo W D, Park D S, Jang K C, Choi K J, Kim S Y, Oh S H, Ra J E, Yi G, Park S K, Hwang U H, Song Y C, Park B R, Park M J, Kang H W, Nam M H, Han S I. 2013. Comparative studies on major nutritional components of black waxy rice with giant embryos and its rice bran. Food Sci Biotechnol, 22(1): 121-128. |
| [7] | Koh H J, Heu M H, McCouch S R. 1996. Molecular mapping of the ges gene controlling the super-giant embryo character in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 93: 257-261. |
| [8] | Martin M, Fitzgerald M A. 2002. Proteins in rice grains influence cooking properties. J Cereal Sci, 36(3): 285-294. |
| [9] | Mikkelsen M D, Hansen C H, Wittstock U, Halkier B A. 2000. Cytochrome P450 CYP79B2 from Arabidopsis catalyzes the conversion of tryptophan to indole-3-acetaldoxime, a precursor of indole glucosinolates and indole-3-acetic acid. J Biol Chem, 275: 33712-33717. |
| [10] | Nagasawa N, Hibara K I, Heppard E P, Velden K A V, Luck S, Beatty M, Nagato Y, Sakai H. 2013. GIANT EMBRYO encodes CYP78A13, required for proper size balance between embryo and endosperm in rice. Plant J, 75(4): 592-605. |
| [11] | Noda T, Tsuda S, Mori M, Takigawa S, Matsuura-Endo C, Saito K, Mangalika W H A, Hanaoka A, Suzuki Y, Yamauchi H. 2004. The effect of harvest dates on the starch properties of various potato cultivars. Food Chem, 86(1): 119-125. |
| [12] | Park D S, Park S K, Lee B C, Song S Y, Jun N S, Manigbas N L, Cho J H, Nam M H, Jeon J S, Han C D, Choi K J, Kim D H, Woo Y M, Koh H J, Kang H W, Yi G. 2009. Molecular characterization and physico-chemical analysis of a new giant embryo mutant allele (get) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genes Genom, 31(4): 277-282. |
| [13] | Pelissari F M, Andrade-Mahecha M M, do Amaral Sobral P J, Menegalli F C. 2012. Isolation and characterization of the flour and starch of plantain bananas (Musa paradisiaca). Starch/ Stärke, 64(5): 382-391. |
| [14] | Qian Q, Xiong Z M, Min S K, Zhu L H. 1996. The RFLP of tagging of giant embryo gene. Chin J Rice Sci, 10(2): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Sakata M, Seno M, Matsusaka H, Takahashi K, Nakamura Y, Yamagata Y, Angeles E R, Mochizuki T, Kumamaru T, Sato M, Enomoto A, Tashiro K, Kuhara S, Satoh H, Yoshimura A. 2016. Development and evaluation of rice giant embryo mutants for high oil content originated from a high-yielding cultivar ‘Mizuhochikara’. Breeding Sci, 66(3): 425-433. |
| [16] | Satoh H, Omura T. 1981. New endosperm mutations induced by chemical mutagens in rice Oryza sativa L. Jpn J Breeding, 31(3): 316-326. |
| [17] | Seo W D, Kim J Y, Park D S, Han S I, Jang K C, Choi K J, Kim S Y, Oh S H, Ra J E, Yi G, Park S K, Hwang W H, Song Y C, Park B R, Kang H W. 2011. Comparative analysis of physico- chemicals and antioxidative properties of new giant embryo mutant, YR23517Acp79, in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Kor Soc Appl Biol Chem, 54(5): 700-709. |
| [18] | Wahlqvist M L, Hsu-Hage B H H, Lukito W. 1999. Clinical trials in nutrition. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr, 8(3): 231-241. |
| [19] | Yang W B, Gao M J, Yin X, Liu J Y, Xu Y H, Zeng L J, Li Q, Zhang S B, Wang J M, Zhang X M, He Z H. 2013. Control of rice embryo development, shoot apical meristem maintenance, and grain yield by a novel cytochrome P450. Mol Plant, 6(6): 1945-1960. |
| [20] | Yangcheng H Y, Blanco M, Gardner C, Li X H, Jane J L. 2016. Dosage effects of Waxy gene on the structures and properties of corn starch. Carbohydr Polym, 149: 282-288. |
| [21] | Zhang C Q, Chen S J, Ren X Y, Lu Y, Liu D R, Cai X L, Li Q F, Gao J P, Liu Q Q, 2017. Molecular structure and physic- chemical properties of starches from rice with different amylose contents resulting from modification of OsGBSSI activity. J Agric Food Chem, 65(10): 2222-2232. |
| [22] | Zhang L L, Hu P S, Tang S Q, Zhao H J, Wu D X. 2005. Comparative studies on major nutritional components of rice with a giant embryo and a normal embryo. J Food Biochem, 29(6): 653-661. |
| [23] | Zhao G C, Xie M X, Wang Y C, Li J Y. 2017. Molecular mechanisms underlying γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) accumulation in giant embryo rice seeds. J Agric Food Chem, 65(24): 4883-4889. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||